Java教程
JavaScript 权威指南-学习笔记(一)
本文主要是介绍JavaScript 权威指南-学习笔记(一),对大家解决编程问题具有一定的参考价值,需要的程序猿们随着小编来一起学习吧!
| 本文所有教程及源码、软件仅为技术研究。不涉及计算机信息系统功能的删除、修改、增加、干扰,更不会影响计算机信息系统的正常运行。不得将代码用于非法用途,如侵立删! |
JavaScript 权威指南-学习笔记
- JavaScript是一门高级、动态、解释型变成语言,非常适合面向对象和函数式编程风格。
- JavaScript的变量是无类型的。
- JavaScript和Java除了表面语法大致相似,它与Java是完全不同的两门变成语言。
Hello World
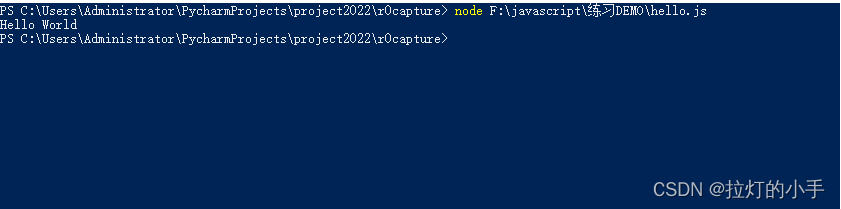
Node:交互式模式输出Hello World
node
console.log("Hello World")
Node:非交互式环境输出Hello World
1.新建hello.js文件
2.文件写入:console.log(“Hello World”)
3.使用node 执行hello.js文件
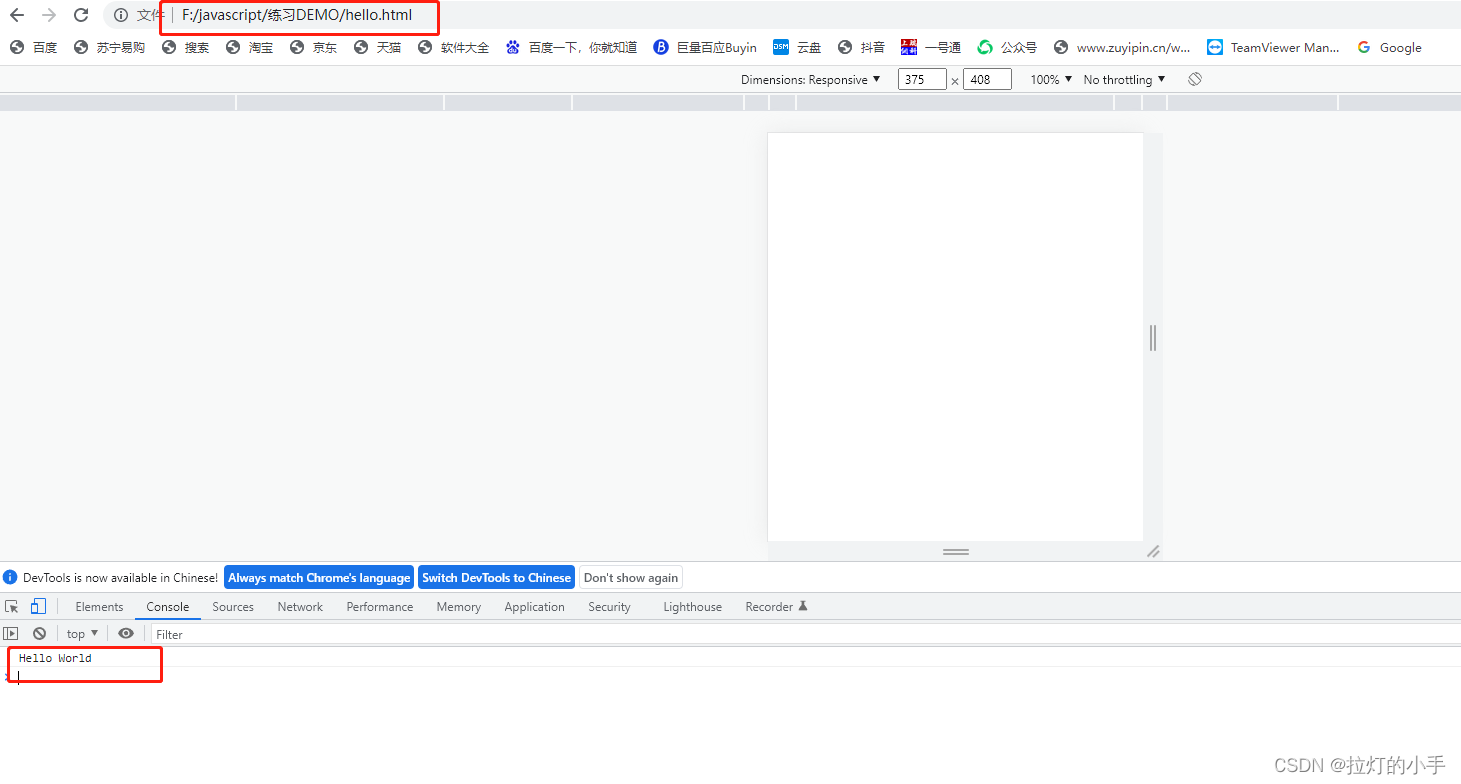
浏览器JavaScript控制台输出
1.新建hello.js文件并写入:console.log(“Hello World”)
2.新建hello.html并写入:
3.在浏览器打开hello.html:file:///F:/javascript/%E7%BB%83%E4%B9%A0DEMO/hello.html
F12打开开发者工具窗口,就可以在控制台看到输出信息。
声明-关键词
- const:声明常量(不可被修改,重新赋值会抛出TypeError)
- let:声明变量(在同一作用域中重新声明相同变量会导致语法错误)推荐使用此方法声明变量
- var:声明变量(使用var声明的变量作用域为包含函数,而非包含块,这可能会导致隐含的错误,推荐使用let)
- funtion:定义函数
- class:定义类
对象
创建对象
-
直接创建对象
let empty = {}; //没有属性的对象 let point = {x:0, y:0}; //包含两个属性的对象 -
使用new创建对象
let a = new Object(); //创建一个空对象,与{}相同 let b = new Array(); //创建一个空数组,与[]相同 let c = new Date(); //创建一个表示当前时间的日期对象 let d = new Map(); //创建一个映射对象,用于存储键值对 -
使用Object.create()创建对象
Object.create()用于创建一个新对象,使用其第一个参数作为新对象的原型:
let a = object.create({x: 1, y: 2}); // a继承属性x和y a.x + a.y // =>3
读取对象属性
要获取一个对象的值,可以使用(.)或([])操作符
let point = {x:0, y:0}; //包含两个属性的对象
let a = point.x // 获取point的x属性值
let b = point["y"] // 获取point的y属性值
写入对象属性
要创建或设置属性,与查询属性一样,可以使用(.)或([]),只是要把他们放到赋值表达式的左边
let point = {x:0, y:0}; //包含两个属性的对象
point.a = 0;
point["b"] = 0;
删除对象属性
- delete操作符用于从对象中移除属性
- delete并不操作属性的值,而是操作属性本身
- delete操作符只删除自身属性,不删除继承属性
检查对象属性
-
in
let o = {x: 1}; "x" in o // =>true: o有自身属性"x" "y" in o // =>false: o没有属性"y" "toString" in o // =>true: o继承了toString的属性 -
hasOwnProperty().
对象hasOwnProperty()方法用于测试对象是否有给定名字的属性,对继承的属性返回false
let o = {x: 1}; o.hasOwnProperty("x"); // =>true: o有自身属性"x" o.hasOwnProperty("y") // =>false: o没有属性"y" o.hasOwnProperty("toString") // =>false: toString是继承属性 -
object.assign():从一个对象向另一个对象复制属性
数组
创建数组
-
直接创建
let empty = []; // 没有元素的数组 let primes = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]; // 有5个数值元素的数组 let misc = [1.1, true, "a",]; // 3种不同类型的元素,最后还有一个逗号
-
Array()创建数组
-
不传参调用
let a = new Array(); // 创建一个空数组
-
创建一个数组,并指定长度
let a = new Array(10); // 创建一个指定长度的数组
-
创建两个或更多个数组元素,或传入一个非数值元素
let a = new Array(5, 4, 3, 2,1, "testing, testing"); // 创建一个指定长度的数组
-
-
Array.of()创建一个带元素的数组
Array.of() // =>[]; 返回没有参数的空数组 Array.of(10) // =>[10]; 创建只有一个数值元素的数组 Array.of(1,2,3) // =>[1,2,3];
-
Array.from()通过字符串创建一个数组
var myArr = Array.from("RUNOOB"); // =>[ 'R', 'U', 'N', 'O', 'O', 'B' ]
读写数组
-
使用 [] 操作符访问数组元素
let a = ["world"]; // 先创建包含一个元素的数组 let value = a[0]; // 读取元素0 a[1] = 3.14; // 写入元素1
超出索引会返回undefined,不会报错
添加和删除数组元素
-
数组添加元素
let a = []; //创建一个空数组 a[0] = "zero"; //添加一个元素 a.push("one"); //在末尾添加一个值
flat()和flatMap()打平数组
-
flat()打平一级嵌套
[1, [2, 3]].flat() //=>[1, 2, 3] [1, [2, [3]]]].flat() //=>[1, 2, [3]]
-
flat() 传参打平多层级嵌套
let a = [1,[2,[3,4]]]; a.flat(1) //=> [1,2,[3,4]] a.flat(2) //=> [1,2,3,4]
数组转换为字符串
-
join()
let a = [1, 2, 3]; a.join() //=>"1,2,3" a.join(" ") //=>"1 2 3" a.join("") //=>"123" let b = new Array(10); //长度为10但没有元素的数组 b.join("-") //=>"---------":包含9个连字符的字符串 -
toString()
[1,2,3].toString() //=>"1,2,3" ["a", "b", "c"].toString() //=>"a,b,c" [1, [2, "c"]].toString() //=>"1,2,c"
如果想把数组的文本内容保存起来以备后用,可以使用JSON.stringify()
数组迭代
1.数组循环
var officers = [s
{ id: 20, name: 'Captain' },
{ id: 24, name: 'General' },
{ id: 56, name: 'Admiral' },
{ id: 88, name: 'Commander' }
];
2.for循环,使用率最高,也是最基本的一种遍历方式
var officersIds = [];
for(var i=0,len=officers.length;i<len; i++){
officersIds.push(officers[i].id);
}
console.log(officersIds); // [20,24,56,88]
3.forEach循环
forEach中传入要执行的回调函数,函数有三个参数。第一个参数为数组元素(必选),第二个参数为数组元素索引值(可选),第三个参数为数组本身(可选)
var officersIds = [];
officers.forEach(function (officer,index,array) {
console.log(index); //0,1,2,3,
console.log(officer); //{id: 20, name: "Captain Piett"},{id: 24, name: "General Veers"},{id: 56, name: "Admiral Ozzel"},{id: 88, name: "Commander Jerjerrod"}
officersIds.push(officer.id);
});
console.log(officersIds); //[20,24,56,88]
4.for in循环
for...in循环可用于循环对象和数组,推荐用于循环对象,可以用来遍历JSON
var officersIds = [];
for(var key in officers){
console.log(key); // 0 1 2 3 返回数组索引
console.log(officers[key]); //{id: 20, name: "Captain Piett"},{id: 24, name: "General Veers"},{id: 56, name: "Admiral Ozzel"},{id: 88, name: "Commander Jerjerrod"}
officersIds.push(officers[key].id);
}
console.log(officersIds); //[20,24,56,88]
5.for of循环
可循环数组和对象,推荐用于遍历数组。
for...of提供了三个新方法:
key()是对键名的遍历;
value()是对键值的遍历;
entries()是对键值对的遍历;
let arr = ['科大讯飞', '政法BG', '前端开发'];
for (let item of arr) {
console.log(item); // 科大讯飞 政法BG 前端开发
}
// 输出数组索引
for (let item of arr.keys()) {
console.log(item); // 0 1 2
}
// 输出内容和索引
for (let [item, val] of arr.entries()) {
console.log(item + ':' + val); // 0:科大讯飞 1:政法BG 2:前端开发
}
var officersIds = [];
for (var item of officers) {
console.log(item); //{id: 20, name: "Captain Piett"},{id: 24, name: "General Veers"},{id: 56, name: "Admiral Ozzel"},{id: 88, name: "Commander Jerjerrod"}
officersIds.push(item.id);
}
console.log(officersIds); // [20,24,56,88]
// 输出数组索引
for(var item of officers.keys()){
console.log(item); // 0 1 2 3
}
// 输出内容和索引
for (let [item, val] of officers.entries()) {
console.log(item) // 0 1 2 3 输出数组索引
console.log(val);//{id: 20, name: "Captain Piett"},{id: 24, name: "General Veers"},{id: 56, name: "Admiral Ozzel"},{id: 88, name: "Commander Jerjerrod"}
console.log(item + ':' + val);
}
6.map循环
map() 会返回一个新数组,数组中的元素为原始数组元素调用函数处理后的值。
map() 方法按照原始数组元素顺序依次处理元素。
map 不修改调用它的原数组本身。
map()中传入要执行的回调函数,函数有三个参数。第一个参数为数组元素(必选),第二个参数为数组元素索引值(可选),第三个参数为数组本身(可选)
var arr = [
{name:'a',age:'18'},
{name:'b',age:'19'},
{name:'c',age:'20'}
];
arr.map(function(item,index) {
if(item.name == 'b') {
console.log(index) // 1
}
})
7.filter
filter() 方法创建一个新的数组,新数组中的元素是通过检查指定数组中符合条件的所有元素。
array.filter(function(currentValue,index,arr){
}, thisValue)
var designer = peoples.filter(function (people) {
return people.job === "designer";
});
组合使用
var totalScore = peoples
.filter(function (person) {
return person.isForceUser;
})
.map(function (choose) {
return choose.mathScore + choose.englishScore;
})
.reduce(function (total, score) {
return total + score;
}, 0);
Array.from()
var divs = document.querySelectorAll('div.pane');
var text = Array.from(divs, (d) => d.textContent);
console.log("div text:", text);
// Old, ES5 way to get array from arguments
function() {
var args = [].slice.call(arguments);
//...
}
// Using ES6 Array.from
function() {
var args = Array.from(arguments);
//..
}
var filled = Array.from([1,,2,,3], (n) => n || 0);
console.log("filled:", filled);
// => [1,0,2,0,3]
| 本文仅供学习交流使用,如侵立删! |
这篇关于JavaScript 权威指南-学习笔记(一)的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对大家有所帮助,也希望大家多多支持为之网!
您可能喜欢
-
Java中定时任务实现方式及源码剖析11-24
-
Java中定时任务实现方式及源码剖析11-24
-
鸿蒙原生开发手记:03-元服务开发全流程(开发元服务,只需要看这一篇文章)11-24
-
细说敏捷:敏捷四会之每日站会11-24
-
Springboot应用的多环境打包入门11-23
-
Springboot应用的生产发布入门教程11-23
-
Python编程入门指南11-23
-
Java创业入门:从零开始的编程之旅11-23
-
Java创业入门:新手必读的Java编程与创业指南11-23
-
Java对接阿里云智能语音服务入门详解11-23
-
Java对接阿里云智能语音服务入门教程11-23
-
JAVA对接阿里云智能语音服务入门教程11-23
-
Java副业入门:初学者的简单教程11-23
-
JAVA副业入门:初学者的实战指南11-23
-
JAVA项目部署入门:新手必读指南11-23
栏目导航