Python教程
使用ipython来实现代码自动补全,自动缩进等功能
主旨
python自带的shell交互界面,对于使用不太友好,全程需要手动输入,不能自动提示,也不能自动缩进。我们有没有别的方式可以代替这个东西呢?
在这里,我们引入一个ipython,通过ipython可以代替python自带的shell交互界面,且上面提到的问题都能得到一个友好的解决。并且看下如何使用。
功能
运行ipython控制台 使用ipython作为系统shell 使用历史输入(history) Tab补全 使用%run命令运行脚本 使用%timeit命令快速测量时间 使用%pdb命令快速debug 使用pylab进行交互计算 使用IPython Notebook
环境
linux 环境 python3+ 环境,建议3.7.5 以上的版本
注意事项
我这里是安装了python3,所以pip命令也用的pip3,具体是pip还是pip3,要根据你实际情况来确定。
安装ipython
[yunweijia@localhost ~]$ sudo pip3 install ipython
以上一条命令即安装成功了,如果还需要别的功能,或者别的方式,可以再安装如下模块(自选),推荐安装jupyter:
# 浏览器访问编辑,并进行交互 [yunweijia@localhost ~]$ sudo pip3 install jupyter # 高性能多维数组矢量运算库 [yunweijia@localhost ~]$ sudo pip3 install numpy # 绘图以及交互式可视化 [yunweijia@localhost ~]$ sudo pip3 install matplotlib
交互式使用ipython
IPython支持所有python的标准输入输出,也就是我们在IDLE(pycharm)中或者Python shell中能用的,在IPython中都能够使用,唯一的不同之处是ipython会使用In [x]和Out [x]表示输入输出,并表示出相应的序号。
进入Ipython,直接在命令行输入ipython,即可进入:
[yunweijia@localhost ~]$ ipython
/usr/local/python3/lib/python3.7/site-packages/IPython/core/history.py:226: UserWarning: IPython History requires SQLite, your history will not be saved
warn("IPython History requires SQLite, your history will not be saved")
Python 3.7.1 (default, Jan 29 2022, 15:20:20)
Type 'copyright', 'credits' or 'license' for more information
IPython 7.32.0 -- An enhanced Interactive Python. Type '?' for help.
In [1]: print(1+2)
3
In [2]:
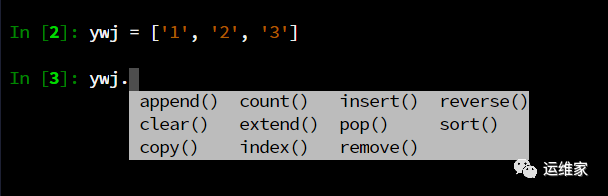
自动补全
输入命令的前面部分,然后直接按“tab”按键即可,如下:
亦或者,你要输入“import” 的时候,不需要每次都输入全部,只需要输入“im”,然后按“tab”,即可显示“import”,这里只是举个例子,别的类似的使用方式,都可。
内省
在变量的前面或者后面加上一个问号?,就可以将有关该对象的一些通用信息显示出来,这就叫做对象的内省,如下:
In [2]: ywj = ['1', '2', '3'] In [3]: ywj? Type: list String form: ['1', '2', '3'] Length: 3 Docstring: Built-in mutable sequence. If no argument is given, the constructor creates a new empty list. The argument must be an iterable if specified. In [4]:
不只是变量可以,就算是函数也不例外,如下:
In [4]: def ywj(a,b): ...: print(a + b) ...: In [5]: ywj? Signature: ywj(a, b) Docstring: <no docstring> File: ~/<ipython-input-4-ba6bddc1383d> Type: function In [6]:
那么如果使用两个问号(??)呢,我们又会获取什么信息?我们将会获取这个变量的源代码,如下:
In [7]: ywj??
Signature: ywj(a, b)
Docstring: <no docstring>
Source:
def ywj(a,b):
print(a + b)
File: ~/<ipython-input-6-ba6bddc1383d>
Type: function
In [8]:
另外,我们可以使用通配符字符串查找出所有与该通配符字符串相匹配的名称,比如我们查找 “re” 模块下所有的包含 “find” 的函数:
In [9]: re.*find*? re.findall re.finditer In [10]:
使用历史命令history
使用hist或者histoy可以查看该shell中之前输入过的历史命令:
In [11]: hist
print(1+2)
ywj = ['1', '2', '3']
ywj?
def ywj(a,b):
print(a + b)
ywj?
def ywj(a,b):
print(a + b)
ywj??
import re
re.*find*?
hist
In [12]:
如果我们在hist或者history后面加上“-n”,也可以显示输入内容的序号:
In [13]: history -n
1: print(1+2)
2: ywj = ['1', '2', '3']
3: ywj?
4:
def ywj(a,b):
print(a + b)
5: ywj?
6:
def ywj(a,b):
print(a + b)
7: ywj??
8: import re
9: re.*find*?
10: re.*find*
11: hist
12: history
13: history -n
In [14]:
在任何的交互会话中,我们的输入历史和输出历史都会被保存在In和Out变量中,并被序号进行索引。
另外,_,__,___和_i,_ii,_iii变量保存着最后三个输出和输入对象。_n和_in(这里的n表示具体的数字)变量返回第n个输出和输入的历史命令。比如:
In [17]: _i1 Out[17]: 'print(1+2)' In [18]: _ Out[18]: 'print(1+2)' In [19]:
使用%run命令运行脚本
在ipython会话环境中,所有文件都可以通过%run命令当做Python程序来运行,输入%run 路径+python文件名称即可
使用%time测算代码运行时间
在一个交互式会话中,我们可以使用%timeit魔法命令快速测量代码运行时间。相同的命令会在一个循环中多次执行,多次运行时长的平均值作为该命令的最终评估时长。-n 选项可以控制命令在单词循环中执行的次数,-r选项控制执行循环的次数。
In [22]: %timeit [x for x in range(1000)] 25.8 µs ± 408 ns per loop (mean ± std. dev. of 7 runs, 10000 loops each) In [23]:
使用%debug命令快速进行debug
-
用FastAPI掌握Python异步IO:轻松实现高并发网络请求处理01-03
-
封装学习:Python面向对象编程基础教程01-02
-
Python编程基础教程12-28
-
Python编程入门指南12-27
-
Python编程基础12-27
-
Python编程基础教程12-27
-
Python编程基础指南12-27
-
Python编程入门指南12-24
-
Python编程基础入门12-24
-
Python编程基础:变量与数据类型12-24
-
使用python部署一个usdt合约,部署自己的usdt稳定币12-23
-
Python编程入门指南12-20
-
Python编程基础与进阶12-20
-
Python基础编程教程12-19
-
python 文件的后缀名是什么 怎么运行一个python文件?-icode9专业技术文章分享12-19