Java教程
路由之跳转与传参
路由跳转
通常理解的页面跳转是,发生点击事件时,从一个页面跳转到另一个页面的过程。
但对于 Angular 这种单页面应用而言,页面跳转只是与路径进行匹配,若匹配成功则渲染相应的组件,并通过 html5 的history.pushState方法更新历史记录。
模板中的指令跳转
在模板文件中,通过 RouterLink 指令来设置路由跳转。
例子:
app-routing.module.ts
import { NgModule } from '@angular/core';
import { RouterModule, Routes } from '@angular/router';
import { LoginComponent } from './components/login/login.component';
import { WelcomeComponent } from './components/welcome/welcome.component';
import { PageNotFoundComponent } from './components//page-not-found/page-not-found.component';
import { AboutComponent } from './components//about/about.component';
const routes: Routes = [
{
path: 'login',
component: LoginComponent
},
{
path: 'welcome',
component: WelcomeComponent
},
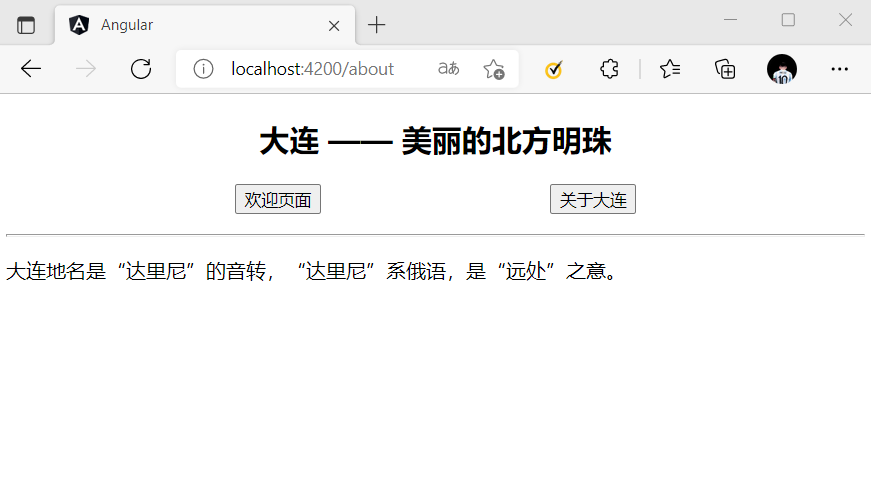
{
path: 'about',
component: AboutComponent
},
{
path: '',
redirectTo: '/login',
pathMatch: 'full'
},
{ path: '**',
component: PageNotFoundComponent
}
];
@NgModule({
imports: [RouterModule.forRoot(routes)],
exports: [RouterModule]
})
export class AppRoutingModule { }
app.component.html
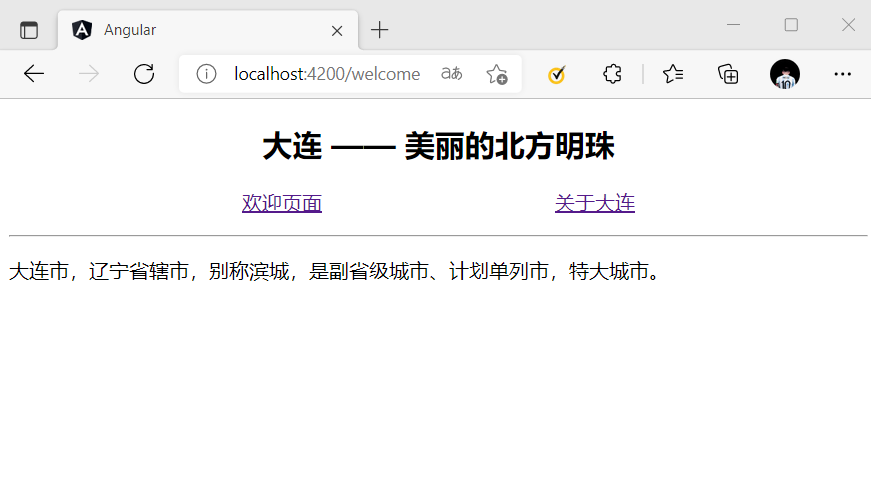
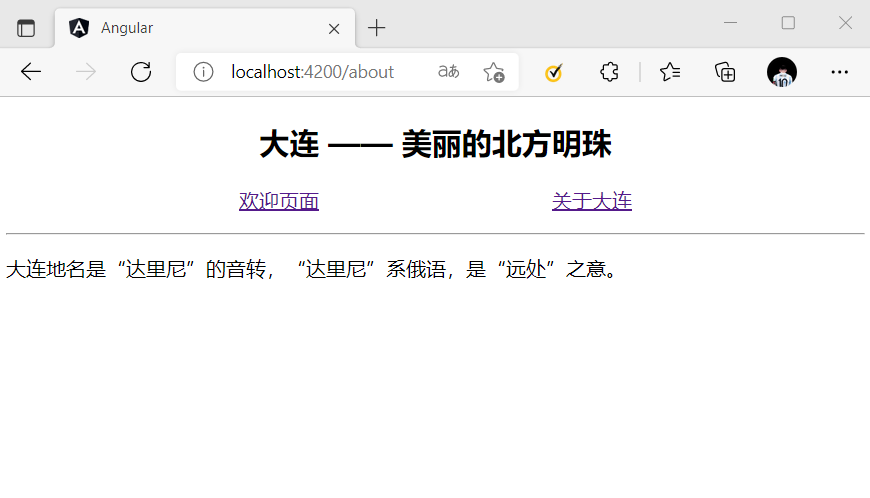
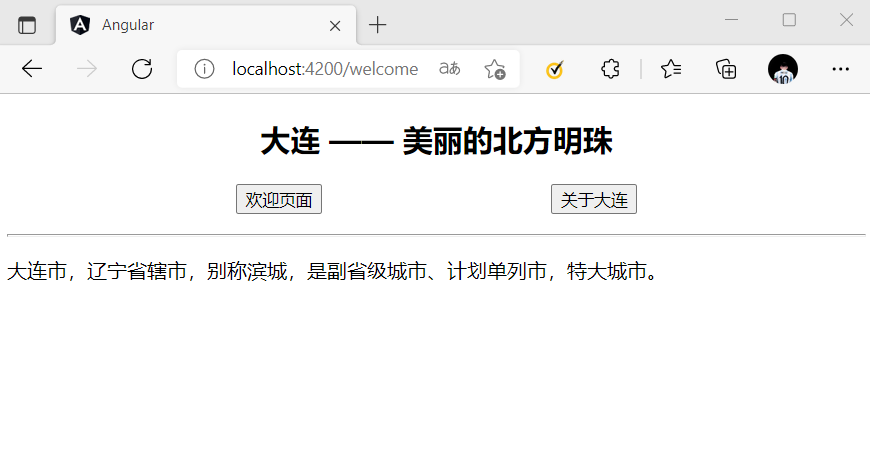
<section>
<header style="text-align: center;">
<h2>大连 —— 美丽的北方明珠</h2>
</header>
<p style="display: flex; justify-content: space-evenly;">
<a [routerLink]="['/welcome']">欢迎页面</a>
<a [routerLink]="['/about']">关于大连</a>
</p>
<hr>
<router-outlet></router-outlet>
<footer></footer>
</section>
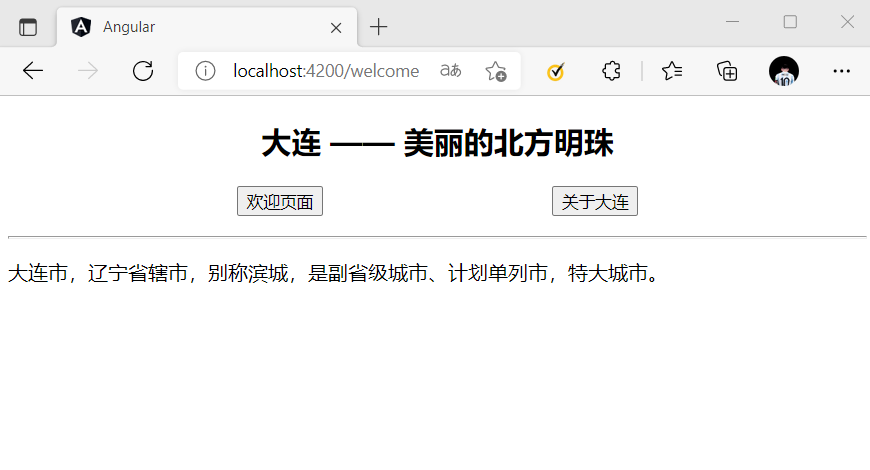
RouterLink 指令不局限于
<a>标签,它可以被应用在任何 html 标签上,比如常用的<button>。
例子:
// app.component.html <p style="display: flex; justify-content: space-evenly;"> <button [routerLink]="['/welcome']">欢迎页面</button> <button [routerLink]="['/about']">关于大连</button> </p>
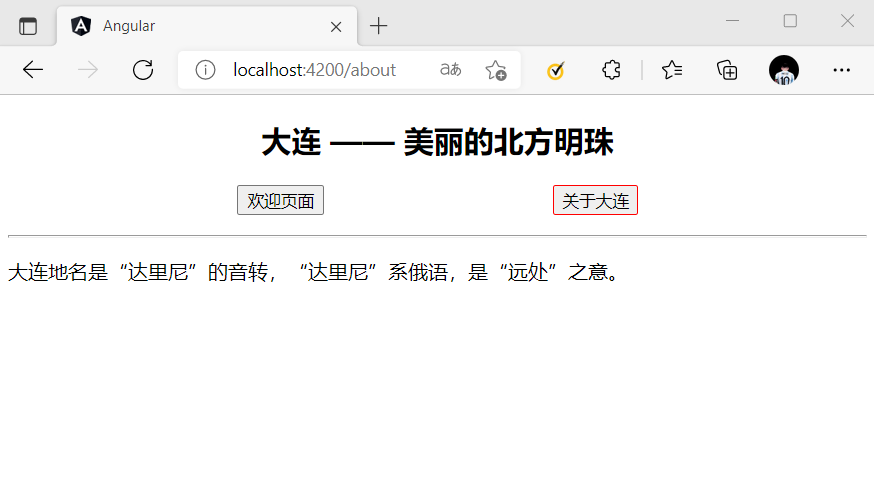
当 RouterLink 被激活时,可以通过 routerLinkActive 指令指定 CSS 类。
例子:
// app.component.scss
.active{
border: 1px solid red;
}
// app.component.html
<p style="display: flex; justify-content: space-evenly;">
<button [routerLink]="['/welcome']" [routerLinkActive]="['active']">欢迎页面</button>
<button [routerLink]="['/about']" [routerLinkActive]="['active']">关于大连</button>
</p>
组件中的代码跳转
在组件中,通过 Router.navigate() 方法来完成跳转。
例子:
app.component.html
<p style="display: flex; justify-content: space-evenly;"> <button (click)="toWelcome()">欢迎页面</button> <button (click)="toAbout()">关于大连</button> </p>
app.component.ts
import { Component } from '@angular/core';
// 导入 Router 对象
import { Router } from '@angular/router';
@Component({
selector: 'app-root',
templateUrl: './app.component.html',
styleUrls: ['./app.component.scss']
})
export class AppComponent {
constructor(
// 初始化 Router 对象
private router: Router,
) { }
// 跳转 welcome 页面
toWelcome(){
this.router.navigate(['/welcome']);
}
// 跳转 about 页面
toAbout(){
this.router.navigate(['/about']);
}
}
路由传参
Angular 路由具有传递参数的功能,可以通过 URL 向目标组件传递数据。
路径参数
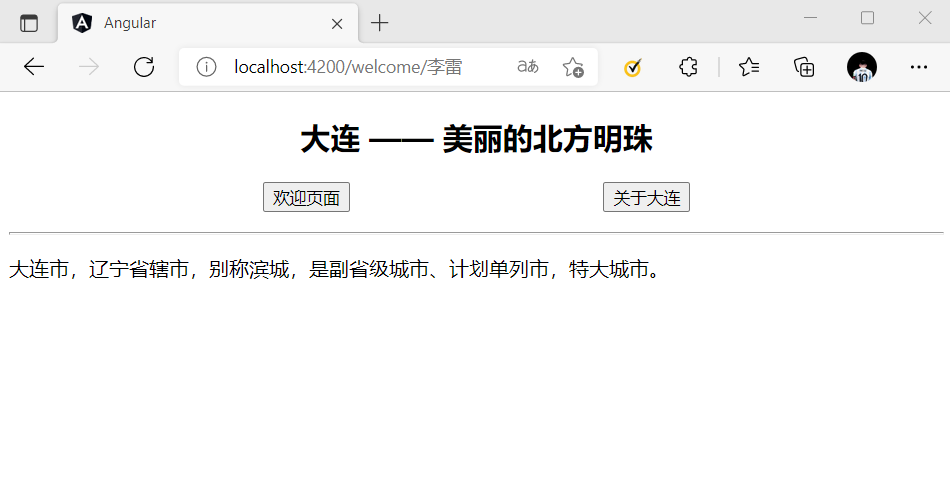
// 基本形式 http://localhost:4200/welcome/李雷
路径参数,顾名思义,在配置路由的 path 属性时,可以在路径一段的前面添加冒号,表明这是一个参数。
// 在 path 下配置路由参数 name
{
path: 'welcome/:name',
component: WelcomeComponent
}
接下来,不管是手动输入 URL,还是通过 RouterLink,或者 Router.navigate() 完成跳转,都需要给参数 name 赋值。
[routerLink]="['/welcome','李雷']" this.router.navigate(['/welcome','李雷']);
获取参数
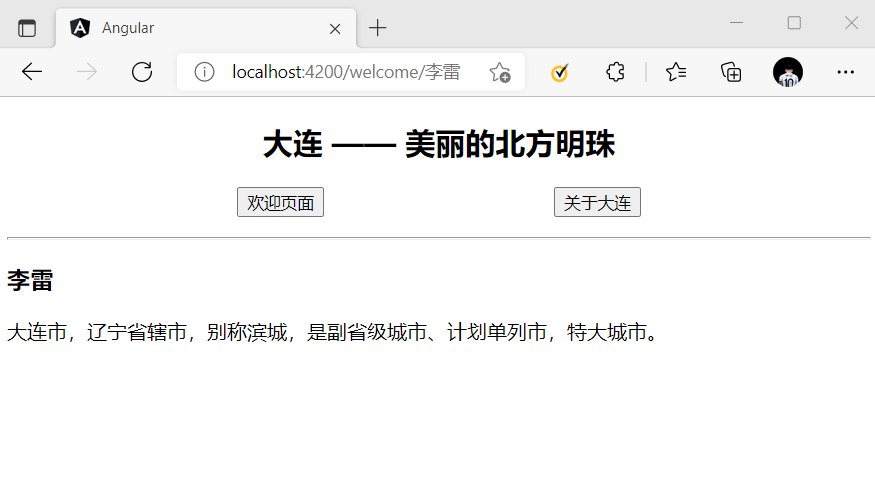
为了使用路径参数,我们需要在目标组件中导入 ActivatedRoute 对象。
该 ActivatedRoute 对象包含了一个 params 参数订阅,可以从 URL 中解析出路径参数。
例子:
welcome.component.ts
import { Component, OnInit } from '@angular/core';
// 导入 ActivatedRoute
import { ActivatedRoute } from '@angular/router';
@Component({
selector: 'app-welcome',
templateUrl: './welcome.component.html',
styleUrls: ['./welcome.component.scss']
})
export class WelcomeComponent implements OnInit {
name!:string;
constructor(
// 初始化 ActivatedRoute
private activedRoute: ActivatedRoute,
) { }
ngOnInit() {
// 使用参数订阅
this.activedRoute.params.subscribe((params:any)=>{
this.name = params['name'];
});
}
}
查询参数
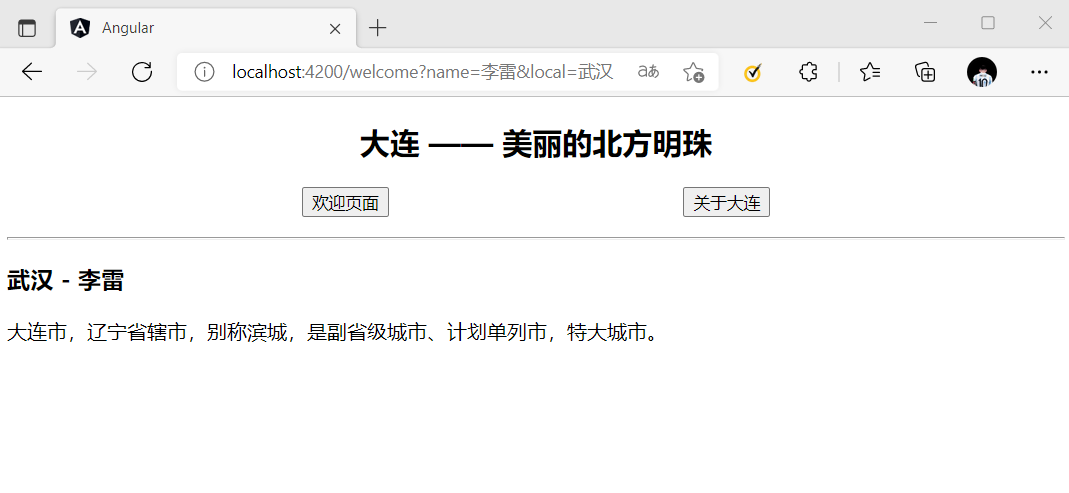
// 基本形式 http://localhost:4200/welcome?name=李雷&local=武汉
查询参数无需在 path 属性中进行配置,而且可以拥有任意多个参数。
同样通过 RouterLink 或者 Router.navigate() 来赋值。
[routerLink]="['/welcome']" [queryParams]="{name:'李雷', local:'武汉'}"
this.router.navigate(
['/welcome'],
{
queryParams:{
name:'李雷',
local:'武汉'
}
}
);
获取参数
通过 ActivatedRoute 对象的 queryParams 参数订阅,获取到查询参数。
this.activedRoute.queryParams.subscribe((queryParams:any)=>{
this.name = queryParams['name'];
this.local = queryParams['local'];
});
end
-
如何利用看板工具优化品牌内容创作与审批,确保按时发布?01-07
-
百万架构师第十一课:源码分析:Spring 源码分析:Spring源码分析前篇|JavaGuide01-07
-
质量检测标准严苛,这 6 款办公软件达标了吗?01-07
-
提升品牌活动管理的效率:看板工具助力品牌活动日历的可视化管理01-07
-
宠物商场的精准营销秘籍:揭秘看板软件的力量01-07
-
“30了,资深骑手” | 程序员能有什么好出路?01-07
-
宠物公园的营销秘籍:看板软件如何帮你精准触达目标客户?01-07
-
从任务分解到资源优化:甘特图工具全解析01-07
-
企业升级必备指南:从传统办公软件到SaaS工具的转型攻略01-07
-
一文告诉你IT项目管理如何做到高效01-07
-
好用的备忘录待办提醒APP 任务管理工具怎么选?01-07
-
如何在小团队中实现高效协作?6个关键步骤01-07
-
如何在快节奏行业中实现高效项目管理?5大实用策略01-07
-
零部件采购求精准,这 6 款办公软件匹配度咋样?01-07
-
提高团队协作效率:如何通过可视化看板工具提升执行力与透明度01-07