Nginx教程
cache and nginx
Cache
https://xie.infoq.cn/article/373f75d884a28aff8f32c3d9a
什么是缓存?

缓存是将请求的结果存储在与原始存储位置或临时存储位置不同的位置的过程,这样我们就可以避免重复执行相同的操作。基本上,缓存是文件和数据的临时存储,从这个新位置访问数据会更快。
例子
Web 浏览器缓存 HTML、CSS、JS 和图像,以便在再次请求时更快的访问网站。
CDN 存储静态文件,有助于减少延迟。
DNS 用于获取查询的 IP 地址,查询结果可以存储在缓存中,因此当我们多次请求 IP 地址时,不必再次执行 DNS 查询,从而可以更快的访问网页。
nginx architect
https://www.zhihu.com/people/ji-fo-74
在nginx架构中,本身的 proxy cache 和 memcache 为缓存组件。
- nginx模块结构:

- Nginx主要是用于Http服务器,反向代理服务器,邮件服务器
- Nginx由多个模块组成,每个请求的完成都是由一个或多个模块共同完成的。
- Nginx 默认采用守护模式启动,守护模式让master进程启动后在后台运行。在Nginx运行期间主要由一个master主进程和多个worker进程(数目一般与cpu数目相同)
nginx - browser cache for static file
https://stackoverflow.com/questions/19515132/nginx-cache-static-files
通过http报文头,指令客户端缓存30天。
## All static files will be served directly.
location ~* ^.+\.(?:css|cur|js|jpe?g|gif|htc|ico|png|html|xml|otf|ttf|eot|woff|woff2|svg)$ {
access_log off;
expires 30d;
add_header Cache-Control public;
## No need to bleed constant updates. Send the all shebang in one
## fell swoop.
tcp_nodelay off;
## Set the OS file cache.
open_file_cache max=3000 inactive=120s;
open_file_cache_valid 45s;
open_file_cache_min_uses 2;
open_file_cache_errors off;
}
nginx - proxy cache for static file
https://docs.nginx.com/nginx/admin-guide/content-cache/content-caching/
代理缓存规则
http {
# ...
proxy_cache_path /data/nginx/cache keys_zone=one:10m;
server {
proxy_cache mycache;
location / {
proxy_pass http://localhost:8000;
}
}
}
https://developpaper.com/using-nginx-to-cache-static-files-on-the-server/
代理服务器作为缓存功能,为静态文件
server {
listen 80 default_server;
server_name localhost;
root /mnt/blog/;
location / {
}
#To cache the suffix of a file, you can set it below.
location ~ .*.(gif|jpg|png|css|js)(.*) {
proxy_ pass http://ip Address: 90;
proxy_redirect off;
proxy_set_header Host $host;
proxy_cache cache_one;
proxy_cache_valid 200 302 24h;
proxy_cache_valid 301 30d;
proxy_cache_valid any 5m;
expires 90d;
add_header wall "hey!guys!give me a star.";
}
}
nginx - proxy for static file
https://belvg.com/blog/static-content-caching-with-nginx.html
静态文件特殊响应,
server {
listen 80;
server_name www.example.com;
root /var/www/html/example.com/;
proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $remote_addr;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-Proto $scheme;
proxy_set_header Host $host;
location ~* .(ico|jpg|png|gif|jpeg|css|swf|js|woff)$ {
access_log off;
gzip_static on;
gzip_comp_level 5;
expires 1M;
add_header Cache-Control private;
# add_header Cache-Control public;
try_files $uri @proxy;
}
location @proxy {
proxy_pass http://www.example.com:8080;
}
location ~ {
proxy_pass http://www.example.com:8080;
}
}
nginx memcache for URL - response
https://nginx.org/en/docs/http/ngx_http_memcached_module.html
先向缓存中查询response, 如果缓存中不存在, 则向后台请求。
server {
location / {
set $memcached_key "$uri?$args";
memcached_pass host:11211;
error_page 404 502 504 = @fallback;
}
location @fallback {
proxy_pass http://backend;
}
}
https://juejin.cn/post/6844903556013785096
主要使用了
nginx的memcached_module模块,直接从Memcache服务器中读取并输出。如若不存在,则执行相应程序,并将结果写入
Memcahce。结构图:
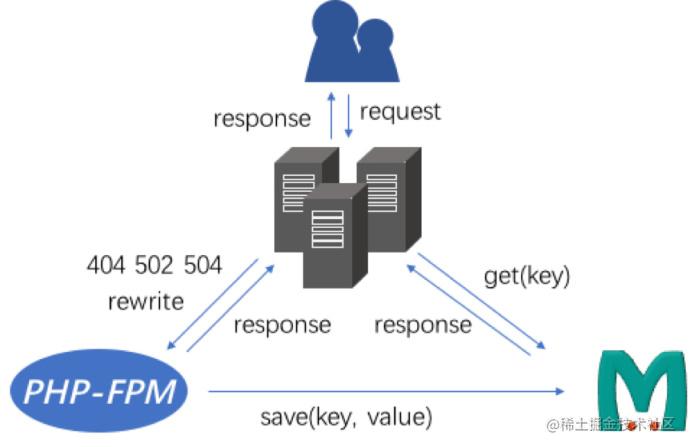
主要流程是:
用户的请求进来,
Nginx向Memcache获取数据,如若成功,则直接返回给客服端。如若失败,则Nginx会报not found错误,这个时候,需要rewirte执行相关应用程序,在页面渲染结束后,将结果写入Memcache。那么下次请求,将直接从Memcache获取。
upstream memcacheds {
server 127.0.0.1:11211;
}
server {
... # 这里的配置不变
location @rewrite {
rewrite ^/(.*)$ /index.php?/$1 last;
}
set $memcached_key 0; # 初始化一下$memcached_key
location ~ /(articles) {
set $memcached_key $host$uri; # 用url作为标识
add_header X-IMJCW-Key $memcached_key; # 加到header里,方便管理
default_type text/html;
memcached_connect_timeout 1s;
memcached_read_timeout 2s;
memcached_send_timeout 2s;
memcached_pass memcacheds;
memcached_gzip_flag 2;
error_page 404 502 504 = @rewrite;
}
... # 这里的配置不变
location ~ \.php$ {
... # 这里的配置不变
fastcgi_param X-MEMCACHE-KEY $memcached_key; # 设置参数,为程序是否需要缓存页面做判断
... # 这里的配置不变
}
... # 这里的配置不变
}
https://learnku.com/articles/42113
memcached_pass 直接指明 host
server{
location / {
set $memcached_key "$uri"; #192.168.1.200/1.html 会把 /1.html 当作 key 去判断 mem中有没有缓存。
memcached_pass 127.0.0.1:11211;
error_page 404 /callback.php;#捕捉 404 信息 ,就回调 callback 页面,在根目录 html 目录下
}
}
nginx dynamic route based on redis
https://openresty.org/en/dynamic-routing-based-on-redis.html
worker_processes 2;
error_log logs/error.log info;
events {
worker_connections 1024;
}
http {
server {
listen 8080;
location / {
resolver 8.8.4.4; # use Google's open DNS server
set $target '';
access_by_lua '
local key = ngx.var.http_user_agent
if not key then
ngx.log(ngx.ERR, "no user-agent found")
return ngx.exit(400)
end
local redis = require "resty.redis"
local red = redis:new()
red:set_timeout(1000) -- 1 second
local ok, err = red:connect("127.0.0.1", 6379)
if not ok then
ngx.log(ngx.ERR, "failed to connect to redis: ", err)
return ngx.exit(500)
end
local host, err = red:get(key)
if not host then
ngx.log(ngx.ERR, "failed to get redis key: ", err)
return ngx.exit(500)
end
if host == ngx.null then
ngx.log(ngx.ERR, "no host found for key ", key)
return ngx.exit(400)
end
ngx.var.target = host
';
proxy_pass http://$target;
}
}
}
-
用Nginx防范DDoS攻击的那些事儿12-13
-
用Terraform在AWS上搭建简单NGINX服务器指南12-13
-
Nginx发布学习:从入门到实践的简单教程10-29
-
Nginx发布:新手入门教程10-28
-
nginx 怎么设置文件上传最大20M限制-icode9专业技术文章分享10-21
-
关闭 nginx的命令是什么?-icode9专业技术文章分享10-17
-
Nginx实用篇:实现负载均衡、限流与动静分离09-17
-
宝塔nginx新增8022端口方法步骤-icode9专业技术文章分享08-21
-
nginx配置,让ws升级为wss访问的方法步骤-icode9专业技术文章分享08-21
-
nginx ws代理配置方法步骤-icode9专业技术文章分享08-15
-
nginx 让访问带有/relid的地址返回404 ,例子 /relid-x-0.36-y-131.html-icode9专业技术文章分享08-14
-
nginx 判断地址有/statics/的路径,指向到/home/html/statics/目录-icode9专业技术文章分享08-14
-
解锁Nginx日志的宝藏:GoAccess——你的实时、交互式Web日志分析神器!07-24
-
fail2ban nginx03-29
-
install nginx proxy manager03-18

