Java教程
聊聊如何通过自定义注解实现springmvc和sentinel整合
前言
之前写过一篇文章[聊聊因不恰当使用alibaba sentinel而踩到的坑]。其实这里面有些坑是因为在sentinel在mvc项目统计时,是基于mvc的拦截器来实现。这种方式会导致比如热点参数规则,比较难获取到参数,因此要在项目中额外配置@SentinelResource注解才会生效。今天我们就来聊下如何通过自定义注解把springmvc请求的功能和sentinel功能给整合起来
实现思路
核心思路通过一个注解把springmvc的@RequestMapping具备的功能 + @SentinelResource具备的功能给聚合起来
实现步骤
1、自定义注解
@Target({ElementType.TYPE, ElementType.METHOD})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Mapping
public @interface CircuitBreakerMapping {
//----------------RequestMapping-------------------------------
/**
* Assign a name to this mapping.
* <p><b>Supported at the type level as well as at the method level!</b>
* When used on both levels, a combined name is derived by concatenation
* with "#" as separator.
* @see org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.MvcUriComponentsBuilder
* @see org.springframework.web.servlet.handler.HandlerMethodMappingNamingStrategy
*/
String name() default "";
/**
* The primary mapping expressed by this annotation.
* <p>This is an alias for {@link #path}. For example
* {@code @RequestMapping("/foo")} is equivalent to
* {@code @RequestMapping(path="/foo")}.
* <p><b>Supported at the type level as well as at the method level!</b>
* When used at the type level, all method-level mappings inherit
* this primary mapping, narrowing it for a specific handler method.
*/
@AliasFor("path")
String[] value() default {};
/**
* The path mapping URIs (e.g. "/myPath.do").
* Ant-style path patterns are also supported (e.g. "/myPath/*.do").
* At the method level, relative paths (e.g. "edit.do") are supported
* within the primary mapping expressed at the type level.
* Path mapping URIs may contain placeholders (e.g. "/${connect}").
* <p><b>Supported at the type level as well as at the method level!</b>
* When used at the type level, all method-level mappings inherit
* this primary mapping, narrowing it for a specific handler method.
* @see org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ValueConstants#DEFAULT_NONE
* @since 4.2
*/
@AliasFor("value")
String[] path() default {};
/**
* The HTTP request methods to map to, narrowing the primary mapping:
* GET, POST, HEAD, OPTIONS, PUT, PATCH, DELETE, TRACE.
* <p><b>Supported at the type level as well as at the method level!</b>
* When used at the type level, all method-level mappings inherit
* this HTTP method restriction (i.e. the type-level restriction
* gets checked before the handler method is even resolved).
*/
RequestMethod[] method() default {};
/**
* The parameters of the mapped request, narrowing the primary mapping.
* <p>Same format for any environment: a sequence of "myParam=myValue" style
* expressions, with a request only mapped if each such parameter is found
* to have the given value. Expressions can be negated by using the "!=" operator,
* as in "myParam!=myValue". "myParam" style expressions are also supported,
* with such parameters having to be present in the request (allowed to have
* any value). Finally, "!myParam" style expressions indicate that the
* specified parameter is <i>not</i> supposed to be present in the request.
* <p><b>Supported at the type level as well as at the method level!</b>
* When used at the type level, all method-level mappings inherit
* this parameter restriction (i.e. the type-level restriction
* gets checked before the handler method is even resolved).
* <p>Parameter mappings are considered as restrictions that are enforced at
* the type level. The primary path mapping (i.e. the specified URI value)
* still has to uniquely identify the target handler, with parameter mappings
* simply expressing preconditions for invoking the handler.
*/
String[] params() default {};
/**
* The headers of the mapped request, narrowing the primary mapping.
* <p>Same format for any environment: a sequence of "My-Header=myValue" style
* expressions, with a request only mapped if each such header is found
* to have the given value. Expressions can be negated by using the "!=" operator,
* as in "My-Header!=myValue". "My-Header" style expressions are also supported,
* with such headers having to be present in the request (allowed to have
* any value). Finally, "!My-Header" style expressions indicate that the
* specified header is <i>not</i> supposed to be present in the request.
* <p>Also supports media type wildcards (*), for headers such as Accept
* and Content-Type. For instance,
* <pre class="code">
* @RequestMapping(value = "/something", headers = "content-type=text/*")
* </pre>
* will match requests with a Content-Type of "text/html", "text/plain", etc.
* <p><b>Supported at the type level as well as at the method level!</b>
* When used at the type level, all method-level mappings inherit
* this header restriction (i.e. the type-level restriction
* gets checked before the handler method is even resolved).
* @see org.springframework.http.MediaType
*/
String[] headers() default {};
/**
* The consumable media types of the mapped request, narrowing the primary mapping.
* <p>The format is a single media type or a sequence of media types,
* with a request only mapped if the {@code Content-Type} matches one of these media types.
* Examples:
* <pre class="code">
* consumes = "text/plain"
* consumes = {"text/plain", "application/*"}
* </pre>
* Expressions can be negated by using the "!" operator, as in "!text/plain", which matches
* all requests with a {@code Content-Type} other than "text/plain".
* <p><b>Supported at the type level as well as at the method level!</b>
* When used at the type level, all method-level mappings override
* this consumes restriction.
* @see org.springframework.http.MediaType
* @see javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest#getContentType()
*/
String[] consumes() default {};
/**
* The producible media types of the mapped request, narrowing the primary mapping.
* <p>The format is a single media type or a sequence of media types,
* with a request only mapped if the {@code Accept} matches one of these media types.
* Examples:
* <pre class="code">
* produces = "text/plain"
* produces = {"text/plain", "application/*"}
* produces = MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON_UTF8_VALUE
* </pre>
* <p>It affects the actual content type written, for example to produce a JSON response
* with UTF-8 encoding, {@link org.springframework.http.MediaType#APPLICATION_JSON_UTF8_VALUE} should be used.
* <p>Expressions can be negated by using the "!" operator, as in "!text/plain", which matches
* all requests with a {@code Accept} other than "text/plain".
* <p><b>Supported at the type level as well as at the method level!</b>
* When used at the type level, all method-level mappings override
* this produces restriction.
* @see org.springframework.http.MediaType
*/
String[] produces() default {};
//------------------------CircuitBreaker-------------------------------------
EntryType entryType() default EntryType.OUT;
int resourceType() default COMMON_WEB;
String blockHandler() default "";
Class<?>[] blockHandlerClass() default {};
String fallback() default "";
String defaultFallback() default "";
Class<?>[] fallbackClass() default {};
Class<? extends Throwable>[] exceptionsToTrace() default {Throwable.class};
Class<? extends Throwable>[] exceptionsToIgnore() default {};
}
其实这个注解就是把@RequestMapping和@SentinelResource参数给整合一块
2、实现@RequestMapping功能
1、重写RequestMappingHandlerMapping
public class CircuitBreakerMappingHandlerMapping extends RequestMappingHandlerMapping {
private RequestMappingInfo.BuilderConfiguration config = new RequestMappingInfo.BuilderConfiguration();
private Map<String, Predicate<Class<?>>> pathPrefixes = new LinkedHashMap<>();
@Nullable
private StringValueResolver embeddedValueResolver;
@Override
protected boolean isHandler(Class<?> beanType) {
return (AnnotatedElementUtils.hasAnnotation(beanType, Controller.class) ||
AnnotatedElementUtils.hasAnnotation(beanType, RequestMapping.class) ||
AnnotatedElementUtils.hasAnnotation(beanType, CircuitBreakerMapping.class)
);
}
@Nullable
@Override
protected RequestMappingInfo getMappingForMethod(Method method, Class<?> handlerType) {
RequestMappingInfo info = this.createRequestMappingInfo(method);
if (info != null) {
RequestMappingInfo typeInfo = this.createRequestMappingInfo(handlerType);
if (typeInfo != null) {
info = typeInfo.combine(info);
}
String prefix = this.getPathPrefix(handlerType);
if (prefix != null) {
info = RequestMappingInfo.paths(new String[]{prefix}).build().combine(info);
}
}
return info;
}
@Nullable
private RequestMappingInfo createRequestMappingInfo(AnnotatedElement element) {
CircuitBreakerMapping requestMapping = AnnotatedElementUtils.findMergedAnnotation(element, CircuitBreakerMapping.class);
RequestCondition<?> condition = element instanceof Class ? this.getCustomTypeCondition((Class)element) : this.getCustomMethodCondition((Method)element);
return requestMapping != null ? this.createRequestMappingInfo(requestMapping, condition) : null;
}
protected RequestMappingInfo createRequestMappingInfo(
CircuitBreakerMapping requestMapping, @Nullable RequestCondition<?> customCondition) {
RequestMappingInfo.Builder builder = RequestMappingInfo
.paths(resolveEmbeddedValuesInPatterns(requestMapping.path()))
.methods(requestMapping.method())
.params(requestMapping.params())
.headers(requestMapping.headers())
.consumes(requestMapping.consumes())
.produces(requestMapping.produces())
.mappingName(requestMapping.name());
if (customCondition != null) {
builder.customCondition(customCondition);
}
return builder.options(this.config).build();
}
@Nullable
String getPathPrefix(Class<?> handlerType) {
for (Map.Entry<String, Predicate<Class<?>>> entry : this.pathPrefixes.entrySet()) {
if (entry.getValue().test(handlerType)) {
String prefix = entry.getKey();
if (this.embeddedValueResolver != null) {
prefix = this.embeddedValueResolver.resolveStringValue(prefix);
}
return prefix;
}
}
return null;
}
}
ps: 该重写核心点是要兼容springmvc已有的功能
2、将springmvc默认的RequestMappingHandlerMapping替换为我们自己实现的RequestMappingHandlerMapping
public class CircuitBreakerMappingWebMvcRegistrations implements WebMvcRegistrations {
@Override
public RequestMappingHandlerMapping getRequestMappingHandlerMapping() {
return new CircuitBreakerMappingHandlerMapping();
}
}
3、实现@SentinelResource功能
因为@SentinelResource是基于aop进行实现,所以只需将aop使用@SentinelResource替换为我们自定义的注解即可
核心代码块
@Aspect
public class CircuitBreakerAspect extends AbstractCircuitBreakerAspectSupport {
@Around("@annotation(circuitBreakerMapping)")
public Object invokeResourceWithSentinel(ProceedingJoinPoint pjp, CircuitBreakerMapping circuitBreakerMapping) throws Throwable {
Method originMethod = resolveMethod(pjp);
CircuitBreakerMapping controllerCircuitBreakerMapping = AnnotationUtils.findAnnotation(pjp.getTarget().getClass(),CircuitBreakerMapping.class);
String baseResouceName = "lybgeek:";
if(circuitBreakerMapping != null){
baseResouceName = baseResouceName + controllerCircuitBreakerMapping.value()[0];
}
baseResouceName = baseResouceName + circuitBreakerMapping.value()[0];
String resourceName = getResourceName(baseResouceName, originMethod);
EntryType entryType = circuitBreakerMapping.entryType();
int resourceType = circuitBreakerMapping.resourceType();
Entry entry = null;
try {
String contextName = "lybgeek_circuitbreaker_context";
RequestOriginParser parser = SpringUtil.getBean(RequestOriginParser.class);
ContextUtil.enter(contextName,parser.parseOrigin(getRequest()));
entry = SphU.entry(resourceName, resourceType, entryType, pjp.getArgs());
Object result = pjp.proceed();
return result;
} catch (BlockException ex) {
return handleBlockException(pjp, circuitBreakerMapping, ex);
} catch (Throwable ex) {
Class<? extends Throwable>[] exceptionsToIgnore = circuitBreakerMapping.exceptionsToIgnore();
// The ignore list will be checked first.
if (exceptionsToIgnore.length > 0 && exceptionBelongsTo(ex, exceptionsToIgnore)) {
throw ex;
}
if (exceptionBelongsTo(ex, circuitBreakerMapping.exceptionsToTrace())) {
traceException(ex, circuitBreakerMapping);
return handleFallback(pjp, circuitBreakerMapping, ex);
}
// No fallback function can handle the exception, so throw it out.
throw ex;
} finally {
if (entry != null) {
entry.exit(1, pjp.getArgs());
}
ContextUtil.exit();
}
}
}
集成效果演示
1、编写测试控制器
@RestController
@CircuitBreakerMapping(value = "/test")
public class TestController {
@CircuitBreakerMapping(value = "/flow/{username}")
public String flow(@PathVariable("username") String username){
return "flow circuit breaker mapping : " + username;
}
@CircuitBreakerMapping(value = "/degrade/{username}")
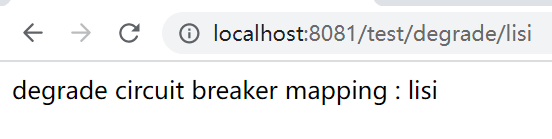
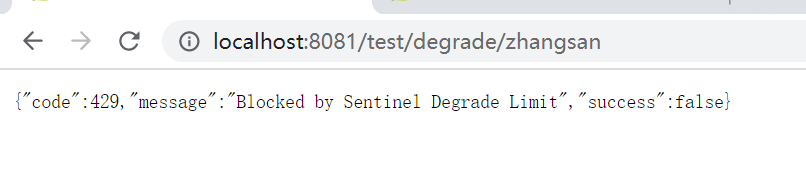
public String degrade(@PathVariable("username") String username){
if("zhangsan".equals(username)){
throw new BizException(400,String.format("illgel username --> %s",username));
}
return "degrade circuit breaker mapping : " + username;
}
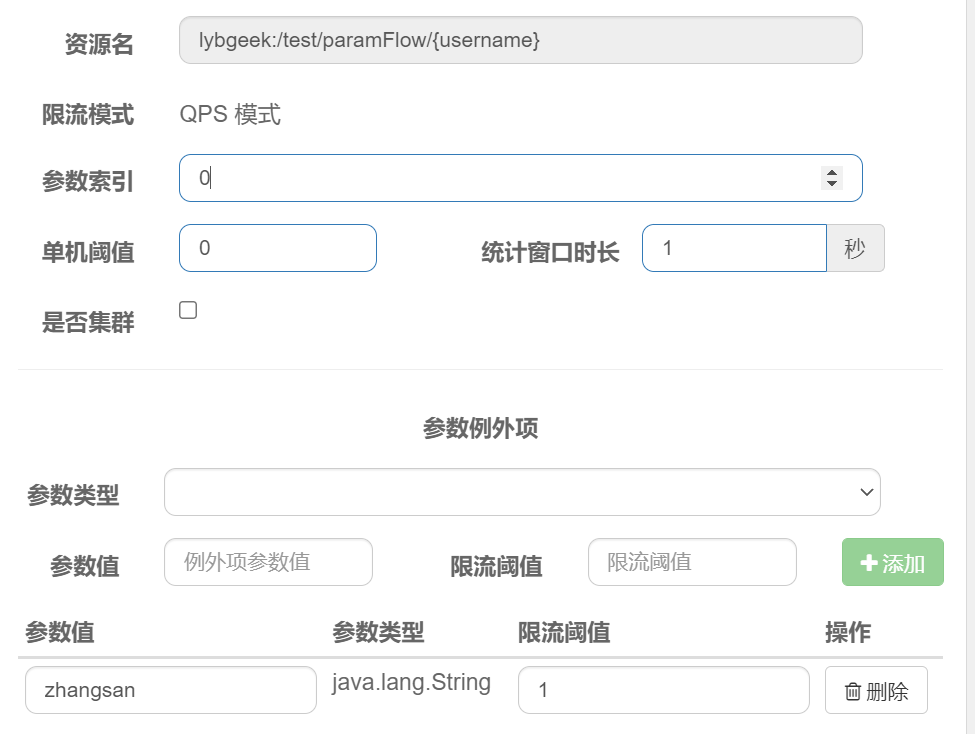
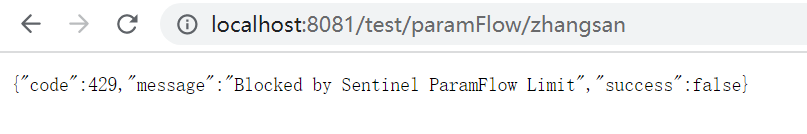
@CircuitBreakerMapping(value = "/paramFlow/{username}")
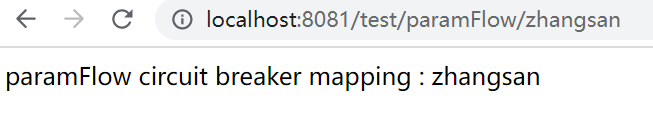
public String paramFlow(@PathVariable("username") String username){
return "paramFlow circuit breaker mapping : " + username;
}
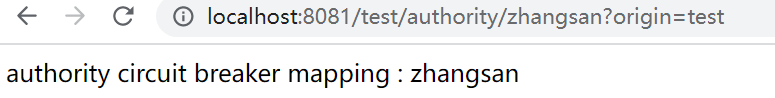
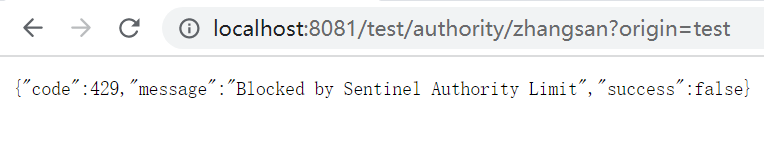
@CircuitBreakerMapping(value = "/authority/{username}",fallback = "fallback")
public String authority(@PathVariable("username") String username,String origin){
System.out.println("origin:-->" + origin);
return "authority circuit breaker mapping : " + username;
}
@CircuitBreakerMapping(value = "/{username}",fallback = "fallback")
public String username(@PathVariable("username") String username){
return " circuit breaker mapping : " + username;
}
public String fallback(String username){
return "fallback circuit breaker mapping : " + username;
}
}
2、application.yml中配置sentinel dashbord地址
spring:
cloud:
sentinel:
transport:
dashboard: localhost:8080
3、测试
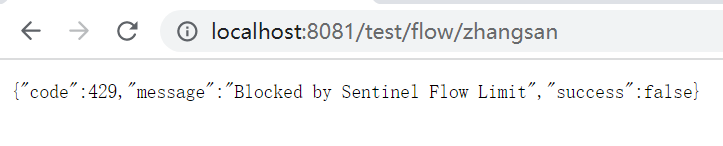
3.1、流控效果
a、 未配置流控效果:
b、 配置流控效果
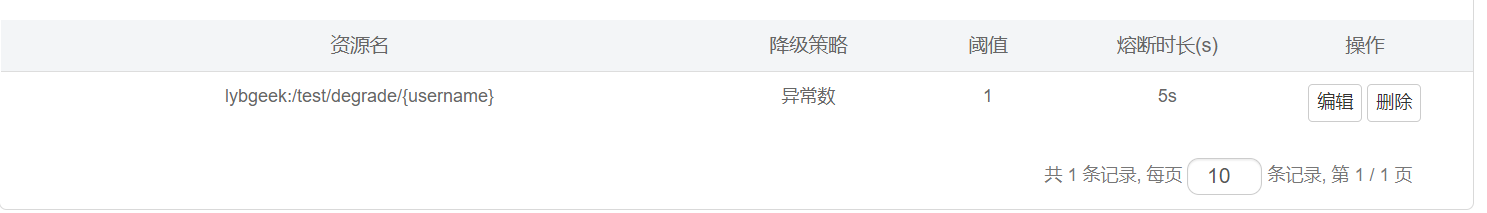
3.2、降级效果
a、 未配置降级效果:
b、 配置降级效果
3.3、热点参数流控效果
a、 未配置热点参数流控效果:
b、 配置热点参数流控效果
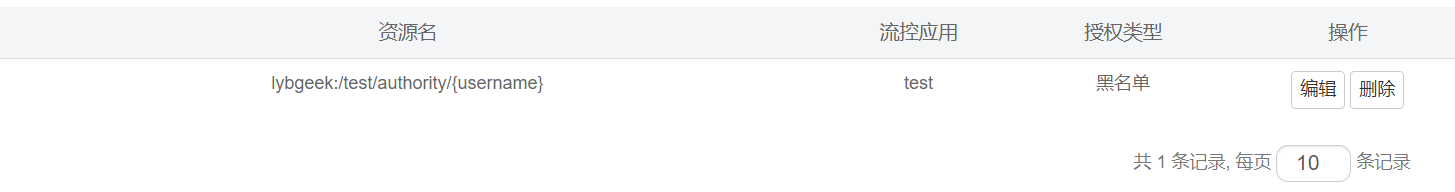
3.3、授权流控效果
a、 未配置授权流控效果:
b、 配置授权流控效果
总结
总体来说思路不是很难,实现的时候注意要兼容原本的功能,不能实现一个功能,把原来具备的功能也弄没了。其次实现的时候,注意一下是基于哪个版本进行实现,这个很重要,因为不同版本,它可能废除一些api也可能新增一些api,甚至可能api没变,但是包名变了
-
JavaMailSender是什么,怎么使用?-icode9专业技术文章分享11-15
-
JWT 用户校验学习:从入门到实践11-15
-
Nest学习:新手入门全面指南11-15
-
RestfulAPI学习:新手入门指南11-15
-
Server Component学习:入门教程与实践指南11-15
-
动态路由入门:新手必读指南11-15
-
JWT 用户校验入门:轻松掌握JWT认证基础11-15
-
Nest后端开发入门指南11-15
-
Nest后端开发入门教程11-15
-
RestfulAPI入门:新手快速上手指南11-15
-
Server Action入门:新手必读教程11-15
-
Server Component入门:新手必读教程11-15
-
抽离公共代码教程:简单易懂的入门指南11-15
-
动态路由教程:轻松入门与实战指南11-15
-
Restful API教程:入门与实践指南11-15