Javascript
NodeJS http请求
本文简介
点赞 + 关注 + 收藏 = 学会了
对于前端来说,网络请求主要就是用 ajax 的方式去处理。所以本文也会站在前端角度简单讲解 Node 中如何使用 http 模块。
前后端对接时,现在常用的请求方法有 GET、POST、PUT、PATCH、DELETE。当然,还有其他方法,但本文主要面向新手,希望能做到快速起步。所以本文只讲 GET 和 POST 这两种最最最常用的方法。
在敲代码前,你首先需要准备一个 编辑器(我用vs code)、浏览器、postman 还有安装好 Node.js 。
创建服务
Node.js 提供了 http 模块,可用于网络请求。
创建一个 js 文件,输入以下代码。(本例的文件命名为 index.js)
const http = require('http')
const server = http.createServer((res, req) => {
req.end('hello world')
})
server.listen(8000, () => {
console.log('http://localhost:8000')
})
解释:
Node.js使用commonjs语法,所以引入http模块使用了require的方法。http模块有一个createServer方法,该方法的参数是一个函数,函数里又有2个参数,res是前端发送请求带过来的信息;req是后端返回信息给前端时的一些方法和属性的集合。- 通过
req.end方法,可以返回一段字符串给前端。 - 通过
listen方法可以设置需要监听的端口号,第二个参数是一个函数,我在控制台里输出http://localhost:8000是方便启动服务后方便自己打开这个地址。
使用 Node.js 运行上面的代码:
node index.js
运行完上面的命令,控制台应该会输出 http://localhost:8000 ,此时打开浏览器,输入 http://localhost:8000 后页面上会出现 “hello world”,证明服务创建成功,并且可以访问了。
GET
其实上一步所用的也是 GET 方法来访问后端,但上一步并没有解析参数。
get 请求的参数通常是挂在 url 后面的,比如 http://localhost:8000?msg=hello
如果有参数,会用 ? 开始,然后使用 参数名=值 的写法。
如果有多个参数,会使用 & 将参数区分开来:
http://localhost:8000?key1=value1&key2=value2&key3=value3
在 Node.js 里,如果需要解析 url 的参数,可以使用 node:querystring 模块。
const http = require('http') // 引入 htpp 模块
const querystring = require('node:querystring') // 引入 node:querystring 模块解析url
const server = http.createServer((req, res) => {
console.log('method: ', req.method) // 打印请求方法,GET
const url = req.url
console.log('url: ', url) // 打印被访问的url
req.query = querystring.parse(url.split('?')[1]) // 通过 ? 问号 分隔参数,并使用 querystring.parse 解析问号后面的参数
console.log('query: ', req.query) // 输出参数
res.end(JSON.stringify(req.query)) // 将参数返回给前端
})
server.listen(8000, () => {
console.log('http://localhost:8000')
})
执行上面的代码,并在浏览器访问 http://localhost:8000/?msg=123&name=leihou
在浏览器会显示出如下内容
解析:
req.url可以获取到当前访问后端的url路径url.split('?')[1]使用字符串的方法根据?进行切割,然后获取后面那段- 使用
querystring.parse方法将参数转换成对象的形式 res.end将参数返回给前端。- 前端在浏览器地址栏输入
http://localhost:8000/?msg=123&name=leihou时,后端会把参数返回,前端在页面中渲染出返回的参数。
POST
POST 请求会被 GET 更安全,同时也更麻烦。不能直接在浏览器地址栏输入 url 请求。
你可以写一段前端代码,通过 ajax 的方式请求。但本文主要讲解 Node.js ,所以我还是建议你使用 postman 发起 POST 请求。因为 postman 无需你处理跨域等问题。
const http = require('http')
const server = http.createServer((req, res) => {
if (req.method === 'POST') {
// 数据格式
console.log('content-type', req.headers['content-type'])
// 接收数据
let postData = ''
req.on('data', chunk => {
postData += chunk.toString()
})
req.on('end', () => {
console.log(postData)
res.end('hello world') // 在这里返回,因为是异步
})
}
})
server.listen(8000 () => {
console.log('http://localhost:8000')
})
和 GET 不同,POST 接收数据需要用 req.on('data') 进行接收,用 req.on('end') 处理接收数据完成的操作。
在 Node.js 里除了接收数据外,其他用法和 GET 有点像。
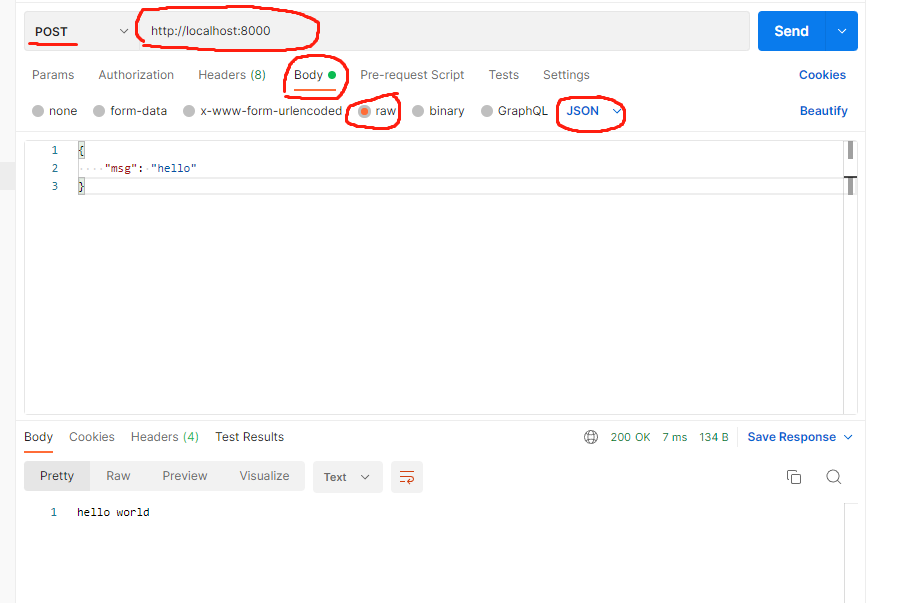
最后在 postman 访问 http://localhost:8000 ,并在 Body 的 raw 里填写 JSON 数据
按下 Send 键后,控制台会输出 postman 发送过来的数据。
综合实例
如果理解了 GET 和 POST 请求的话,我们就可以尝试将这两个请求结合起来使用了。
const http = require('http')
const querystring = require('node:querystring')
const server = http.createServer((req, res) => {
const method = req.method
const url = req.url
const path = url.split('?')[0]
const query = querystring.parse(url.split('?')[1])
// 设置返回格式 JSON
res.setHeader('Content-type', 'application/json') // 这里返回JSON。如果是 text/html 返回html
// 返回的数据
const resData = {
method,
url,
path,
query,
}
// 返回
if (method === 'GET') {
res.end(
JSON.stringify(resData)
)
}
if (method === 'POST') {
let postData = ''
req.on('data', chunk => {
postData += chunk.toString()
})
req.on('end', () => {
resData.postData = JSON.parse(postData)
// 返回
res.end(
JSON.stringify(resData)
)
})
}
})
server.listen(8000, () => {
console.log('http://localhost:8000')
})
上面的代码最主要是判断 method 是 GET 还是 POST ,因为两者接收数据的方式是不一样的。
你可以运行上面的代码,尝试在浏览器和 postman 各发送一下 GET 和 POST 测试一下。
-
Vue3教程:新手入门到实践应用12-21
-
VueRouter4教程:从入门到实践12-21
-
Vue3项目实战:从入门到上手12-20
-
Vue3项目实战:新手入门教程12-20
-
VueRouter4项目实战:新手入门教程12-20
-
如何实现JDBC和jsp的关系?-icode9专业技术文章分享12-20
-
Vue项目中实现TagsView标签栏导航的简单教程12-20
-
Vue3入门教程:从零开始搭建你的第一个Vue3项目12-20
-
从零开始学习vueRouter4:基础教程12-20
-
Vuex4课程:新手入门到上手实战全攻略12-20
-
Vue3资料:新手入门及初级教程12-20
-
Vuex4入门指南:轻松掌握Vue状态管理12-20
-
Vue3学习:从入门到实践的简单教程12-20
-
Vue学习:从入门到简单项目实战12-20
-
Vue3教程:初学者快速入门指南12-20