Java教程
【Java数据结构及算法实战】系列011:数组实现的优先级队列PriorityQueue
PriorityQueue是基于数组实现的无界优先级队列。PriorityQueue中的元素按其自然顺序排序,或由队列构造时提供的比较器根据所使用的构造函数排序。优先级队列不允许空元素,依赖自然顺序的优先级队列也不允许插入不可比较的对象。
PriorityQueue本质上就是一个最小堆存储结构数组,通过“极大优先级堆”实现的,即堆顶元素是优先级最大的元素。堆的操作,主要就是两个:siftUp(向上调整堆)和siftDown(向下调整堆)。
PriorityQueue的队首是相对于指定顺序来说优先级的值最小的元素。如果多个元素优先级的值都是最小,那么头部就是其中一个元素。PriorityQueue的检索操作poll、remove和peek等都是访问位于队首的元素。
PriorityQueue是无界队列,因此插入的元素是无限制的,但其具有一个内部容量,它控制用于在队列上存储元素的数组的大小。它总是至少和队列一样大。当元素被添加到优先级队列时,其容量会自动增长。
PriorityQueue及其迭代器实现了Collection和Iterator接口的所有可选方法。方法itilerator()提供的迭代器和方法spliterator()提供的分离器并不保证以任何特定的顺序遍历优先级队列的元素。如果需要有序遍历,请考虑使用Arrays.sort(pq.toArray()).。
注意PriorityQueue是唯一一个非线程安全的队列实现类,适合用于单线程存放数据并且将数据排序。如果是在多个线程中有修改了队列的场景,那么不应该用线程PriorityQueue,而应该使用线程安全的java.util.concurrent.PriorityBlockingQueue类。
PriorityQueue是Java Collections Framework的一个成员。
1. PriorityQueue的声明
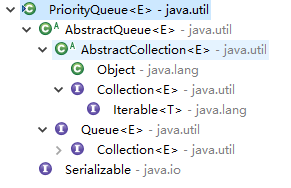
PriorityQueue的接口和继承关系如下
public class PriorityQueue<E> extends AbstractQueue<E>
implements java.io.Serializable {
…
}
完整的接口继承关系如下图所示。
从上述代码可以看出,PriorityQueue既实现了java.io.Serializable接口,又继承了java.util.AbstractQueue<E>。
2. PriorityQueue的成员变量和构造函数
以下是PriorityQueue的构造函数和成员变量。
// 默认数组容量
private static final int DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY = 11;
// 元素数组
transient Object[] queue;
// 队列中的元素个数
int size;
// 比较器
private final Comparator<? super E> comparator;
// 结构性修改的次数
transient int modCount;
public PriorityQueue() {
this(DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY, null);
}
public PriorityQueue(int initialCapacity) {
this(initialCapacity, null);
}
public PriorityQueue(Comparator<? super E> comparator) {
this(DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY, comparator);
}
public PriorityQueue(int initialCapacity,
Comparator<? super E> comparator) {
if (initialCapacity < 1)
throw new IllegalArgumentException();
this.queue = new Object[initialCapacity];
this.comparator = comparator;
}
public PriorityQueue(Collection<? extends E> c) {
if (c instanceof SortedSet<?>) {
SortedSet<? extends E> ss = (SortedSet<? extends E>) c;
this.comparator = (Comparator<? super E>) ss.comparator();
initElementsFromCollection(ss);
}
else if (c instanceof PriorityQueue<?>) {
PriorityQueue<? extends E> pq = (PriorityQueue<? extends E>) c;
this.comparator = (Comparator<? super E>) pq.comparator();
initFromPriorityQueue(pq);
}
else {
this.comparator = null;
initFromCollection(c);
}
}
public PriorityQueue(PriorityQueue<? extends E> c) {
this.comparator = (Comparator<? super E>) c.comparator();
initFromPriorityQueue(c);
}
public PriorityQueue(SortedSet<? extends E> c) {
this.comparator = (Comparator<? super E>) c.comparator();
initElementsFromCollection(c);
}
从上述代码可以看出,构造函数有6种。构造函数中的参数含义如下
l initialCapacity用于设置队列中内部数组的容量。如果没有指定,则会使用默认数组容量DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY的值。
l comparator为比较器
l c用于设置最初包含给定集合的元素,按集合迭代器的遍历顺序添加
类成员queue是一个数组,用于存储队列中的元素。size用于记录队列中的元素个数。
modCount主要用于记录PriorityQueue被结构性修改的次数,比如像offer、clear、poll等操作的时候,modCount都会自增。
3. PriorityQueue的核心方法
以下对PriorityQueue常用核心方法的实现原理进行解释。
3.1. offer(e)
执行offer(e)方法后有两种结果
l 队列未达到容量时,返回 true
l 队列达到容量时,先扩容,再返回 true
PriorityQueue的offer (e)方法源码如下:
public boolean offer(E e) {
if (e == null) // 判空
throw new NullPointerException();
modCount++;
int i = size;
if (i >= queue.length)
grow(i + 1); // 扩容
siftUp(i, e); // 插入数据
size = i + 1;
return true;
}
从上面代码可以看出,执行offer(e)方法时,分为以下几个步骤:
l 判断待入队的元素e是否为null。为null则抛出NullPointerException异常。
l 判断当前队列中的元素是否已经大于等于队列的容量,如果是则证明队列已经满了,需要先通过grow ()方法扩容。
l 通过siftUp()方法插入数据元素
l 返回true。
grow()方法源码如下:
private void grow(int minCapacity) {
int oldCapacity = queue.length;
int newCapacity = ArraysSupport.newLength(oldCapacity,
minCapacity - oldCapacity,
oldCapacity < 64 ? oldCapacity + 2 : oldCapacity >> 1
);
queue = Arrays.copyOf(queue, newCapacity);
}
siftUp()方法源码如下:
private void siftUp(int k, E x) {
if (comparator != null)
siftUpUsingComparator(k, x, queue, comparator);
else
siftUpComparable(k, x, queue);
}
private static <T> void siftUpComparable(int k, T x, Object[] es) {
Comparable<? super T> key = (Comparable<? super T>) x;
while (k > 0) {
int parent = (k - 1) >>> 1;
Object e = es[parent];
if (key.compareTo((T) e) >= 0)
break;
es[k] = e;
k = parent;
}
es[k] = key;
}
private static <T> void siftUpUsingComparator(
int k, T x, Object[] es, Comparator<? super T> cmp) {
while (k > 0) {
int parent = (k - 1) >>> 1;
Object e = es[parent];
if (cmp.compare(x, (T) e) >= 0)
break;
es[k] = e;
k = parent;
}
es[k] = x;
}
在上述代码中,在位置k处插入项x,通过向上提升x到树形结构中来维护堆的不变性,直到x大于或等于它的父节点或根节点。
3.2. add(e)
执行add(e)方法后有有两种结果
l 队列未达到容量时,返回 true
l 队列达到容量时,先扩容,再返回 true
PriorityQueue的add(e)方法源码如下:
public boolean add(E e) {
return offer(e);
}
从上面代码可以看出,add(e)方法等同于offer(e)方法的实现。
。
3.3. poll ()
执行poll()方法后有两种结果:
l 队列不为空时,返回队首值并移除
l 队列为空时,返回 null
PriorityQueue的poll()方法源码如下:
public E poll() {
final Object[] es;
final E result;
if ((result = (E) ((es = queue)[0])) != null) {
modCount++;
final int n;
final E x = (E) es[(n = --size)];
es[n] = null;
if (n > 0) {
final Comparator<? super E> cmp;
if ((cmp = comparator) == null)
siftDownComparable(0, x, es, n);
else
siftDownUsingComparator(0, x, es, n, cmp);
}
}
return result;
}
从上面代码可以看出,执行poll()方法时,分为以下几个步骤:
l 先取队列的队首元素。
l 如果队首元素不存在,直接返回null。
l 如果队首元素存在,则返回该元素同时通过siftDownComparable() 或者siftDownUsingComparator()方法来移除元素。
siftDownComparable()和siftDownUsingComparator()方法源码如下:
private static <T> void siftDownComparable(int k, T x, Object[] es, int n) {
Comparable<? super T> key = (Comparable<? super T>)x;
int half = n >>> 1;
while (k < half) {
int child = (k << 1) + 1;
Object c = es[child];
int right = child + 1;
if (right < n &&
((Comparable<? super T>) c).compareTo((T) es[right]) > 0)
c = es[child = right];
if (key.compareTo((T) c) <= 0)
break;
es[k] = c;
k = child;
}
es[k] = key;
}
private static <T> void siftDownUsingComparator(
int k, T x, Object[] es, int n, Comparator<? super T> cmp) {
int half = n >>> 1;
while (k < half) {
int child = (k << 1) + 1;
Object c = es[child];
int right = child + 1;
if (right < n && cmp.compare((T) c, (T) es[right]) > 0)
c = es[child = right];
if (cmp.compare(x, (T) c) <= 0)
break;
es[k] = c;
k = child;
}
es[k] = x;
}
3.4. remove()
执行remove()方法后有两种结果:
l 队列不为空时,返回队首值并移除
l 队列为空时,抛出异常
PriorityQueue的remove()方法其实是调用了父类AbstractQueue的remove ()方法,源码如下:
public E remove() {
E x = poll();
if (x != null)
return x;
else
throw new NoSuchElementException();
}
从上面代码可以看出,remove()直接调用了poll()方法。如果poll()方法返回结果为null,则抛出NoSuchElementException异常。
poll()方法此处不再赘述。
3.5. peek()
执行peek()方法后有两种结果:
l 队列不为空时,返回队首值但不移除
l 队列为空时,返回null
peek()方法源码如下:
public E peek() {
return (E) queue[0];
}
从上面代码可以看出,peek()方法比较简单,直接就是获取了数组里面的索引为0的元素。
3.6. element()
执行element()方法后有两种结果:
l 队列不为空时,返回队首值但不移除
l 队列为空时,抛出异常
element()方法其实是调用了父类AbstractQueue的element()方法,源码如下:
public E element() {
E x = peek();
if (x != null)
return x;
else
throw new NoSuchElementException();
}
从上面代码可以看出,执行element()方法时,先是获取peek()方法的结果,如果结果是null,则抛出NoSuchElementException异常。
4. PriorityQueue的单元测试
PriorityQueue的单元测试如下:
package com.waylau.java.demo.datastructure;
import static org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions.assertEquals;
import static org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions.assertNull;
import static org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions.assertThrows;
import static org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions.assertTrue;
import java.util.NoSuchElementException;
import java.util.PriorityQueue;
import java.util.Queue;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
/**
* PriorityQueue Tests
*
* @since 1.0.0 2020年5月24日
* @author <a href="https://waylau.com">Way Lau</a>
*/
class PriorityQueueTests {
@Test
void testOffer() {
// 初始化队列
Queue<String> queue = new PriorityQueue<String>(3);
// 测试队列未满时,返回 true
boolean resultNotFull = queue.offer("Java");
assertTrue(resultNotFull);
// 测试队列达到容量时,会自动扩容
queue.offer("C");
queue.offer("Python");
boolean resultFull = queue.offer("C++"); // 扩容
assertTrue(resultFull);
}
@Test
void testAdd() {
// 初始化队列
Queue<String> queue = new PriorityQueue<String>(3);
// 测试队列未满时,返回 true
boolean resultNotFull = queue.add("Java");
assertTrue(resultNotFull);
// 测试队列满则扩容,返回 true
queue.add("C");
queue.add("Python");
boolean resultFull = queue.add("C++"); // 扩容
assertTrue(resultFull);
}
@Test
void testPoll() throws InterruptedException {
// 初始化队列
Queue<String> queue = new PriorityQueue<String>(3);
// 测试队列为空时,返回 null
String resultEmpty = queue.poll();
assertNull(resultEmpty);
// 测试队列不为空时,返回队首值并移除
queue.add("Java");
queue.add("C");
queue.add("Python");
String resultNotEmpty = queue.poll();
assertEquals("C", resultNotEmpty);
}
@Test
void testRemove() throws InterruptedException {
// 初始化队列
Queue<String> queue = new PriorityQueue<String>(3);
// 测试队列为空时,抛出异常
Throwable excpetion = assertThrows(NoSuchElementException.class, () -> {
queue.remove();// 抛异常
});
assertEquals(null, excpetion.getMessage());
// 测试队列不为空时,返回队首值并移除
queue.add("Java");
queue.add("C");
queue.add("Python");
String resultNotEmpty = queue.remove();
assertEquals("C", resultNotEmpty);
}
@Test
void testPeek() throws InterruptedException {
// 初始化队列
Queue<String> queue = new PriorityQueue<String>(3);
// 测试队列不为空时,返回队首值并但不移除
queue.add("Java");
queue.add("C");
queue.add("Python");
String resultNotEmpty = queue.peek();
assertEquals("C", resultNotEmpty);
resultNotEmpty = queue.peek();
assertEquals("C", resultNotEmpty);
resultNotEmpty = queue.peek();
assertEquals("C", resultNotEmpty);
// 测试队列为空时,返回null
queue.clear();
String resultEmpty = queue.peek();
assertNull(resultEmpty);
}
@Test
void testElement() throws InterruptedException {
// 初始化队列
Queue<String> queue = new PriorityQueue<String>(3);
// 测试队列不为空时,返回队首值并但不移除
queue.add("Java");
queue.add("C");
queue.add("Python");
String resultNotEmpty = queue.element();
assertEquals("C", resultNotEmpty);
resultNotEmpty = queue.element();
assertEquals("C", resultNotEmpty);
resultNotEmpty = queue.element();
assertEquals("C", resultNotEmpty);
// 测试队列为空时,抛出异常
queue.clear();
Throwable excpetion = assertThrows(NoSuchElementException.class, () -> {
queue.element();// 抛异常
});
assertEquals(null, excpetion.getMessage());
}
}
5. PriorityQueue的应用案例:英雄战力排行榜
以下是一个英雄战力排行榜的示例。该示例模拟了6个英雄,可以根据英雄的战力由高至低排序。
以下是Hero类,用来代表英雄:
package com.waylau.java.demo.datastructure;
/**
* Hero
*
* @since 1.0.0 2020年5月23日
* @author <a href="https://waylau.com">Way Lau</a>
*/
public class Hero {
private String name;
private Integer power; // 战力
public Hero(String name, Integer power) {
this.name = name;
this.power = power;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Integer getPower() {
return power;
}
public void setPower(Integer power) {
this.power = power;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Hero [name=" + name + ", power=" + power + "]";
}
}
以下是应用主程序:
package com.waylau.java.demo.datastructure;
import java.util.Comparator;
import java.util.PriorityQueue;
import java.util.Queue;
/**
* PriorityQueue Demo
*
* @since 1.0.0 2020年5月24日
* @author <a href="https://waylau.com">Way Lau</a>
*/
public class PriorityQueueDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int n = 6;
Queue<Hero> queue = new PriorityQueue<Hero>(n, new Comparator<Hero>() {
// 战力由大到小排序
@Override
public int compare(Hero hero0, Hero hero1) {
return hero1.getPower().compareTo(hero0.getPower());
}
});
queue.add(new Hero("Nemesis", 95));
queue.add(new Hero("Edifice Rex", 88));
queue.add(new Hero("Marquis of Death", 91));
queue.add(new Hero("Magneto", 96));
queue.add(new Hero("Hulk", 85));
queue.add(new Hero("Doctor Strange", 94));
for (int i = 0; i<n ; i++) {
System.out.println(queue.poll());
}
}
}
运行上述程序,输出内容如下:
Hero [name=Magneto, power=96]
Hero [name=Nemesis, power=95]
Hero [name=Doctor Strange, power=94]
Hero [name=Marquis of Death, power=91]
Hero [name=Edifice Rex, power=88]
Hero [name=Hulk, power=85]
6. 参考引用
本系列归档至《Java数据结构及算法实战》:https://github.com/waylau/java-data-structures-and-algorithms-in-action
《数据结构和算法基础(Java语言实现)》(柳伟卫著,北京大学出版社出版):https://item.jd.com/13014179.html
-
Mybatis官方生成器资料详解与应用教程11-26
-
Mybatis一级缓存资料详解与实战教程11-26
-
Mybatis一级缓存资料详解:新手快速入门11-26
-
SpringBoot3+JDK17搭建后端资料详尽教程11-26
-
Springboot单体架构搭建资料:新手入门教程11-26
-
Springboot单体架构搭建资料详解与实战教程11-26
-
Springboot框架资料:新手入门教程11-26
-
Springboot企业级开发资料入门教程11-26
-
SpringBoot企业级开发资料详解与实战教程11-26
-
Springboot微服务资料:新手入门全攻略11-26
-
SpringBoot微服务资料入门教程11-26
-
Springboot项目开发资料详解与入门指南11-26
-
SpringBoot项目开发资料详解入门教程11-26
-
SpringBoot应用的生产发布资料详解11-26
-
手写消息中间件:从零开始的指南11-26