Java教程
路由之配置基础路由
本文主要是介绍路由之配置基础路由,对大家解决编程问题具有一定的参考价值,需要的程序猿们随着小编来一起学习吧!
基本概念
路由的概念并不是全新的,只不过一直是在服务器端编写路由代码。通常,服务器在收到 HTTP 请求时,会根据 URL 来显示相应的页面。
Angular 路由是在客户端编写路由,概念与服务器端基本类似,唯一不同的是,服务器端路由的核心概念是建立 URL 与页面的关系,而 Angular 路由的核心概念是建立 URL 与 组件的关系。
通过 Angular 编写的程序称之为单页面应用,原因就在于服务器只提供一个页面,其他页面的渲染全部由 Angular 去完成。
前提条件
实现路由第一个需要修改的文件是 index.html:
例子:
// index.html <!doctype html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="utf-8"> <title>App</title> <!-- 添加 <base href="/"> --> <!-- 路由的根目录 --> <base href="/"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1"> <link rel="icon" type="image/x-icon" href="favicon.ico"> </head> <body> <app-root></app-root> </body> </html>
Angular 依靠 base 标签来构建路由信息,比如我们配置的路径为 /home,base 是
href="/app",那么所有的页面会使用 /app/home 作为实际路径。
配置基础路由
最基础的路由就是根路由,它也是其他子路由得以正常运行的基础。
导入
首先需要在路由文件中导入一些配置路由的接口。
例子:
// app-routing.module.ts
import { NgModule } from '@angular/core';
// 导入 RouterModule 和 Routes
import { RouterModule, Routes } from '@angular/router';
const routes: Routes = [];
@NgModule({
imports: [RouterModule.forRoot(routes)],
exports: [RouterModule]
})
export class AppRoutingModule { }
然后,将路由文件导入到根模块。
例子:
// app.module.ts
import { NgModule } from '@angular/core';
import { BrowserModule } from '@angular/platform-browser';
// 导入路由模块 AppRoutingModule
import { AppRoutingModule } from './app-routing.module';
import { AppComponent } from './app.component';
@NgModule({
declarations: [
AppComponent
],
imports: [
BrowserModule,
// 添加 AppRoutingModule 到 imports 数组中
AppRoutingModule
],
providers: [],
bootstrap: [AppComponent]
})
export class AppModule { }
*如果是通过 Angular Cli 构建的项目,以上步骤可省略。
配置根路由
在路由文件中,通过 Routes 来配置 Angular 路由,最基本的配置由 path 和 component 组成。
例子:
import { NgModule } from '@angular/core';
import { RouterModule, Routes } from '@angular/router';
import { LoginComponent } from './components/login/login.component';
import { WelcomeComponent } from './components/welcome/welcome.component';
import { PageNotFoundComponent } from './components//page-not-found/page-not-found.component';
const routes: Routes = [
// path:指定路由的路径
// component:建立与路由相关联的组件
// redirectTo:将当前路径重定向到其他已知路由,常用于处理空路径的情况
// **:通配符,当URL与所有路径都不匹配时,会选择这个路由,常用于展示404页面
{
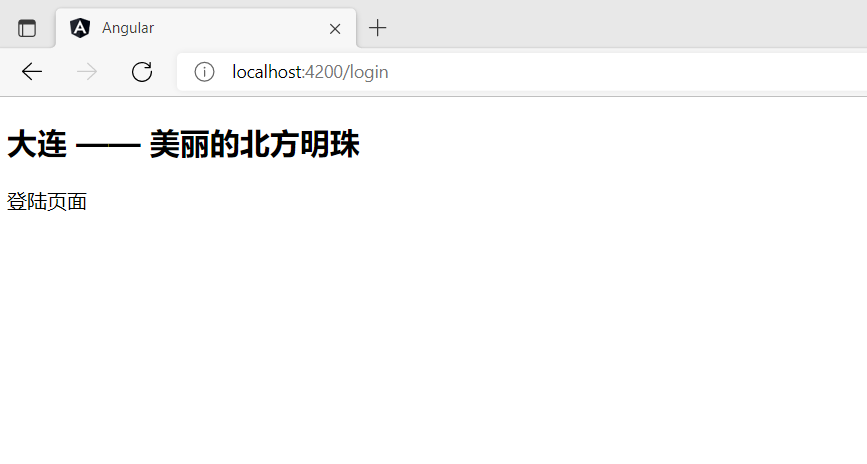
path: 'login',
component: LoginComponent
},
{
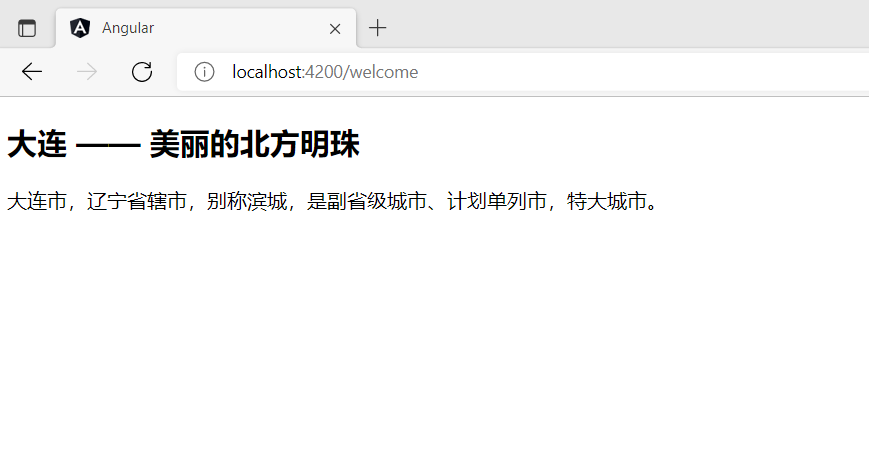
path: 'welcome',
component: WelcomeComponent
},
{
path: '',
redirectTo: '/login',
pathMatch: 'full'
},
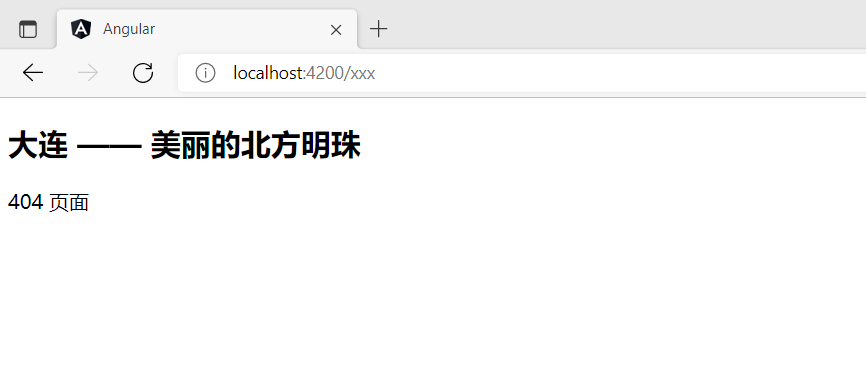
{ path: '**',
component: PageNotFoundComponent
}
];
@NgModule({
// 通过调用 RouterModule.forRoot() 方法安装根路由
imports: [RouterModule.forRoot(routes)],
exports: [RouterModule]
})
export class AppRoutingModule { }
*路由的顺序很重要,因为匹配路径时,遵循的是“先匹配先展示”原则,因此,首先配置具体的路由,然后配置空路径路由,最后是通配符路由。
添加路由出口
在模板中,通过
router-outlet元素指定了各个路由组件的内容在哪里被渲染。
例子:
// app.component.html
<section>
<header>
<h2>大连 —— 美丽的北方明珠</h2>
</header>
<!-- 路由出口 -->
<router-outlet></router-outlet>
<footer></footer>
</section>
end
这篇关于路由之配置基础路由的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对大家有所帮助,也希望大家多多支持为之网!
您可能喜欢
-
初学者必备:订单系统资料详解与实操教程12-25
-
内网穿透资料入门教程12-24
-
微服务资料入门指南12-24
-
微信支付系统资料入门教程12-24
-
微信支付资料详解:新手入门指南12-24
-
Hbase资料:新手入门教程12-24
-
Java部署资料12-24
-
Java订单系统资料:新手入门教程12-24
-
Java分布式资料入门教程12-24
-
Java监控系统资料详解与入门教程12-24
-
Java就业项目资料:新手入门必备教程12-24
-
Java全端资料入门教程12-24
-
Java日志系统资料详解:新手入门指南12-24
-
Java微服务系统资料:入门与初级应用指南12-24
-
Java小程序资料:入门教程与实战技巧12-24
栏目导航