Java教程
神奇!自己 new 出来的对象一样也可以被 Spring 容器管理!
按理说自己 new 出来的对象和容器是没有关系的,但是在 Spring Security 框架中也 new 了很多对象出来,一样也可以被容器管理,那么它是怎么做到的?
今天来和大家聊一个略微冷门的话题,Spring Security 中的 ObjectPostProcessor 到底是干嘛用的?
本文是 Spring Security 系列第 32 篇,阅读前面文章有助于更好的理解本文:
- 挖一个大坑,Spring Security 开搞!
- 松哥手把手带你入门 Spring Security,别再问密码怎么解密了
- 手把手教你定制 Spring Security 中的表单登录
- Spring Security 做前后端分离,咱就别做页面跳转了!统统 JSON 交互
- Spring Security 中的授权操作原来这么简单
- Spring Security 如何将用户数据存入数据库?
- Spring Security+Spring Data Jpa 强强联手,安全管理只有更简单!
- Spring Boot + Spring Security 实现自动登录功能
- Spring Boot 自动登录,安全风险要怎么控制?
- 在微服务项目中,Spring Security 比 Shiro 强在哪?
- SpringSecurity 自定义认证逻辑的两种方式(高级玩法)
- Spring Security 中如何快速查看登录用户 IP 地址等信息?
- Spring Security 自动踢掉前一个登录用户,一个配置搞定!
- Spring Boot + Vue 前后端分离项目,如何踢掉已登录用户?
- Spring Security 自带防火墙!你都不知道自己的系统有多安全!
- 什么是会话固定攻击?Spring Boot 中要如何防御会话固定攻击?
- 集群化部署,Spring Security 要如何处理 session 共享?
- 松哥手把手教你在 SpringBoot 中防御 CSRF 攻击!so easy!
- 要学就学透彻!Spring Security 中 CSRF 防御源码解析
- Spring Boot 中密码加密的两种姿势!
- Spring Security 要怎么学?为什么一定要成体系的学习?
- Spring Security 两种资源放行策略,千万别用错了!
- 松哥手把手教你入门 Spring Boot + CAS 单点登录
- Spring Boot 实现单点登录的第三种方案!
- Spring Boot+CAS 单点登录,如何对接数据库?
- Spring Boot+CAS 默认登录页面太丑了,怎么办?
- 用 Swagger 测试接口,怎么在请求头中携带 Token?
- Spring Boot 中三种跨域场景总结
- Spring Boot 中如何实现 HTTP 认证?
- Spring Security 中的四种权限控制方式
- Spring Security 多种加密方案共存,老破旧系统整合利器!
如果大家研究过松哥的微人事项目,就会发现里边的动态权限配置有这样一行代码:
@Configuration
public class SecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http.authorizeRequests()
.withObjectPostProcessor(new ObjectPostProcessor<FilterSecurityInterceptor>() {
@Override
public <O extends FilterSecurityInterceptor> O postProcess(O object) {
object.setAccessDecisionManager(customUrlDecisionManager);
object.setSecurityMetadataSource(customFilterInvocationSecurityMetadataSource);
return object;
}
})
.and()
...
}
}
这里的 withObjectPostProcessor 到底该如何理解?
今天松哥就来和大家揭开谜题。
1.ObjectPostProcessor 的作用
我们先来看下 ObjectPostProcessor 到底有啥作用,先来看一下这个接口的定义:
package org.springframework.security.config.annotation;
public interface ObjectPostProcessor<T> {
<O extends T> O postProcess(O object);
}
接口中就只有一个 postProcess 方法。
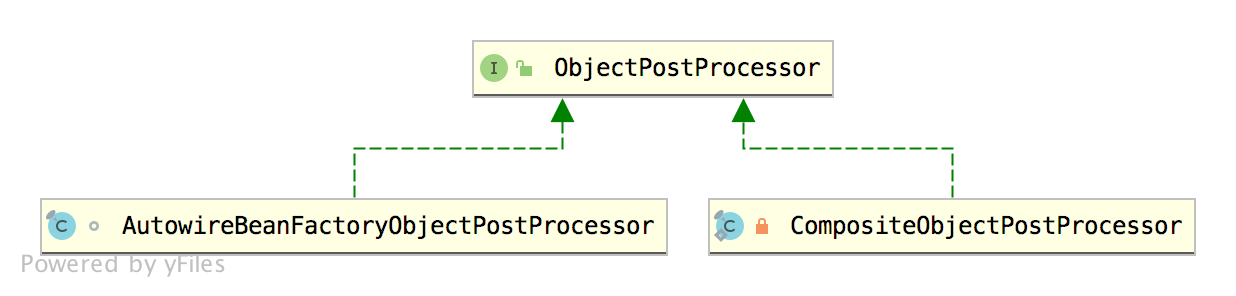
我们再来看看 ObjectPostProcessor 的继承关系:
两个比较重要的实现类,其中 AutowireBeanFactoryObjectPostProcessor 值得一说,来看下 AutowireBeanFactoryObjectPostProcessor 的定义:
final class AutowireBeanFactoryObjectPostProcessor
implements ObjectPostProcessor<Object>, DisposableBean, SmartInitializingSingleton {
AutowireBeanFactoryObjectPostProcessor(
AutowireCapableBeanFactory autowireBeanFactory) {
this.autowireBeanFactory = autowireBeanFactory;
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public <T> T postProcess(T object) {
if (object == null) {
return null;
}
T result = null;
try {
result = (T) this.autowireBeanFactory.initializeBean(object,
object.toString());
}
catch (RuntimeException e) {
Class<?> type = object.getClass();
throw new RuntimeException(
"Could not postProcess " + object + " of type " + type, e);
}
this.autowireBeanFactory.autowireBean(object);
if (result instanceof DisposableBean) {
this.disposableBeans.add((DisposableBean) result);
}
if (result instanceof SmartInitializingSingleton) {
this.smartSingletons.add((SmartInitializingSingleton) result);
}
return result;
}
}
AutowireBeanFactoryObjectPostProcessor 的源码很好理解:
- 首先在构建 AutowireBeanFactoryObjectPostProcessor 对象时,传入了一个 AutowireCapableBeanFactory 对象,看过 Spring 源码的小伙伴就知道,AutowireCapableBeanFactory 可以帮助我们手动的将一个实例注册到 Spring 容器中。
- 在 postProcess 方法中,就是具体的注册逻辑了,都很简单,我就不再赘述。
由此可见,ObjectPostProcessor 的主要作用就是手动注册实例到 Spring 容器中去(并且让实例走一遍 Bean 的生命周期)。
正常来说,我们项目中的 Bean 都是通过自动扫描注入到 Spring 容器中去的,然而在 Spring Security 框架中,有大量的代码不是通过自动扫描注入到 Spring 容器中去的,而是直接 new 出来的,这样做的本意是为了简化项目配置。
这些直接 new 出来的代码,如果想被 Spring 容器管理该怎么办呢?那就得 ObjectPostProcessor 出场了。
2.框架举例
接下来我随便举几个框架中对象 new 的例子,大家看一下 ObjectPostProcessor 的作用:
HttpSecurity 初始化代码(WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter#getHttp):
protected final HttpSecurity getHttp() throws Exception {
if (http != null) {
return http;
}
...
...
http = new HttpSecurity(objectPostProcessor, authenticationBuilder,
sharedObjects);
...
...
}
WebSecurity 初始化代码(WebSecurityConfiguration#setFilterChainProxySecurityConfigurer):
public void setFilterChainProxySecurityConfigurer(
ObjectPostProcessor<Object> objectPostProcessor,
@Value("#{@autowiredWebSecurityConfigurersIgnoreParents.getWebSecurityConfigurers()}") List<SecurityConfigurer<Filter, WebSecurity>> webSecurityConfigurers)
throws Exception {
webSecurity = objectPostProcessor
.postProcess(new WebSecurity(objectPostProcessor));
...
...
}
Spring Security 框架源码中,随处可见手动装配。Spring Security 中,过滤器链中的所有过滤器都是通过对应的 xxxConfigure 来进行配置的,而所有的 xxxConfigure 都是继承自 SecurityConfigurerAdapter,如下:
而在这些 xxxConfigure 的 configure 方法中,无一例外的都会让他们各自配置的管理器去 Spring 容器中走一圈,例如 AbstractAuthenticationFilterConfigurer#configure 方法:
public void configure(B http) throws Exception {
...
...
F filter = postProcess(authFilter);
http.addFilter(filter);
}
其他的 xxxConfigurer#configure 方法也都有类似的实现,小伙伴们可以自行查看,我就不再赘述了。
3.为什么这样
直接将 Bean 通过自动扫描注册到 Spring 容器不好吗?为什么要搞成这个样子?
在 Spring Security 中,由于框架本身大量采用了 Java 配置,并且没有将对象的各个属性都暴露出来,这样做的本意是为了简化配置。然而这样带来的一个问题就是需要我们手动将 Bean 注册到 Spring 容器中去,ObjectPostProcessor 就是为了解决该问题。
一旦将 Bean 注册到 Spring 容器中了,我们就有办法去增强一个 Bean 的功能,或者需修改一个 Bean 的属性。
例如一开始提到的动态权限配置代码:
@Configuration
public class SecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http.authorizeRequests()
.withObjectPostProcessor(new ObjectPostProcessor<FilterSecurityInterceptor>() {
@Override
public <O extends FilterSecurityInterceptor> O postProcess(O object) {
object.setAccessDecisionManager(customUrlDecisionManager);
object.setSecurityMetadataSource(customFilterInvocationSecurityMetadataSource);
return object;
}
})
.and()
...
}
}
权限管理本身是由 FilterSecurityInterceptor 控制的,系统默认的 FilterSecurityInterceptor 已经创建好了,而且我也没办法修改它的属性,那么怎么办呢?我们可以利用 withObjectPostProcessor 方法,去修改 FilterSecurityInterceptor 中的相关属性。
上面这个配置生效的原因之一是因为 FilterSecurityInterceptor 在创建成功后,会重走一遍 postProcess 方法,这里通过重写 postProcess 方法就能实现属性修改,我们可以看下配置 FilterSecurityInterceptor 的方法(AbstractInterceptUrlConfigurer#configure):
abstract class AbstractInterceptUrlConfigurer<C extends AbstractInterceptUrlConfigurer<C, H>, H extends HttpSecurityBuilder<H>>
extends AbstractHttpConfigurer<C, H> {
@Override
public void configure(H http) throws Exception {
FilterInvocationSecurityMetadataSource metadataSource = createMetadataSource(http);
if (metadataSource == null) {
return;
}
FilterSecurityInterceptor securityInterceptor = createFilterSecurityInterceptor(
http, metadataSource, http.getSharedObject(AuthenticationManager.class));
if (filterSecurityInterceptorOncePerRequest != null) {
securityInterceptor
.setObserveOncePerRequest(filterSecurityInterceptorOncePerRequest);
}
securityInterceptor = postProcess(securityInterceptor);
http.addFilter(securityInterceptor);
http.setSharedObject(FilterSecurityInterceptor.class, securityInterceptor);
}
}
可以看到,securityInterceptor 对象创建成功后,还是会去 postProcess 方法中走一遭。
看懂了上面的代码,接下来我再举一个例子小伙伴们应该一下就能明白:
@Configuration
public class SecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http.authorizeRequests()
.antMatchers("/admin/**").hasRole("admin")
...
.and()
.formLogin()
.withObjectPostProcessor(new ObjectPostProcessor<UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter>() {
@Override
public <O extends UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter> O postProcess(O object) {
object.setUsernameParameter("name");
return object;
}
})
...
}
}
在这里,我把配置好的 UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter 过滤器再拎出来,修改一下用户名的 key(正常来说,修改用户名的 key 不用这么麻烦,这里主要是给大家演示 ObjectPostProcessor 的效果),修改完成后,以后用户登录时,用户名就不是 username 而是 name 了。
4.小结
好了,只要小伙伴们掌握了上面的用法,以后在 Spring Security 中,如果想修改某一个对象的属性,但是却不知道从哪里下手,那么不妨试试 withObjectPostProcessor!
小伙伴们如果觉得有收获,记得点个在看鼓励下松哥哦~
-
Springboot应用的多环境打包入门11-23
-
Springboot应用的生产发布入门教程11-23
-
Python编程入门指南11-23
-
Java创业入门:从零开始的编程之旅11-23
-
Java创业入门:新手必读的Java编程与创业指南11-23
-
Java对接阿里云智能语音服务入门详解11-23
-
Java对接阿里云智能语音服务入门教程11-23
-
JAVA对接阿里云智能语音服务入门教程11-23
-
Java副业入门:初学者的简单教程11-23
-
JAVA副业入门:初学者的实战指南11-23
-
JAVA项目部署入门:新手必读指南11-23
-
Java项目部署入门:新手必看指南11-23
-
Java项目部署入门:新手必读指南11-23
-
Java项目开发入门:新手必读指南11-23
-
JAVA项目开发入门:从零开始的实用教程11-23