Java教程
面试官问你Mybatis的Mapper代理 你能答多少
大家都知道我的风格,喜欢用故事带入技术学习。
但是… 我讲源码怎么用故事带入呢?
用我的万能故事模板,小明探宝旅程。
这天小明来到的Mybatis王国,他问门口老者,这城门上写的是iBatis,怎么改成Mybatis了呢。
老者回答:哦,原本呀这是iBatis,这如今啊改名Mybatis了。
小明挠了挠头,老者回答了问题,但又好像没回答。
反正知道了,现在就是Mybatis。
小明知道Mybatis王国有一神奇之物,名为Mapper代理。
由于对此物的执着,小明带着他的武器(IntelliJ IDEA)进入城内一探究竟。
一、好奇心
好奇心是驱动我们人类发展必不可少的因素之一,都说好奇心害死猫,这句话在技术领域是不成立的,身为技术人员一定要对事物充满好奇(我说的是技术领域的事物,你可别对特叔叔的服务好奇,就去找特叔叔)
你平时用Mybatis没有什么能让你好奇的吗?
你创建一个Mapper接口,然后写一个Mapper.xml
最后直接使用Mapper接口就能进行增删改查操作了。
首先它是个接口呀,其次他怎么知道执行什么操作呢?
不知道你好奇不好奇,反正我很好奇,就是因为这份好奇心,我才来了这场探险之旅。
二、崎岖的路
我已经给大家趟平了路,有好奇心的同学可以跟着我的脚印来,或许你也能发现很多精彩。
首先得有小儿国,不对是有Mybatis王国。
pom.xml
添加maven依赖后记得reload项目,让他去下载对应jar包到本地仓库。
<dependencies>
<!--Mybatis-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis</artifactId>
<version>3.4.5</version>
</dependency>
<!--mysql驱动-->
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<version>5.1.47</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
mybatis-config.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE configuration
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Config 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-config.dtd">
<configuration>
<environments default="development">
<environment id="development">
<transactionManager type="JDBC"/>
<dataSource type="POOLED">
<property name="driver" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"/>
<property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/test?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf-8&useSSL=false&serverTimezone=GMT%2B8"/>
<property name="username" value="root"/>
<property name="password" value="123456"/>
</dataSource>
</environment>
</environments>
<mappers>
<mapper resource="TestMapper.xml"/>
</mappers>
</configuration>
TestMapper.java
package dao;
import entity.TestEntity;
import java.util.List;
/**
* @author 木子的昼夜编程
*/
public interface TestMapper {
List<TestEntity> list();
}
TestEntity.java
package entity;
import java.math.BigDecimal;
/**
* @author 木子的昼夜编程
*/
public class TestEntity {
private Long id;
private String name;
private BigDecimal salary;
// getter setter
}
TestMapper.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="dao.TestMapper">
<!--查询所有数据-->
<select id="list" resultType="entity.TestEntity">
select * from test
</select>
</mapper>
Test.java
import dao.TestMapper;
import entity.TestEntity;
import org.apache.ibatis.io.Resources;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSession;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSessionFactory;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSessionFactoryBuilder;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.util.List;
/**
* @author 木子的昼夜编程
*/
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// 1. mybatis 配置文件
String resource = "mybatis-config.xml";
// 2. 获取输入流
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource);
// 3. 创建SqlSessionFactory工厂 这一步会进行Mapper的动态代理操作
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream);
// 4. 创建SqlSession
try (SqlSession session = sqlSessionFactory.openSession()) {
// 5. 通过sesson获取Mapper 这个Mapper会编程Mybatis的代理Mapper
TestMapper mapper = session.getMapper(TestMapper.class);
// 6. 调用方法
List<TestEntity> list = mapper.list();
System.out.println(list);
}
}
}
经过我的探索,主要逻辑在第三步就完成了,那句话怎么说来着,偷天换日。
前边我们文章写到过:反射、动态代理、工厂模式
这里就是用了这2中技术,把我们的Mapper进行了包装,你以为你用的是你自己的Mapper,但是,你以为的你以为就是对的吗?是不对的。
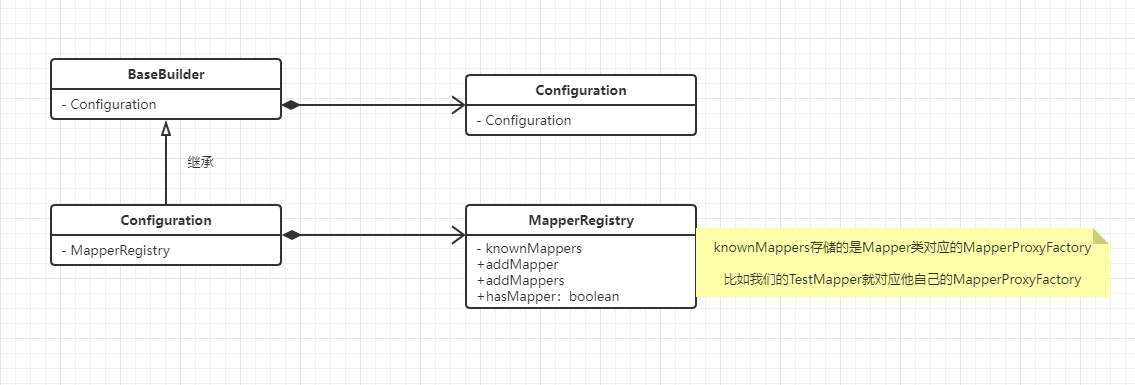
1. SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream); 2. XMLConfigBuilder parser = new XMLConfigBuilder(inputStream, environment, properties); 3. super(new Configuration()); 有一个属性是: protected final MapperRegistry mapperRegistry = new MapperRegistry(this);
画了一个简单的类图,其实就是在读取配置文件的时候创建了一个MapperRegistry
而这个MapperRegistry就是存储宝藏(我们写的接口Mapper的代理)的地方。
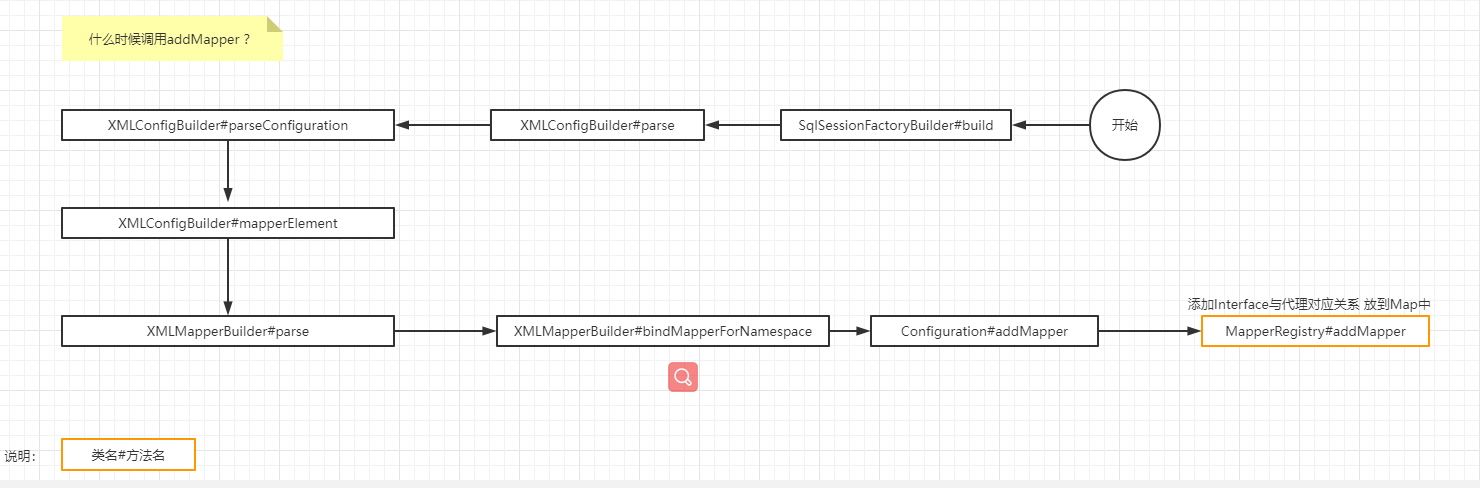
我们可以看到什么时候出来的MapperRegistry
那我们看一下什么时候用他的addMapper方法了,当然了还有addMappers方法
我们就盯着addMapper方法分析就阔以了,不必太执着
1. 上边已经创建了parser
parser.parse()
2. 可以看到这里开始解析配置文件了 configuration就是我们配置文件的根节点
parseConfiguration(parser.evalNode("/configuration"));
3. 看Mapper的话就看这个 解析mappers其他的标签可以先忽略
mapperElement(root.evalNode("mappers"));
private void mapperElement(XNode parent) throws Exception {
if (parent != null) {
// 开始循环遍历mappers的子标签 他的子标签可以使mapper、package
for (XNode child : parent.getChildren()) {
// 如果是package 巴拉巴拉一顿操作 我们不看这个
if ("package".equals(child.getName())) {
String mapperPackage = child.getStringAttribute("name");
configuration.addMappers(mapperPackage);
} else {
// 我们看这个 获取字标签的属性
String resource = child.getStringAttribute("resource");
String url = child.getStringAttribute("url");
String mapperClass = child.getStringAttribute("class");
if (resource != null && url == null && mapperClass == null) {
// 如果只配置了resource 我们只看这种方式 因为我们配置的就是这种
// 读取资源
ErrorContext.instance().resource(resource);
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource);
// 转成XMLMapperBuilder
XMLMapperBuilder mapperParser = new XMLMapperBuilder(inputStream, configuration, resource, configuration.getSqlFragments());
// 走解析
mapperParser.parse();
} else if (resource == null && url != null && mapperClass == null) {
// 如果只配置了url
ErrorContext.instance().resource(url);
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getUrlAsStream(url);
XMLMapperBuilder mapperParser = new XMLMapperBuilder(inputStream, configuration, url, configuration.getSqlFragments());
mapperParser.parse();
} else if (resource == null && url == null && mapperClass != null) {
// 如果只配置了class
Class<?> mapperInterface = Resources.classForName(mapperClass);
configuration.addMapper(mapperInterface);
} else {
// 一个mapper只能有一个属性 或者是url 或者是 resource 或者是 class
// 如果你开发的时候报这个错误了 那你应该就是配置了多个属性
// 经过我的验证 确实是 信我就好
throw new BuilderException("A mapper element may only specify a url, resource or class, but not more than one.");
}
}
}
}
}
XMLMapperBuilder.java
public void parse() {
// 判断是否解析过这个文件 解析过的都放在一个set中
if (!configuration.isResourceLoaded(resource)) {
// 进过了一系列操作
configurationElement(parser.evalNode("/mapper"));
// 放入set中标记为已解析过资源
configuration.addLoadedResource(resource);
// 开始绑定Mapper与Mapper.xml
bindMapperForNamespace();
}
parsePendingResultMaps();
parsePendingCacheRefs();
parsePendingStatements();
}
private void bindMapperForNamespace() {
// 获取命名空间 dao.TestMapper
String namespace = builderAssistant.getCurrentNamespace();
// 如果没有配置命名空间 是不会进行Mapepr与Mapper.xml的绑定的
// 如果namespace为空 前边解析会直接报异常 不知道什么情况能走到这里
if (namespace != null) {
Class<?> boundType = null;
try {
// 获取命名空间对应的类 TestMapper.class
boundType = Resources.classForName(namespace);
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
// 如果找不见类 就算了 因为不是必须的
// 我们自己的业务上也可以参考这种写法 其实就是
// if 类存在 巴拉巴拉一顿操作
// else 不操作
}
if (boundType != null) {
// 先判断是否已经包含这个类了 其实是调用的mapperRegistry的hasMapper
if (!configuration.hasMapper(boundType)) {
// 这里是为了适配spring做了 设置了一个标记 防止多次加载这个资源
// 可以看MapperAnnotationBuilder#loadXmlResource了解更多
configuration.addLoadedResource("namespace:" + namespace);
// 我们不关注那些 我们只关注这个
configuration.addMapper(boundType);
}
}
}
}
还是我们之前说的那句话,看代码尤其是源码,千万不要进黑洞,你一定要明确你这次看的目的是什么。
就像我上边按个configuration.addLoadedResource(“namespace:” + namespace); 这里你知道是为了适配Spring做了一个标记就可以了,至于为什么适配,怎么做到的适配你不用管,你这次的目的应该很明确,就是想探索Mapper代理是怎么代理的,所以千万千万不要陷进去。
Configuration.java
public <T> void addMapper(Class<T> type) {
mapperRegistry.addMapper(type);
}
public class MapperRegistry {
// 这个是对Configuration的一个引用 因为注册的时候肯定会用到一些个配置
private final Configuration config;
// 百宝箱 最后会存放再这里 代理工厂 我们最后代码调用getMapper就是用这个工厂给我们创建一个
// 代理对象 我们前几篇篇文章写得反射、代理模式、工厂模式 很贴合这里
private final Map<Class<?>, MapperProxyFactory<?>> knownMappers = new HashMap<Class<?>, MapperProxyFactory<?>>();
public MapperRegistry(Configuration config) {
this.config = config;
}
// 获取代理 代码一般调用的就是这个方法
public <T> T getMapper(Class<T> type, SqlSession sqlSession) {
final MapperProxyFactory<T> mapperProxyFactory = (MapperProxyFactory<T>) knownMappers.get(type);
// 如没有Mapper类型对应的工厂 抛异常
if (mapperProxyFactory == null) {
throw new BindingException("Type " + type + " is not known to the MapperRegistry.");
}
try {
// 创建一个代理对象
return mapperProxyFactory.newInstance(sqlSession);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new BindingException("Error getting mapper instance. Cause: " + e, e);
}
}
// 判断是否存在 hashMap的containsKey
public <T> boolean hasMapper(Class<T> type) {
return knownMappers.containsKey(type);
}
// 注册Mapper
public <T> void addMapper(Class<T> type) {
// 判断是不是接口类型 如果不是接口类型不做处理
if (type.isInterface()) {
// 如果已经存在了 那就不添加 抛异常
if (hasMapper(type)) {
throw new BindingException("Type " + type + " is already known to the MapperRegistry.");
}
// 标记是否加载成功
boolean loadCompleted = false;
try {
// 先占位 占位是非常重要的
// 如果不占位 就可能被尝试自动绑定
// 如果类型已经存在就不会尝试 上边那个判断hasMapper就是在判断这个
// 没有很理解 不过无所谓 意思就是这样写比较好
knownMappers.put(type, new MapperProxyFactory<T>(type));
MapperAnnotationBuilder parser = new MapperAnnotationBuilder(config, type);
// 解析进行一些初始化
parser.parse();
loadCompleted = true;
} finally {
// 如果没有加载成功 从map中移除
if (!loadCompleted) {
knownMappers.remove(type);
}
}
}
}
}
看过我昨天文章的人都知道 接下来我们看一下媒婆MapperProxyFactory
// 媒婆 负责介绍对象 负责创建我们Mapper接口代理的工厂类
public class MapperProxyFactory<T> {
// 接口的Class对象
private final Class<T> mapperInterface;
// 方法对象 与 方法对象的封装
private final Map<Method, MapperMethod> methodCache = new ConcurrentHashMap<Method, MapperMethod>();
// 构造函数
public MapperProxyFactory(Class<T> mapperInterface) {
this.mapperInterface = mapperInterface;
}
public Class<T> getMapperInterface() {
return mapperInterface;
}
public Map<Method, MapperMethod> getMethodCache() {
return methodCache;
}
//创建代理对象
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
protected T newInstance(MapperProxy<T> mapperProxy) {
// 创建一个代理类 并返回 至于这个Proxy可以看我前边动态代理的文章
return (T) Proxy.newProxyInstance(mapperInterface.getClassLoader(),
new Class[] { mapperInterface },
mapperProxy);
}
// 这里是传入一个sql会话 然后创建一个Mapper接口代理类
public T newInstance(SqlSession sqlSession) {
// 在这里创建了Mapper的代理 这个代理实现了InvocationHandler(还是要看我前几篇动态代理文章)
final MapperProxy<T> mapperProxy = new MapperProxy<T>(sqlSession,
mapperInterface,
methodCache);
return newInstance(mapperProxy);
}
}
MapperProxy.java
/**
* Copyright 2009-2017 the original author or authors.
*
* Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
* you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
* You may obtain a copy of the License at
*
* http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
*
* Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
* distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
* WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
* See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
* limitations under the License.
*/
package org.apache.ibatis.binding;
import java.io.Serializable;
import java.lang.invoke.MethodHandles;
import java.lang.reflect.Constructor;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.lang.reflect.Modifier;
import java.util.Map;
import org.apache.ibatis.lang.UsesJava7;
import org.apache.ibatis.reflection.ExceptionUtil;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSession;
// JKD动态代理 都需要实现InvocationHandler
// 具体代理的事情 在invoke中做
public class MapperProxy<T> implements InvocationHandler, Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = -6424540398559729838L;
// sqlSession
private final SqlSession sqlSession;
// 接口对象类型 TestMapper
private final Class<T> mapperInterface;
// 接口中的方法 list 等
private final Map<Method, MapperMethod> methodCache;
public MapperProxy(SqlSession sqlSession, Class<T> mapperInterface, Map<Method, MapperMethod> methodCache) {
this.sqlSession = sqlSession;
this.mapperInterface = mapperInterface;
this.methodCache = methodCache;
}
// 接口代理对象所有方法都会调用这里
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
try {
// 判断是不是基础方法 toString hashCode 如果是的话直接调用不需要代理
if (Object.class.equals(method.getDeclaringClass())) {
return method.invoke(this, args);
} else if (isDefaultMethod(method)) {
// 判断是不是default修改的方法 是的话特殊处理
return invokeDefaultMethod(proxy, method, args);
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
throw ExceptionUtil.unwrapThrowable(t);
}
// 一般我们会走到这里
// 缓存有的话 取缓存数据 没有的话 创建数据 放入缓存
// 朋友们 可以看到 Map是个很神奇的存在 哪儿都有
// 所以面试钱准备 一定要准备map 相关知识
final MapperMethod mapperMethod = cachedMapperMethod(method);
return mapperMethod.execute(sqlSession, args);
}
private MapperMethod cachedMapperMethod(Method method) {
// 先判断有没有
MapperMethod mapperMethod = methodCache.get(method);
// 没有
if (mapperMethod == null) {
// 创建
mapperMethod = new MapperMethod(mapperInterface, method, sqlSession.getConfiguration());
// 放入缓存
methodCache.put(method, mapperMethod);
}
// 返回
return mapperMethod;
}
}
MapperMethod.java
package org.apache.ibatis.binding;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Flush;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.MapKey;
import org.apache.ibatis.cursor.Cursor;
import org.apache.ibatis.mapping.MappedStatement;
import org.apache.ibatis.mapping.SqlCommandType;
import org.apache.ibatis.reflection.MetaObject;
import org.apache.ibatis.reflection.ParamNameResolver;
import org.apache.ibatis.reflection.TypeParameterResolver;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.Configuration;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.ResultHandler;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.RowBounds;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSession;
import java.lang.reflect.Array;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.lang.reflect.ParameterizedType;
import java.lang.reflect.Type;
import java.util.*;
// 这个类可就厉害了 这是最核心的类 这里就是封装了我们使用SqlSession的操作
public class MapperMethod {
// Sql标签的类型 Insert Update Delete Select
private final SqlCommand command;
// 方法的参数信息 返回信息等
private final MethodSignature method;
// 构造
public MapperMethod(Class<?> mapperInterface, Method method, Configuration config) {
this.command = new SqlCommand(config, mapperInterface, method);
this.method = new MethodSignature(config, mapperInterface, method);
}
// 这里就是封装了SqlSession的一系列方法selectOne、select、insert、delete等
public Object execute(SqlSession sqlSession, Object[] args) {
Object result;
switch (command.getType()) {
// 为什么我们经常说Insert update delete 三个标签其实功能一样
// 平时只是语义上有区分
// 我们可以点进sqlSession源码看看 最后都是调用了update方法
case INSERT: {
// 处理参数
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
// 调用sqlSessioninsert
result = rowCountResult(sqlSession.insert(command.getName(), param));
break;
}
case UPDATE: {
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
result = rowCountResult(sqlSession.update(command.getName(), param));
break;
}
case DELETE: {
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
result = rowCountResult(sqlSession.delete(command.getName(), param));
break;
}
// 如果是Select那就多了
case SELECT:
// 如果返回类型void 并且有自定义ResultHandler
if (method.returnsVoid() && method.hasResultHandler()) {
executeWithResultHandler(sqlSession, args);
result = null;
} else if (method.returnsMany()) {
// 返回类型多行
result = executeForMany(sqlSession, args);
} else if (method.returnsMap()) {
// 范湖Map
result = executeForMap(sqlSession, args);
} else if (method.returnsCursor()) {
// 返回Cursor
result = executeForCursor(sqlSession, args);
} else {
// 返回单个
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
result = sqlSession.selectOne(command.getName(), param);
}
break;
case FLUSH:
// 清空缓存
result = sqlSession.flushStatements();
break;
default:
// 这个一般不出现 除非你是个傻子 哈哈
throw new BindingException("Unknown execution method for: " + command.getName());
}
// 这里很有意思
// 我们可能遇到过 查询结果是基础类型(boolean、char、byte、short、int、long、float、double)的话 很容易报空异常
// 我们写代码一定注意了 基础类型一定要保证有返回值 否则你就用封装类型Integer Double等
if (result == null && method.getReturnType().isPrimitive() && !method.returnsVoid()) {
throw new BindingException("Mapper method '"
+ command.getName()
+ " attempted to return null from a method with a primitive return type ("
+ method.getReturnType() + ").");
}
// 返回结果
return result;
}
// insert update delete 返回处理 rowCount是Sqlsession执行完返回的受影响行数
private Object rowCountResult(int rowCount) {
final Object result;
// 如果返回类型是void 就直接返回空
if (method.returnsVoid()) {
result = null;
// 返回类型 Integer int
} else if (Integer.class.equals(method.getReturnType()) || Integer.TYPE.equals(method.getReturnType())) {
result = rowCount;
// 返回类型Long long
} else if (Long.class.equals(method.getReturnType()) || Long.TYPE.equals(method.getReturnType())) {
result = (long)rowCount;
// 返回类型Boolean boolean
} else if (Boolean.class.equals(method.getReturnType()) || Boolean.TYPE.equals(method.getReturnType())) {
result = rowCount > 0;
} else {
// 其他返回类型 直接抛异常
throw new BindingException("Mapper method '" + command.getName() + "' has an unsupported return type: " + method.getReturnType());
}
return result;
}
// 有自定义的ResuleHandler
private void executeWithResultHandler(SqlSession sqlSession, Object[] args) {
MappedStatement ms = sqlSession.getConfiguration().getMappedStatement(command.getName());
//
if (void.class.equals(ms.getResultMaps().get(0).getType())) {
throw new BindingException("method " + command.getName()
+ " needs either a @ResultMap annotation, a @ResultType annotation,"
+ " or a resultType attribute in XML so a ResultHandler can be used as a parameter.");
}
//
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
//
if (method.hasRowBounds()) {
RowBounds rowBounds = method.extractRowBounds(args);
sqlSession.select(command.getName(), param, rowBounds, method.extractResultHandler(args));
} else {
//
sqlSession.select(command.getName(), param, method.extractResultHandler(args));
}
}
// 多条返回结果
private <E> Object executeForMany(SqlSession sqlSession, Object[] args) {
// 返回值
List<E> result;
// 把参数转换为ParamMap
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
// 是否有分页参数
if (method.hasRowBounds()) {
RowBounds rowBounds = method.extractRowBounds(args);
result = sqlSession.<E>selectList(command.getName(), param, rowBounds);
} else {
// 直接执行 sqlSession的selectList
result = sqlSession.<E>selectList(command.getName(), param);
}
// class1.isAssignableFrom(class2)
// 判断 class2是否是class1的子类或者子接口
if (!method.getReturnType().isAssignableFrom(result.getClass())) {
// 如果返回类型是Array 转换为Array
if (method.getReturnType().isArray()) {
return convertToArray(result);
} else {
// 否者转换为声明的集合集合
return convertToDeclaredCollection(sqlSession.getConfiguration(), result);
}
}
return result;
}
// 返回Cursor
private <T> Cursor<T> executeForCursor(SqlSession sqlSession, Object[] args) {
Cursor<T> result;
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
if (method.hasRowBounds()) {
RowBounds rowBounds = method.extractRowBounds(args);
result = sqlSession.<T>selectCursor(command.getName(), param, rowBounds);
} else {
result = sqlSession.<T>selectCursor(command.getName(), param);
}
return result;
}
// 转换成集合
private <E> Object convertToDeclaredCollection(Configuration config, List<E> list) {
// 先创建一个声明的集合类型的对象
Object collection = config.getObjectFactory().create(method.getReturnType());
// 转换为代理
MetaObject metaObject = config.newMetaObject(collection);
// 元素都放进去
metaObject.addAll(list);
return collection;
}
// 转换成数组
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
private <E> Object convertToArray(List<E> list) {
// 创建数组对象
Class<?> arrayComponentType = method.getReturnType().getComponentType();
Object array = Array.newInstance(arrayComponentType, list.size());
// 判断是不是基础类型数组 int[] longp[]
if (arrayComponentType.isPrimitive()) {
// 如果是基础类型需要一个一个转换
for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++) {
//
Array.set(array, i, list.get(i));
}
return array;
} else {
// 如果不是直接调用toArray转换为Array
return list.toArray((E[])array);
}
}
// 返回Map
private <K, V> Map<K, V> executeForMap(SqlSession sqlSession, Object[] args) {
Map<K, V> result;
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
if (method.hasRowBounds()) {
RowBounds rowBounds = method.extractRowBounds(args);
result = sqlSession.<K, V>selectMap(command.getName(), param, method.getMapKey(), rowBounds);
} else {
result = sqlSession.<K, V>selectMap(command.getName(), param, method.getMapKey());
}
return result;
}
// 自定义Map
// 我们业务中也可以参考这种写法 就是重写了get方法,如果没有获取元素就抛异常
public static class ParamMap<V> extends HashMap<String, V> {
private static final long serialVersionUID = -2212268410512043556L;
@Override
public V get(Object key) {
if (!super.containsKey(key)) {
throw new BindingException("Parameter '" + key + "' not found. Available parameters are " + keySet());
}
return super.get(key);
}
}
}
// 封装了具体执行的动作
public static class SqlCommand {
// xml的id 比如:list
private final String name;
// insert update delete 等类型
private final SqlCommandType type;
public SqlCommand(Configuration configuration, Class<?> mapperInterface, Method method) {
// 名称 list
final String methodName = method.getName();
// 类 dao.TestMapper
final Class<?> declaringClass = method.getDeclaringClass();
MappedStatement ms = resolveMappedStatement(mapperInterface, methodName, declaringClass,
configuration);
if (ms == null) {
// 是否有Flush标签
if (method.getAnnotation(Flush.class) != null) {
name = null;
// 设置类型为Flush
type = SqlCommandType.FLUSH;
} else {
throw new BindingException("Invalid bound statement (not found): "
+ mapperInterface.getName() + "." + methodName);
}
} else {
name = ms.getId();
type = ms.getSqlCommandType();
// 类型不识别 直接抛异常 INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE, SELECT, FLUSH;
if (type == SqlCommandType.UNKNOWN) {
throw new BindingException("Unknown execution method for: " + name);
}
}
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public SqlCommandType getType() {
return type;
}
private MappedStatement resolveMappedStatement(Class<?> mapperInterface, String methodName,
Class<?> declaringClass, Configuration configuration) {
// statementId ==> dao.TestMapper.list
String statementId = mapperInterface.getName() + "." + methodName;
// 如果已经有了 直接返回
if (configuration.hasStatement(statementId)) {
return configuration.getMappedStatement(statementId);
} else if (mapperInterface.equals(declaringClass)) {
return null;
}
for (Class<?> superInterface : mapperInterface.getInterfaces()) {
if (declaringClass.isAssignableFrom(superInterface)) {
MappedStatement ms = resolveMappedStatement(superInterface, methodName,
declaringClass, configuration);
if (ms != null) {
return ms;
}
}
}
return null;
}
}
public static class MethodSignature {
// 是否返回多条结果
private final boolean returnsMany;
// 是否返回Map
private final boolean returnsMap;
// 是否返回void
private final boolean returnsVoid;
//是否返回Cursor
private final boolean returnsCursor;
// 返回类型
private final Class<?> returnType;
// mapKey
private final String mapKey;
// resultHandler 类型参数的位置
private final Integer resultHandlerIndex;
// rowBound类型参数的位置
private final Integer rowBoundsIndex;
// 参数处理器
private final ParamNameResolver paramNameResolver;
}
三、唠唠
探险的最后结果是我蒙了,看着看着,看得我心灰意冷了。
这个架构太牛了,各种封装,各种模式,各种
最主要的是我们看到了,是用了代理模式和工厂模式,把我们的Mapper接口进行了代理,
我们通过getMapper获取的接口其实就是代理对象,这时候所有操作都是通过代理MapperProxy
实现了InvocationHandler 进行的Jdk动态代理
我已经是第二次看源码了,依旧是不那么明朗,所以我们没必要一次把所有的点都掌握,先掌握一个小点儿,比如先了解怎么通过动态代理实现的Mapper接口的代理,至于其他的代理的具体内容,再慢慢聊。
-
手写消息中间件:从零开始的指南11-26
-
Java语音识别项目资料:新手入门教程11-26
-
JAVA语音识别项目资料:新手入门教程11-26
-
Java语音识别项目资料:入门与实践指南11-26
-
Java云原生资料入门教程11-26
-
Java云原生资料入门教程11-26
-
Java云原生资料:新手入门教程11-26
-
Java创意资料:新手入门的创意学习指南11-25
-
JAVA对接阿里云智能语音服务资料详解:新手入门指南11-25
-
Java对接阿里云智能语音服务资料详解11-25
-
Java对接阿里云智能语音服务资料详解11-25
-
JAVA副业资料:新手入门及初级提升指南11-25
-
Java副业资料:入门到实践的全面指南11-25
-
Springboot应用的多环境打包项目实战11-25
-
SpringBoot应用的生产发布项目实战入门教程11-25