Java教程
SpringBatch从入门到精通-3.2-并行处理-远程分区
1. 背景
上章讲到了并行处理相关内容。但远程分区还是讲的不够细。还差
远程分区的db轮询模式
分区器Partitioner 和PartitionHandler的使用,
聚合器的使用。
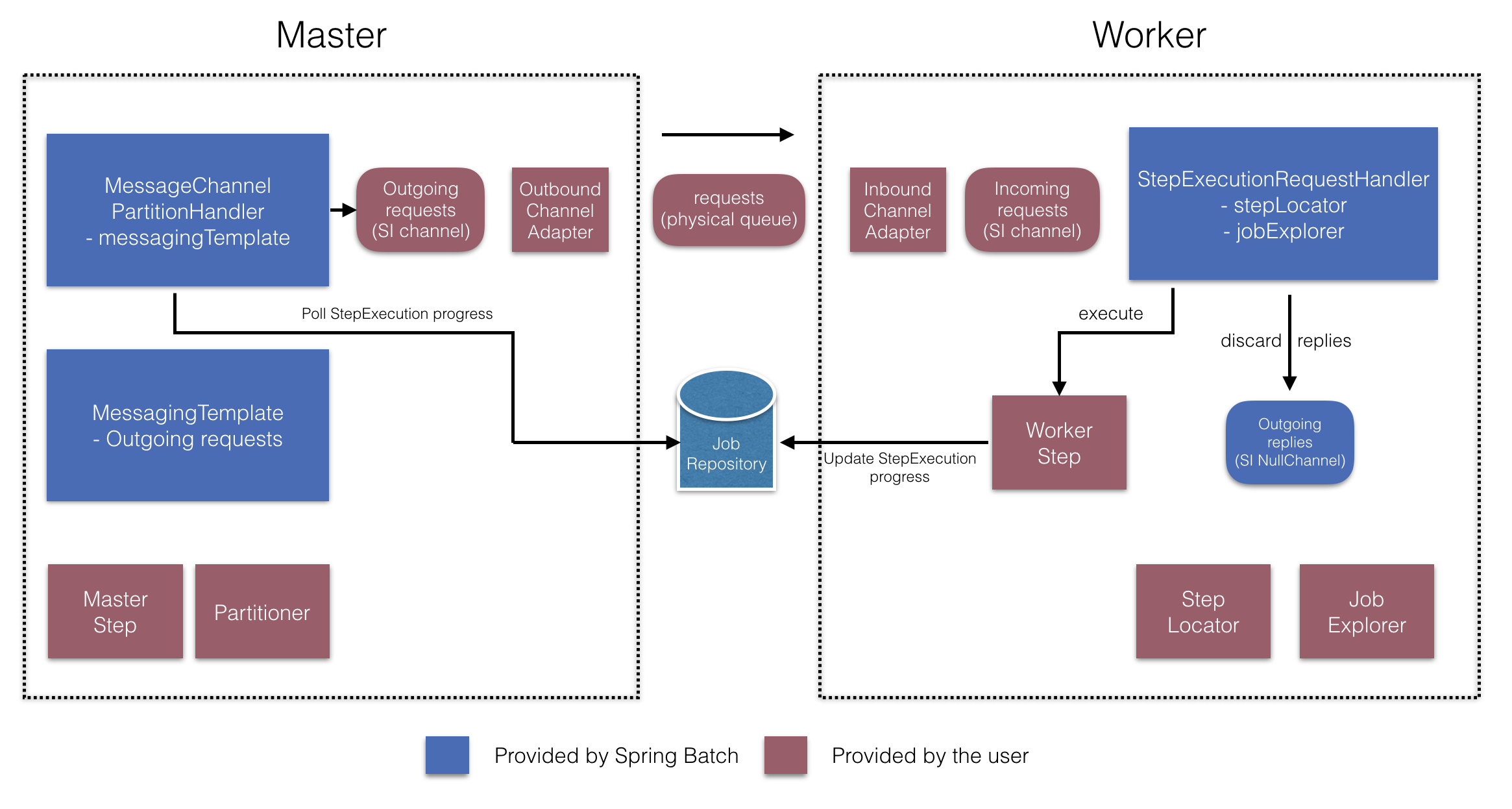
远程分区的整体流程
2. 远程分区的db轮询模式
- Master用户端需要实现 outgoIng,outband
@Bean //定义channle
public DirectChannel managerDBPollRequests() {
return new DirectChannel();
}
@Bean // 定义从channel内容经过amqp发送到requests队列中
public IntegrationFlow managerDBPollOutboundFlow() {
return IntegrationFlows.from(managerDBPollRequests())
.handle(Amqp.outboundAdapter(rabbitTemplate).routingKey("requests"))
.get();
}
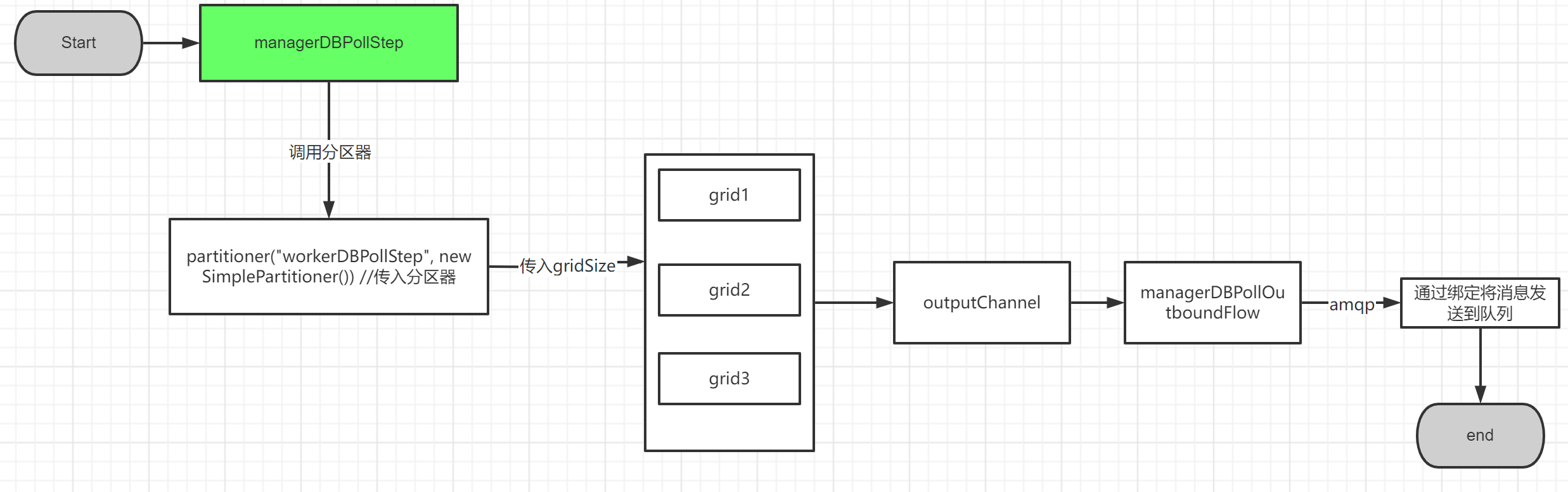
// 定义远程分区step Manager端(master)
@Bean
public Step managerDBPollStep() {
return this.managerStepBuilderFactory.get("managerDBPollStep") // 定义名称
.partitioner("workerDBPollStep", new SimplePartitioner()) //传入分区器
.gridSize(GRID_SIZE) // 传入分区器可以分几个区
.outputChannel(managerDBPollRequests()) //将分区结果发送到对应的channel
.build();
}
代码流程大概是上图的样子。
-
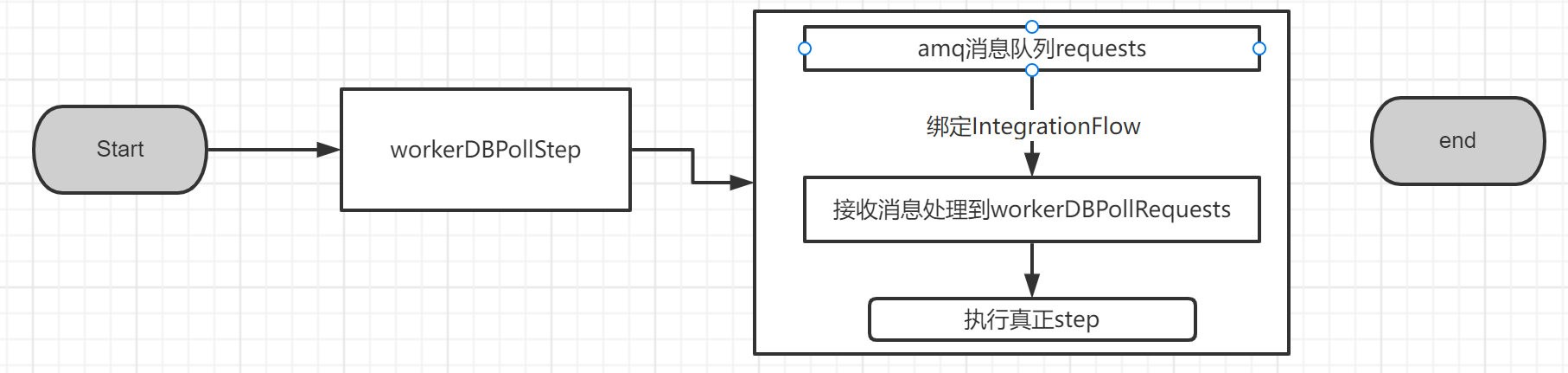
worker用户端需要实现 incomingRequest,inband
// 定义消息接收channel @Bean public DirectChannel workerDBPollRequests() { return new DirectChannel(); } @Bean public IntegrationFlow workerDBPollInboundFlow(ConnectionFactory rabbitmqConnectionFactory) { return IntegrationFlows .from(Amqp.inboundAdapter( rabbitmqConnectionFactory,"requests"))//从消息队列request来消息 .channel(workerDBPollRequests()//执行完的消息内容,发送到channel ).get(); } @Bean public Step workerDBPollStep() { return this.workerStepBuilderFactory .get("workerDBPollStep") //step名称 .inputChannel(workerDBPollRequests()) // 接收channel .tasklet(workerDBPollStepTasklet(null)) .build(); }
3. 分区器Partitioner 和PartitionHandler的使用
- PartitionHandler 分区执行器
这PartitionHandler是了解远程处理或网格环境结构的组件。它能够向StepExecution远程实例发送请求Step ,以某种特定于结构的格式(如 DTO)进行包装。它不必知道如何拆分输入数据或如何聚合多次Step执行的结果。一般来说,它可能也不需要了解弹性或故障转移,因为在许多情况下,这些都是结构的特性。在任何情况下,Spring Batch 始终提供独立于结构的可重启性。失败的Job总是可以重新启动,只有失败Steps的才会重新执行。
该PartitionHandler接口可以为各种结构类型提供专门的实现,包括简单的 RMI 远程处理、EJB 远程处理、自定义 Web 服务、JMS、Java 空间、共享内存网格(如 Terracotta 或 Coherence)和网格执行结构(如 GridGain)。Spring Batch 不包含任何专有网格或远程结构的实现。
然而,Spring Batch 确实提供了一个有用的实现,它使用Spring 的策略在单独的执行线程中本地PartitionHandler执行Step实例 。TaskExecutor该实现称为 TaskExecutorPartitionHandler.
可以在TaskExecutorPartitionHandlerjava 配置中显式配置,如下例所示:
@Bean
public Step step1Manager() {
return stepBuilderFactory.get("step1.manager")
.partitioner("step1", new SimplePartitioner())
.partitionHandler(partitionHandler())
.build();
}
@Bean
public PartitionHandler partitionHandler() {
TaskExecutorPartitionHandler retVal = new TaskExecutorPartitionHandler();
retVal.setTaskExecutor(new SimpleAsyncTaskExecutor());
retVal.setStep(step1());
retVal.setGridSize(10);
return retVal;
}
gridSize属性确定要创建的单独步骤执行的数量,因此它可以与TaskExecutor中线程池的大小相匹配。或者,可以将其设置为大于可用的线程数,这使得工作块更小。
TaskExecutionPartitionHandler对于IO密集型步骤实例非常有用,例如复制大量文件或将文件系统复制到内容管理系统中。它还可以通过提供作为远程调用代理的步骤实现(例如使用Spring远程处理)来用于远程执行。
- 分区器Partitioner
有一个更简单的Partitioner职责:仅生成执行上下文作为新步骤执行的输入参数(无需担心重新启动)。它只有一个方法,如下面的接口定义所示:
public interface Partitioner {
Map<String, ExecutionContext> partition(int gridSize);
}
此方法的返回值将每个步骤执行的唯一名称 (Map中的key) ,值为具体的step的ExecutionContext信息。这些名称稍后在批处理元数据中显示为分区中的步骤名称StepExecutions。它 ExecutionContext只是一个名称-值对的包,因此它可能包含一系列主键、行号或输入文件的位置。然后远程Step通常使用占位符绑定到上下文输入#{…} 使用stepScope 中的@Value来获取
{partition2={start=20}, partition1={start=10}, partition0={start=1}}
4. StepExecutionAggregator聚合器的使用
-
StepExecutionAggregator 最后的统计分析聚合逻辑
void aggregate(StepExecution result, Collection<StepExecution> executions);
该接口只有一个方法。一个方法从入参来看是。接受Collection executions 的集合。也就是和partitioner的反过程。分而治之的思想,汇总聚合分区step完成manager状态的更新。
默认实现如下 DefaultStepExecutionAggregator.java
public void aggregate(StepExecution result, Collection<StepExecution> executions) { Assert.notNull(result, "To aggregate into a result it must be non-null."); if (executions == null) { return; } for (StepExecution stepExecution : executions) { BatchStatus status = stepExecution.getStatus(); result.setStatus(BatchStatus.max(result.getStatus(), status)); result.setExitStatus(result.getExitStatus().and(stepExecution.getExitStatus())); result.setFilterCount(result.getFilterCount() + stepExecution.getFilterCount()); result.setProcessSkipCount(result.getProcessSkipCount() + stepExecution.getProcessSkipCount()); result.setCommitCount(result.getCommitCount() + stepExecution.getCommitCount()); result.setRollbackCount(result.getRollbackCount() + stepExecution.getRollbackCount()); result.setReadCount(result.getReadCount() + stepExecution.getReadCount()); result.setReadSkipCount(result.getReadSkipCount() + stepExecution.getReadSkipCount()); result.setWriteCount(result.getWriteCount() + stepExecution.getWriteCount()); result.setWriteSkipCount(result.getWriteSkipCount() + stepExecution.getWriteSkipCount()); } }这个aggregate是在什么时候设置进去的呢 PartitionStep#doExecute
protected void doExecute(StepExecution stepExecution) throws Exception { stepExecution.getExecutionContext().put(STEP_TYPE_KEY, this.getClass().getName()); // Wait for task completion and then aggregate the results Collection<StepExecution> executions = partitionHandler.handle(stepExecutionSplitter, stepExecution); stepExecution.upgradeStatus(BatchStatus.COMPLETED); stepExecutionAggregator.aggregate(stepExecution, executions); // If anything failed or had a problem we need to crap out if (stepExecution.getStatus().isUnsuccessful()) { throw new JobExecutionException("Partition handler returned an unsuccessful step"); } }
分区step如何设置aggregate
@Bean
public Step step1Manager() {
return stepBuilderFactory.get("step1.manager")
.partitioner("step1", new SimplePartitioner())
.partitionHandler(partitionHandler())
.aggregator(new DefaultStepExecutionAggregator())
.build();
}
5. 整体流程
整体流程就是partitionStep的执行过程
protected void doExecute(StepExecution stepExecution) throws Exception {
stepExecution.getExecutionContext().put(STEP_TYPE_KEY, this.getClass().getName());
// Wait for task completion and then aggregate the results
// 等待任务结束然后聚合结果。
Collection<StepExecution> executions = partitionHandler.handle(stepExecutionSplitter, stepExecution);
// 不管结果是成功还是失败,直接更新结果为完成
stepExecution.upgradeStatus(BatchStatus.COMPLETED);
// 调用聚合器,将分区结果聚合
stepExecutionAggregator.aggregate(stepExecution, executions);
// If anything failed or had a problem we need to crap out
// 聚合的结果如果不是成功状态,那么直接抛出错误。step异常结束,job异常结束
if (stepExecution.getStatus().isUnsuccessful()) {
throw new JobExecutionException("Partition handler returned an unsuccessful step");
}
}
// 状态为failed 或者 大于FAILED,即 ABANDONED, UNKNOWN都为失败
public boolean isUnsuccessful() {
return this == FAILED || this.isGreaterThan(FAILED);
}
-
Java中定时任务实现方式及源码剖析11-24
-
Java中定时任务实现方式及源码剖析11-24
-
鸿蒙原生开发手记:03-元服务开发全流程(开发元服务,只需要看这一篇文章)11-24
-
细说敏捷:敏捷四会之每日站会11-24
-
Springboot应用的多环境打包入门11-23
-
Springboot应用的生产发布入门教程11-23
-
Python编程入门指南11-23
-
Java创业入门:从零开始的编程之旅11-23
-
Java创业入门:新手必读的Java编程与创业指南11-23
-
Java对接阿里云智能语音服务入门详解11-23
-
Java对接阿里云智能语音服务入门教程11-23
-
JAVA对接阿里云智能语音服务入门教程11-23
-
Java副业入门:初学者的简单教程11-23
-
JAVA副业入门:初学者的实战指南11-23
-
JAVA项目部署入门:新手必读指南11-23