人工智能学习
【2023年】第36天 TF-GAN的实现
一、前置工作
import tensorflow.compat.v1 as tf !pip install tensorflow-gan import tensorflow_gan as tfgan import tensorflow_datasets as tfds import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import numpy as np # Allow matplotlib images to render immediately. %matplotlib inline tf.logging.set_verbosity(tf.logging.ERROR) # Disable noisy outputs.
(1)Overview 概述
- This colab will walk you through the basics of using TF-GAN to define, train, and evaluate Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs).
本专题讨论小组将指导您了解使用 TF-GAN 定义、训练和评估生成对抗网络 (GAN) 的基础知识。 - We describe the library’s core features as well as some extra features.
我们将介绍该库的核心功能以及一些额外功能。 - This colab assumes a familiarity with TensorFlow’s Python API.
本实验假设您熟悉 TensorFlow 的 Python API。
(2)Learning objectives 学习目标
- Use TF-GAN Estimators to quickly train a GAN
使用 TF-GAN 估算器快速训练 GAN
(3)Unconditional MNIST with GANEstimator 使用 GANEstimator 的无条件 MNIST
- This exercise uses TF-GAN’s GANEstimator and the MNIST dataset to create a GAN for generating fake handwritten digits.
本练习使用 TF-GAN 的 GANEstimator 和 MNIST 数据集创建一个生成假手写数字的 GAN。
MNIST - The MNIST dataset contains tens of thousands of images of handwritten digits.
MNIST 数据集包含数以万计的手写数字图像。 - We’ll use these images to train a GAN to generate fake images of handwritten digits.
我们将使用这些图像来训练一个 GAN,以生成假的手写数字图像。 - This task is small enough that you’ll be able to train the GAN in a matter of minutes.
这项任务很小,几分钟内就能完成 GAN 的训练。
GANEstimator - TensorFlow’s Estimator API that makes it easy to train models.
TensorFlow 的 Estimator API 可轻松训练模型。 - TF-GAN offers GANEstimator, an Estimator for training GANs.
TF-GAN 提供用于训练 GAN 的估算器 GANEstimator。
Input Pipeline - We set up our input pipeline by defining an input_fn. in the “Train and Eval Loop” section below we pass this function to our GANEstimator’s train method to initiate training.
在下面的 "训练和评估循环 "部分,我们将该函数传递给 GANEstimator 的 train 方法,以启动训练。
The input_fn: - Generates the random inputs for the generator.
为生成器生成随机输入。 - Uses tensorflow_datasets to retrieve the MNIST data.
使用 tensorflow_datasets 获取 MNIST 数据。 - Uses the tf.data API to format the data.
使用 tf.data API 来格式化数据。
import tensorflow_datasets as tfds
import tensorflow.compat.v1 as tf
def input_fn(mode, params):
assert 'batch_size' in params
assert 'noise_dims' in params
bs = params['batch_size']
nd = params['noise_dims']
split = 'train' if mode == tf.estimator.ModeKeys.TRAIN else 'test'
shuffle = (mode == tf.estimator.ModeKeys.TRAIN)
just_noise = (mode == tf.estimator.ModeKeys.PREDICT)
noise_ds = (tf.data.Dataset.from_tensors(0).repeat()
.map(lambda _: tf.random.normal([bs, nd])))
if just_noise:
return noise_ds
def _preprocess(element):
# Map [0, 255] to [-1, 1].
images = (tf.cast(element['image'], tf.float32) - 127.5) / 127.5
return images
images_ds = (tfds.load('mnist:3.*.*', split=split)
.map(_preprocess)
.cache()
.repeat())
if shuffle:
images_ds = images_ds.shuffle(
buffer_size=10000, reshuffle_each_iteration=True)
images_ds = (images_ds.batch(bs, drop_remainder=True)
.prefetch(tf.data.experimental.AUTOTUNE))
return tf.data.Dataset.zip((noise_ds, images_ds))
- 这段代码完成了创建输入数据管道的功能,根据不同的模式(训练、测试或预测)返回相应的数据集,包括噪音数据和经过预处理的图像数据。
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import tensorflow_datasets as tfds
import tensorflow_gan as tfgan
import numpy as np
params = {'batch_size': 100, 'noise_dims':64}
with tf.Graph().as_default():
ds = input_fn(tf.estimator.ModeKeys.TRAIN, params)
numpy_imgs = next(iter(tfds.as_numpy(ds)))[1]
img_grid = tfgan.eval.python_image_grid(numpy_imgs, grid_shape=(10, 10))
plt.axis('off')
plt.imshow(np.squeeze(img_grid))
plt.show()
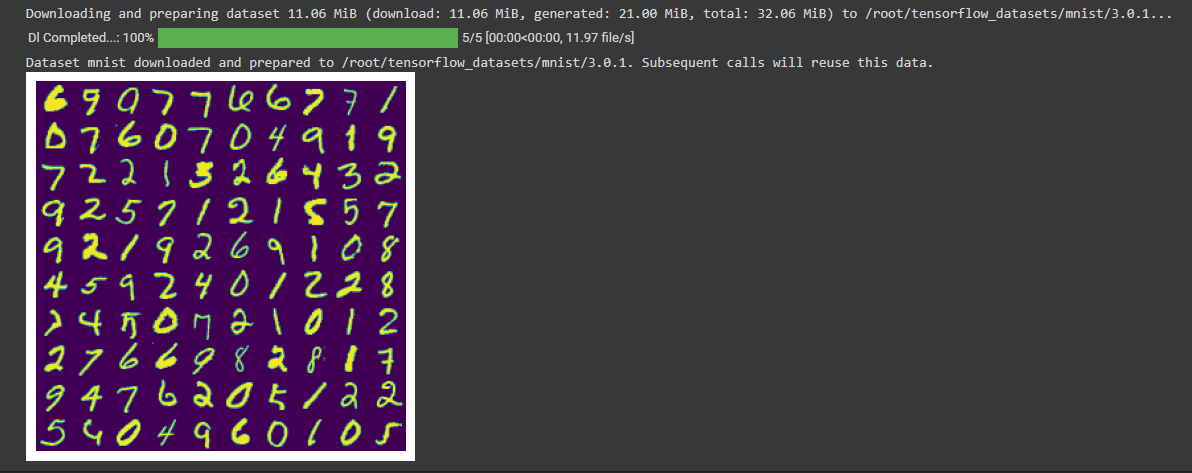
运行结果:
- 这段代码加载训练数据集,生成一个包含图像样本的图像网格,并显示该图像网格。
二、Neural Network Architecture 神经网络架构
- To build our GAN we need two separate networks:
要构建 GAN,我们需要两个独立的网络: - A generator that takes input noise and outputs generated MNIST digits
接收输入噪声并输出生成的 MNIST 数字的生成器 - A discriminator that takes images and outputs a probability of being real or fake
判别器可获取图像并输出真假概率 - We define functions that build these networks. In the GANEstimator section below we pass the builder functions to the GANEstimator constructor.
我们定义了构建这些网络的函数。在下面的 GANEstimator 部分,我们将把构建函数传递给 GANEstimator 构造函数。 - GANEstimator handles hooking the generator and discriminator together into the GAN.
GANEstimator 用于将信号发生器和鉴别器连接到 GAN 中。
def _dense(inputs, units, l2_weight):
return tf.layers.dense(
inputs, units, None,
kernel_initializer=tf.keras.initializers.glorot_uniform,
kernel_regularizer=tf.keras.regularizers.l2(l=l2_weight),
bias_regularizer=tf.keras.regularizers.l2(l=l2_weight))
def _batch_norm(inputs, is_training):
return tf.layers.batch_normalization(
inputs, momentum=0.999, epsilon=0.001, training=is_training)
def _deconv2d(inputs, filters, kernel_size, stride, l2_weight):
return tf.layers.conv2d_transpose(
inputs, filters, [kernel_size, kernel_size], strides=[stride, stride],
activation=tf.nn.relu, padding='same',
kernel_initializer=tf.keras.initializers.glorot_uniform,
kernel_regularizer=tf.keras.regularizers.l2(l=l2_weight),
bias_regularizer=tf.keras.regularizers.l2(l=l2_weight))
def _conv2d(inputs, filters, kernel_size, stride, l2_weight):
return tf.layers.conv2d(
inputs, filters, [kernel_size, kernel_size], strides=[stride, stride],
activation=None, padding='same',
kernel_initializer=tf.keras.initializers.glorot_uniform,
kernel_regularizer=tf.keras.regularizers.l2(l=l2_weight),
bias_regularizer=tf.keras.regularizers.l2(l=l2_weight))
- 包括了全连接层(dense)、批量归一化层(batch normalization)、反卷积层(deconvolutional layer)和卷积层(convolutional layer)的定义。
- _dense 函数是一个全连接层,使用 tf.layers.dense 来创建一个全连接层。它接受输入 inputs、输出单元数量 units 和 L2 正则化权重 l2_weight 作为参数,并返回一个全连接层的输出。
- _deconv2d 函数是一个反卷积层,使用 tf.layers.conv2d_transpose 来创建一个反卷积层。它接受输入 inputs、滤波器数量 filters、卷积核大小 kernel_size、步长 stride 和 L2 正则化权重 l2_weight 作为参数,并返回一个反卷积层的输出。
- _conv2d 函数是一个卷积层,使用 tf.layers.conv2d 来创建一个卷积层。它接受输入 inputs、滤波器数量 filters、卷积核大小 kernel_size、步长 stride 和 L2 正则化权重 l2_weight 作为参数,并返回一个卷积层的输出。
def unconditional_generator(noise, mode, weight_decay=2.5e-5): """Generator to produce unconditional MNIST images.""" is_training = (mode == tf.estimator.ModeKeys.TRAIN) net = _dense(noise, 1024, weight_decay) net = _batch_norm(net, is_training) net = tf.nn.relu(net) net = _dense(net, 7 * 7 * 256, weight_decay) net = _batch_norm(net, is_training) net = tf.nn.relu(net) net = tf.reshape(net, [-1, 7, 7, 256]) net = _deconv2d(net, 64, 4, 2, weight_decay) net = _deconv2d(net, 64, 4, 2, weight_decay) # Make sure that generator output is in the same range as `inputs` # ie [-1, 1]. net = _conv2d(net, 1, 4, 1, 0.0) net = tf.tanh(net) return net
上述代码是一个无条件生成器(unconditional_generator),用于生成MNIST图像。
- 定义了一个函数unconditional_generator,它接受三个参数:noise(噪声输入)、mode(模式)和weight_decay(权重衰减,默认值为2.5e-5)。
- 根据传入的mode参数判断是否处于训练模式(is_training = (mode == tf.estimator.ModeKeys.TRAIN))。
- 使用_dense函数对噪声进行全连接操作,输出1024维的向量,并应用权重衰减。
- 对输出进行批归一化_batch_norm,根据is_training参数决定是否进行归一化操作。
- 使用ReLU激活函数对输出进行非线性变换。
- 再次使用_dense函数对输出进行全连接操作,输出尺寸为7x7x256的张量,并应用权重衰减。
- 继续进行批归一化操作。
- 使用ReLU激活函数对输出进行非线性变换。
- 使用tf.reshape函数将输出重新形状为[-1, 7, 7, 256]的张量。
- 使用_deconv2d函数进行反卷积操作,输出通道数为64,卷积核大小为4x4,步长为2,应用权重衰减。
- 再次使用_deconv2d函数进行反卷积操作,输出通道数为64,卷积核大小为4x4,步长为2,应用权重衰减。
- 使用_conv2d函数进行卷积操作,输出通道数为1,卷积核大小为4x4,步长为1,没有应用权重衰减。
- 使用tf.tanh函数对生成的图像进行激活,以确保其范围在[-1, 1]之间。
- 返回生成的图像net。
_leaky_relu = lambda net: tf.nn.leaky_relu(net, alpha=0.01) def unconditional_discriminator(img, unused_conditioning, mode, weight_decay=2.5e-5): del unused_conditioning is_training = (mode == tf.estimator.ModeKeys.TRAIN) net = _conv2d(img, 64, 4, 2, weight_decay) net = _leaky_relu(net) net = _conv2d(net, 128, 4, 2, weight_decay) net = _leaky_relu(net) net = tf.layers.flatten(net) net = _dense(net, 1024, weight_decay) net = _batch_norm(net, is_training) net = _leaky_relu(net) net = _dense(net, 1, weight_decay) return net
上述代码是一个无条件的判别器(discriminator)函数,用于生成对抗网络(GAN)。
- unconditional_discriminator 函数接受输入参数 img(图像数据)、unused_conditioning(未使用的条件信息)、mode(模式标识符,如训练模式或推理模式)和可选参数 weight_decay(权重衰减)。
- unused_conditioning 被忽略,说明这个判别器函数不需要条件信息。
- is_training 变量根据 mode 判断当前是否处于训练模式。
- _conv2d 是一个卷积操作的辅助函数,它对输入 img 应用 2D 卷积,输出通道数为 64,卷积核大小为 4x4,步幅为 2,并应用了权重衰减。
- _leaky_relu 是一个激活函数的辅助函数,它对输入 net 应用带有负斜率的 Leaky ReLU,其中负斜率参数 alpha 设置为 0.01。
- 函数中通过两次卷积操作和两次 Leaky ReLU 激活函数将输入 img 转换为特征表示 net。
- _dense 是一个全连接层的辅助函数,它对输入 net 应用全连接操作,输出维度为 1024,并应用了权重衰减。
- _batch_norm 是一个批归一化的辅助函数,它对输入 net 进行批归一化操作,根据 is_training 变量判断是否在训练模式下进行归一化。
- 最后通过一次全连接层,输出维度为 1,得到判别器的判别结果 net。
- 函数返回判别器的输出 net。
3. Evaluating Generative Models, and evaluating GANs
TF-GAN provides some standard methods of evaluating generative models. In this example, we measure:
TF-GAN 提供了一些评估生成模型的标准方法。在这个例子中,我们测量
- Inception Score: called mnist_score below.
初始分数:下文称为 mnist_score。 - Frechet Inception Distance
弗雷歇特-因塞普逊距离 - We apply a pre-trained classifier to both the real data and the generated data calculate the Inception Score.
我们将预先训练好的分类器应用于真实数据和生成的数据,计算出初始分数。 - The Inception Score is designed to measure both quality and diversity.
初始分数旨在衡量质量和多样性。 - Frechet Inception Distance measures how close the generated image distribution is to the real image distribution.
Frechet Inception Distance 衡量生成的图像分布与真实图像分布的接近程度。
from tensorflow_gan.examples.mnist import util as eval_util
import os
def get_eval_metric_ops_fn(gan_model):
real_data_logits = tf.reduce_mean(gan_model.discriminator_real_outputs)
gen_data_logits = tf.reduce_mean(gan_model.discriminator_gen_outputs)
real_mnist_score = eval_util.mnist_score(gan_model.real_data)
generated_mnist_score = eval_util.mnist_score(gan_model.generated_data)
frechet_distance = eval_util.mnist_frechet_distance(
gan_model.real_data, gan_model.generated_data)
return {
'real_data_logits': tf.metrics.mean(real_data_logits),
'gen_data_logits': tf.metrics.mean(gen_data_logits),
'real_mnist_score': tf.metrics.mean(real_mnist_score),
'mnist_score': tf.metrics.mean(generated_mnist_score),
'frechet_distance': tf.metrics.mean(frechet_distance),
}
上述代码是一个用于评估生成对抗网络(GAN)模型的评估指标函数。其目的是计算模型在MNIST数据集上的一些度量值。
- 首先,代码导入了所需的模块和依赖项。其中tensorflow_gan.examples.mnist.util模块提供了用于计算MNIST数据集上不同评估指标的工具函数。
- 接下来定义了一个名为get_eval_metric_ops_fn的函数,该函数接受一个GAN模型作为输入,并返回一个字典,包含不同评估指标的计算操作。
- real_data_logits: 实际数据样本在判别器输出上的平均值。
- gen_data_logits: 生成数据样本在判别器输出上的平均值。
- real_mnist_score: 实际数据样本在MNIST评分指标上的平均值。
- mnist_score: 生成数据样本在MNIST评分指标上的平均值。
- frechet_distance: 实际数据样本和生成数据样本之间的MNIST Fréchet距离的平均值。
- 这些评估指标使用了eval_util模块中提供的函数来计算。
- 这段代码只定义了评估指标的计算操作,并没有执行实际的计算。在训练过程中,需要使用这些评估指标来评估模型的性能并监控训练进程。
4. GANEstimator 生成对抗网络估计器
The GANEstimator assembles and manages the pieces of the whole GAN model.
GANEstimator 对整个 GAN 模型的各个部分进行组装和管理。
The GANEstimator constructor takes the following compoonents for both the generator and discriminator:
GANEstimator 构造函数的生成器和判别器都需要以下成分:
- Network builder functions: we defined these in the “Neural Network Architecture” section above.
网络构建器函数:我们在上文 "神经网络架构 "一节中定义了这些函数。 - Loss functions: here we use the wasserstein loss for both.
损失函数:在这里,我们对这两种损失函数都使用了 wasserstein 损失函数。 - Optimizers: here we use tf.train.AdamOptimizer for both generator and discriminator training.
优化器:在这里,我们使用 tf.train.AdamOptimizer 对生成器和鉴别器进行训练。
train_batch_size = 32 #@param
noise_dimensions = 64 #@param
generator_lr = 0.001 #@param
discriminator_lr = 0.0002 #@param
def gen_opt():
gstep = tf.train.get_or_create_global_step()
base_lr = generator_lr
# Halve the learning rate at 1000 steps.
lr = tf.cond(gstep < 1000, lambda: base_lr, lambda: base_lr / 2.0)
return tf.train.AdamOptimizer(lr, 0.5)
gan_estimator = tfgan.estimator.GANEstimator(
generator_fn=unconditional_generator,
discriminator_fn=unconditional_discriminator,
generator_loss_fn=tfgan.losses.wasserstein_generator_loss,
discriminator_loss_fn=tfgan.losses.wasserstein_discriminator_loss,
params={'batch_size': train_batch_size, 'noise_dims': noise_dimensions},
generator_optimizer=gen_opt,
discriminator_optimizer=tf.train.AdamOptimizer(discriminator_lr, 0.5),
get_eval_metric_ops_fn=get_eval_metric_ops_fn)
上述代码定义了一个使用TensorFlow-GAN库的GAN Estimator(生成对抗网络估计器)。
- train_batch_size:训练期间使用的批大小,设置为32。
- noise_dimensions:生成器的随机噪声输入的维度数量,设置为64。
- generator_lr:生成器优化器的学习率,设置为0.001。
- discriminator_lr:判别器优化器的学习率,设置为0.0002。
接下来,定义了一个名为gen_opt的函数。该函数创建了一个Adam优化器,用于生成器,其学习率在1000个步骤之后减半。使用tf.cond函数实现了学习率调度。
然后,代码使用tfgan.estimator.GANEstimator类创建了一个GAN估计器。
- generator_fn:一个构建并返回生成器网络的函数。
- discriminator_fn:一个构建并返回判别器网络的函数。
- generator_loss_fn:一个计算生成器损失的函数。
- discriminator_loss_fn:一个计算判别器损失的函数。
- params:一个包含传递给生成器和判别器函数的其他参数的字典。在这里,包括批大小和噪声维度。
- generator_optimizer:用于训练生成器的优化器实例。在这里,它使用之前定义的gen_opt函数。
- discriminator_optimizer:用于训练鉴别器的优化器实例。它使用指定的学习率和0.5的动量项的Adam优化器。
- get_eval_metric_ops_fn:返回GAN模型的评估指标操作的函数。
5. Train and eval loop 训练和评估循环
- The GANEstimator’s train() method initiates GAN training, including the alternating generator and discriminator training phases.
GANEstimator 的 train() 方法启动了 GAN 训练,包括交替生成器和判别器训练阶段。 - The loop in the code below calls train() repeatedly in order to periodically display generator output and evaluation results.
下面代码中的循环重复调用 train(),以定期显示生成器输出和评估结果。 - But note that the code below does not manage the alternation between discriminator and generator: that’s all handled automatically by train().
但请注意,下面的代码并不管理判别器和生成器之间的交替:所有这些都由 train() 自动处理。
# Disable noisy output.
tf.autograph.set_verbosity(0, False)
import time
steps_per_eval = 500 #@param
max_train_steps = 5000 #@param
batches_for_eval_metrics = 100 #@param
# Used to track metrics.
steps = []
real_logits, fake_logits = [], []
real_mnist_scores, mnist_scores, frechet_distances = [], [], []
cur_step = 0
start_time = time.time()
while cur_step < max_train_steps:
next_step = min(cur_step + steps_per_eval, max_train_steps)
start = time.time()
gan_estimator.train(input_fn, max_steps=next_step)
steps_taken = next_step - cur_step
time_taken = time.time() - start
print('Time since start: %.2f min' % ((time.time() - start_time) / 60.0))
print('Trained from step %i to %i in %.2f steps / sec' % (
cur_step, next_step, steps_taken / time_taken))
cur_step = next_step
# Calculate some metrics.
metrics = gan_estimator.evaluate(input_fn, steps=batches_for_eval_metrics)
steps.append(cur_step)
real_logits.append(metrics['real_data_logits'])
fake_logits.append(metrics['gen_data_logits'])
real_mnist_scores.append(metrics['real_mnist_score'])
mnist_scores.append(metrics['mnist_score'])
frechet_distances.append(metrics['frechet_distance'])
print('Average discriminator output on Real: %.2f Fake: %.2f' % (
real_logits[-1], fake_logits[-1]))
print('Inception Score: %.2f / %.2f Frechet Distance: %.2f' % (
mnist_scores[-1], real_mnist_scores[-1], frechet_distances[-1]))
# Vizualize some images.
iterator = gan_estimator.predict(
input_fn, hooks=[tf.train.StopAtStepHook(num_steps=21)])
try:
imgs = np.array([next(iterator) for _ in range(20)])
except StopIteration:
pass
tiled = tfgan.eval.python_image_grid(imgs, grid_shape=(2, 10))
plt.axis('off')
plt.imshow(np.squeeze(tiled))
plt.show()
# Plot the metrics vs step.
plt.title('MNIST Frechet distance per step')
plt.plot(steps, frechet_distances)
plt.figure()
plt.title('MNIST Score per step')
plt.plot(steps, mnist_scores)
plt.plot(steps, real_mnist_scores)
plt.show()
它是一个使用TensorFlow的GAN(生成对抗网络)进行训练和评估的过程。
- 设置一些参数,例如每次评估的步数(steps_per_eval)、最大训练步数(max_train_steps)和用于评估指标的批次数(batches_for_eval_metrics)。
- 初始化一些列表,用于跟踪度量值。
- 进入一个循环,直到达到最大训练步数为止。每次迭代,训练GAN模型并计算度量值。
- 在每次迭代中,输出当前训练的进度和速度,并记录训练时间。
- 调用gan_estimator.evaluate函数计算评估指标,并将结果添加到相应的列表中。
- 输出当前步数下的判别器对真实数据和生成数据的平均输出,以及Inception Score和Frechet Distance指标的值。
- 使用gan_estimator.predict函数可视化生成的图像。
- 继续循环直到达到最大训练步数。
- 绘制Frechet Distance和MNIST Score随步数变化的曲线。
所以我们在这里主要展示了如何使用TensorFlow构建和训练GAN模型,并使用评估指标来监控训练进度。
-
从零开始学习贪心算法12-26
-
线性模型入门教程:基础概念与实践指南12-26
-
探索随机贪心算法:从入门到初级应用12-25
-
树形模型进阶:从入门到初级应用教程12-25
-
搜索算法进阶:新手入门教程12-25
-
算法高级进阶:新手与初级用户指南12-25
-
随机贪心算法进阶:初学者的详细指南12-25
-
贪心算法进阶:从入门到实践12-25
-
线性模型进阶:初学者的全面指南12-25
-
朴素贪心算法教程:初学者指南12-25
-
树形模型教程:从零开始的图形建模入门指南12-25
-
搜索算法教程:初学者必备指南12-25
-
算法高级教程:入门与初级用户指南12-25
-
随机贪心算法教程:初学者指南12-25
-
贪心算法教程:入门与实践指南12-25