C/C++教程
Nacos 1.3.0-BETA 即将来袭
概述
本次1.3.0-BETA的改动程度很大,涉及两个模块的修改以及新增一个核心模块。
- nacos-core模块修改
a. nacos集群节点成员寻址模式的统一管理
b. nacos内部事件机制
c. nacos一致性协议层 - nacos-config模块修改
a. 新增内嵌分布式数据存储组件
b. 内嵌存储与外置存储细分
c. 内嵌存储简单运维 - nacos-consistency模块新增
a. 对于AP协议以及CP协议的统一抽象
Nacos的未来整体逻辑架构及其组件
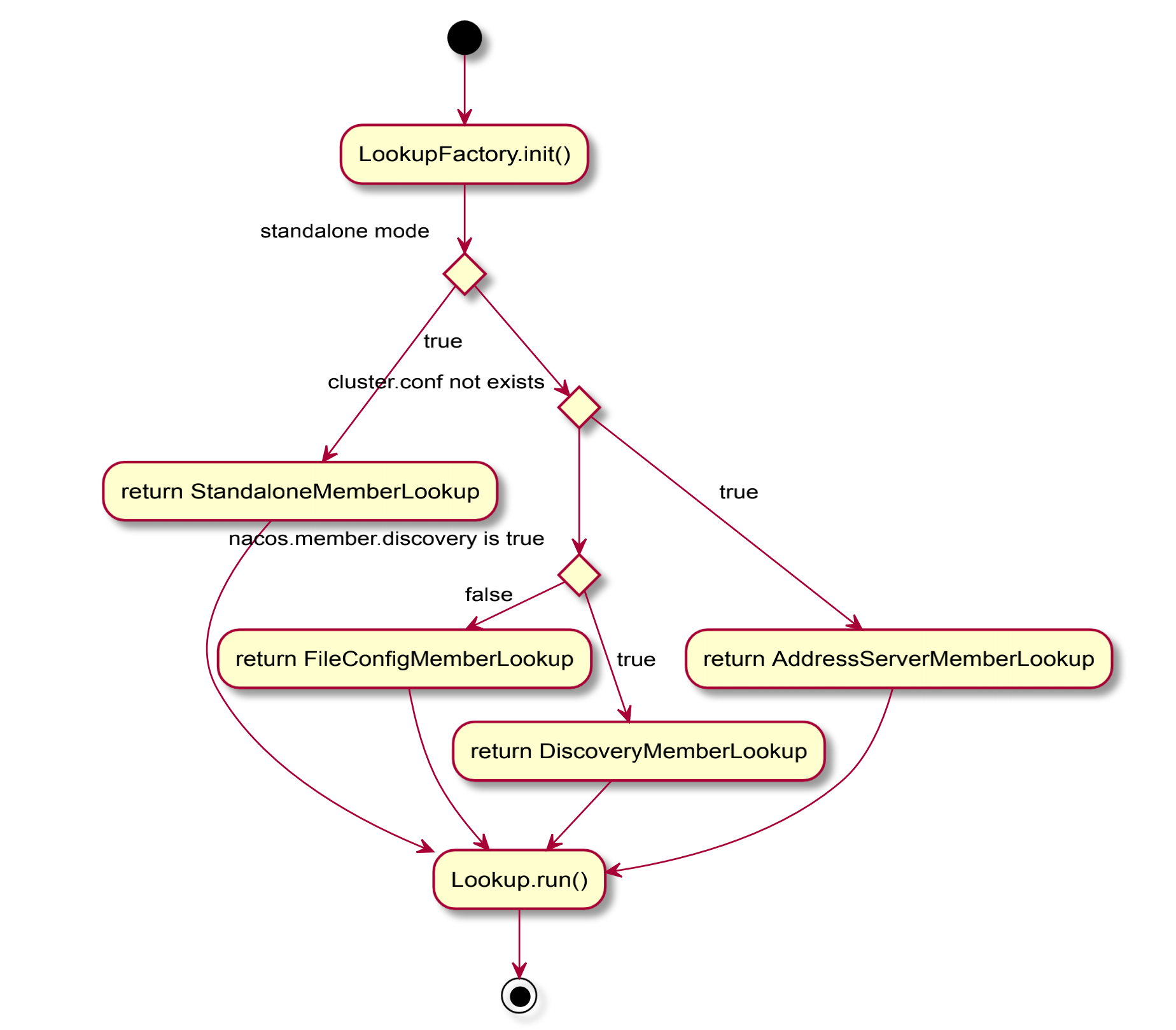
Nacos集群成员节点寻址模式
在1.3.0-BETA之前,nacos的naming模块以及config模块存在各自的集群成员节点列表管理任务。为了统一nacos集群下成员列表的寻址模式,将集群节点管理的实现从naming模块以及config模块剥离出来,统一下沉到了core模块的寻址模式,同时新增命令参数-Dnacos.member.list进行设置nacos集群节点列表,该参数可以看作是cluster.conf 文件的一个替代。 前nacos的寻址模式类别如下:
- a. 单机模式:StandaloneMemberLookup
- b. 集群模式:
- i.cluster.conf 件存在:FileConfigMemberLookup
- ii.nacos.member.discovery==true:DiscoveryMemberLookup
- iii.cluster.conf 件不存在或者 -Dnacos.member.list没有设置:
AddressServerMemberLookup
逻辑图如下:
本次还新增成员节点元数据信息,如site、raft_port、adweight、weight,以支持将来在成员节点之间做相应的负载均衡或者其他操作,因此cluster.conf 件中配置集群成员节点列表的格式如下:
1172.20.10.7:7001?raft_port=8001&site=unknown&adweight=0&weight=1
该格式完全兼容原本的cluster.conf格式,用户在使用 1.3.0-BETA版本时, 无需改动cluster.conf 文件的内容。
寻址模式详细
接下来介绍除了单机模式下的寻址模式的其他三种寻址模式
FileConfigMemberLookup
该寻址模式是基于cluster.conf文件进行管理的,每个节点会读取各${nacos.home}/conf下的cluster.conf 件内的成员节点列表,然后组成一个集群。并且在首次读取完${nacos.home}/conf下的cluster.conf文件后,会自动向操作系统的inotify机制注册一个目录监听器,监听${nacos.home}/conf目录下的所有文件变动(注意,这里只会监听文件,对于目录下的文件变动无法监听),当需要进行集群节点扩缩容时,需要手动去修改每个节点各自${nacos.home}/conf下的cluster.conf的成员节点列表内容。
private FileWatcher watcher = new FileWatcher() {
@Override
public void onChange(FileChangeEvent event) {
readClusterConfFromDisk();
}
@Override
public boolean interest(String context) {
return StringUtils.contains(context, "cluster.conf");
}
};
@Override
public void run() throws NacosException {
readClusterConfFromDisk();
if (memberManager.getServerList().isEmpty()) {
throw new NacosException(NacosException.SERVER_ERROR,
"Failed to initialize the member node, is empty" );
}
// Use the inotify mechanism to monitor file changes and automat ically
// trigger the reading of cluster.conf
try {
WatchFileCenter.registerWatcher(ApplicationUtils.getConfFile Path(), watcher);
}
catch (Throwable e) {
Loggers.CLUSTER.error("An exception occurred in the launch f ile monitor : {}", e);
}
}
首次启动时直接读取cluster.conf文件内的节点列表信息,然后向WatchFileCenter注册一个目录监听器,当cluster.conf 文件发生变动时自动触发readClusterConfFromDisk()重新读取cluster.conf文件。
AddressServerMemberLookup
该寻址模式是基于一个额外的web服务器来管理cluster.conf,每个节点定期向该web服务器请求cluster.conf的文件内容,然后实现集群节点间的寻址,以及扩缩容。
当需要进行集群扩缩容时,只需要修改cluster.conf文件即可,然后每个节点向地址服务器请求时会自动得到最新的cluster.conf文件内容。
public void init(ServerMemberManager memberManager) throws NacosExce ption {
super.init(memberManager);
initAddressSys();
this.maxFailCount =Integer.parseInt(ApplicationUtils.getProperty("maxHealthCheckFailCount", "12"));
}
private void initAddressSys() {
String envDomainName = System.getenv("address_server_domain");
if (StringUtils.isBlank(envDomainName)) {
domainName = System.getProperty("address.server.domain", "jm env.tbsite.net");
} else {
domainName = envDomainName;
}
String envAddressPort = System.getenv("address_server_port");
if (StringUtils.isBlank(envAddressPort)) {
addressPort = System.getProperty("address.server.port", "8080");
} else {
addressPort = envAddressPort;
}
addressUrl = System.getProperty("address.server.url", memberManager.getContextPath() + "/" + "serverlist");
addressServerUrl = "http://" + domainName + ":" + addressPort + addressUrl;envIdUrl = "http://" + domainName + ":" + addressPort + "/env";
Loggers.CORE.info("ServerListService address-server port:" + addressPort);
Loggers.CORE.info("ADDRESS_SERVER_URL:" + addressServerUrl);
}
@SuppressWarnings("PMD.UndefineMagicConstantRule")
@Override
public void run() throws NacosException {
// With the address server, you need to perform a synchronous me mber node pull at startup
// Repeat three times, successfully jump out
boolean success = false;
Throwable ex = null;
int maxRetry = ApplicationUtils.getProperty("nacos.core.address-server.retry", Integer.class, 5);
for (int i = 0; i < maxRetry; i ++) {
try {
syncFromAddressUrl();
success = true;
break;
} catch (Throwable e) {
ex = e;
Loggers.CLUSTER.error("[serverlist] exception, error : {}", ex);
}
}
if (!success) {
throw new NacosException(NacosException.SERVER_ERROR, ex);;
}
task = new AddressServerSyncTask();
GlobalExecutor.scheduleSyncJob(task, 5_000L);
}
在初始化时,会主动去向地址服务器同步当前的集群成员列表信息,如果失败则进行重试,其最大重试次数可通过设置nacos.core.address-server.retry来控制,默认是5次,然后成功之后,将创建定时任务去向地址服务器同步集群成员节点信息。
DiscoveryMemberLookup
该寻址模式是新增的集群节点发现模式,该模式需要cluster.conf或者-Dnacos.member.list提供初始化集群节点列表,假设已有集群cluster-one中有A、B、C三个节点,新节点D要加集群,那么只需要节点D在启动时的集群节点列表存在A、B、C三个中的一个即可,然后节点之间会相互同步各自知道的集群节点列表,在一定的是时间内,A、B、C、D四个节点知道的集群节点成员列表都会是[A、B、C、D]在执行集群节点列表同步时,会随机选取K个处于UP状态的节点进行同步。
Collection<Member> members = MemberUtils.kRandom(memberManager, membe r -> {
// local node or node check failed will not perform task processing
if (memberManager.isSelf(member) || !member.check ()) {
return false;
}
NodeState state = member.getState();
return !(state == NodeState.DOWN || state == Node State.SUSPICIOUS);
});
通过一个简单的流程图看下DiscoveryMemberLookup是怎么工作的
图片正在加载中。。。
RPC端口协商
由于将来Nacos会对整体通信通道做升级,采用GRPC优化nacos-server之间,nacos-client与nacos-server之间的通信,同时为了兼容目前已有的HTTP协议接口,那么势必会带来这个问题,本机用于RPC协议的端口如何让其他节点知道?这里有两个解决方案。
重新设计cluster.conf
之前的cluster.conf格式
ip[:port] ip[:port] ip[:port]
由于nacos默认端口是8848,因此在端口未被修改的情况下,可以直接写IP列表
新的cluster.conf
ip[:port][:RPC_PORT] ip[:port][:RPC_PORT] ip[:port][:RPC_PORT]
对于之前的cluster.conf是完全支持的,因为nacos内部可以通过一些计算来约定RPC_PORT的端口值,也可以通过显示的设置来约定。通过计算来约定RPC_PORT的代码如下:
// member port int port = Member.getPort(); // Set the default Raft port information for security int rpcPort = port + 1000 >= 65535 ? port + 1 : port + 1000;
但是这样会有一个问题,即如果用户手动设置了RPC_PORT的话,那么对于客户端、服务端来说,感知新的RPC_PORT就要修改对应的配置文件或者初始化参数。因此希望说能够让用户无感知的过渡到RPC_PORT通信通道,即用户需要对RPC协议使用的端口无需自己在进行设置。
端口协商
端口协商即利用目前已有的HTTP接口,将RPC协议占用的端口通过HTTP接口进行查询返回,这样无论是客户端还是服务端,都无需修改目前已有的初始化参数或者cluster.conf文件,其大致时序图如下:
通过一个额外的端口获取HTTP接口,直接在内部实现RPC端口的协商,并且只会在初始化时进行拉取,这样,将来nacos新增任何一种协议的端口都无需修改相应的配置信息,自动完成协议端口的感知。
Nacos一致性协议协议层抽象
从nacos的未来的整体架构图可以看出,一致性协议层将是作为nacos的最为核心的模块,将服务于构建在core模块之上的各个功能模块,或者服务与core模块本身。而一致性协议因为分区容错性的存在,需要在可用性与一致性之间做选择,因此就存在两大类一致性:最终一致性和强一致性。在nacos中,这两类致性协议都是可能用到的,比如naming模块,对于服务实例的数据管理分别用到了AP以及CP,而对于config模块,将会涉及使用CP。同时还有如下几个功能需求点:
- 目前持久化服务使用了变种版本的raft,并且业务和raft协议耦合,因此需要抽离解耦,同时是选择一个标准的Java版Raft实现。
- 对于中小用户,配置基本不超过100个,独立一个mysql,相对重一些,需要一个轻量化的存储方案,并且支持2.0不依赖mysql和3.0依赖mysql可配置能力。
- 由于CP或者AP,其存在多种实现,如何对一致性协议层做一次很好的抽象,以便将来可以快速的实现底层一致性协议具体实现的替换,如Raft协议,目前nacos的选型是JRaft,不排除将来nacos会自己实现一个标准raft协议或者实现Paxos协议。
- 由于Nacos存在多个独立工作的功能模块,每个功能模块之间不能出现影响,比如A模块处理请求过慢或者出现异常时,不能影响B模块的正常工作,即每个功能模块在使用一致性协议时,如何将每个模块的数据处理进行隔离?
根据一致协议以及上述功能需求点,本次做了一个抽象的一致协议层以及相关的接口。
一致协议接口:ConsistencyProtocol
所谓一致性,即多个副本之间是否能够保持一致性的特性,而副本的本质就是数据,对数据的操作,不是获取就是修改。同时,一致协议其实是针对分布式情况的,而这必然涉及多个节点,因此,需要有相应的接口能够调整一致性协议的协同工作节点。如果我们要观察一致性协议运行的情况,该怎么办?比如Raft协议,我们希望得知当前集群中的Leader是谁,任期的情况,当前集群中的成员节点有谁?因此,还需要提供一个一致性协议元数据获取。
综上所述,ConsistencyProtcol的大致设计可以出来了
/**
* Has nothing to do with the specific implementation of the consist ency protocol
* Initialization sequence: init(Config)
*
* <ul>
* <li>{@link Config} : Relevant configuration information requi red by the consistency protocol,
* for example, the Raft protocol needs to set the election time out time, the location where
* the Log is stored, and the snapshot task execution interval</ li>
* <li>{@link ConsistencyProtocol#protocolMetaData()} : Returns metadata information of the consistency
* protocol, such as leader, term, and other metadata informatio n in the Raft protocol</li>
* </ul>
*
* @author <a href="mailto:liaochuntao@live.com">liaochuntao</a>
*/
public interface ConsistencyProtocol<T extends Config> extends CommandOperations {
/**
* Consistency protocol initialization: perform initialization o perations based
on the incoming Config
* 一致性协议初始化,根据 Config 实现类
*
* @param config {@link Config}
*/
void init(T config);
/**
* Copy of metadata information for this consensus protocol
* 该一致性协议的元数据信息
*
* @return metaData {@link ProtocolMetaData}
*/
ProtocolMetaData protocolMetaData();
/**
* Obtain data according to the request
* 数据获取操作,根据GetRequest中的请求上下文进行查询相应的数据
*
* @param request request
* @return data {@link GetRequest}
* @throws Exception
*/
GetResponse getData(GetRequest request) throws Exception;
/**
* Data operation, returning submission results synchronously
* 同步数据提交,在 Datum 中已携带相应的数据操作信息
*
* @param data {@link Log}
* @return submit operation result
* @throws Exception
*/
LogFuture submit(Log data) throws Exception;
/**
* Data submission operation, returning submission results async hronously
* 异步数据提交,在 Datum 中已携带相应的数据操作信息,返回一个Future,自行操作,提交发 的异常会在CompleteFuture中
*
* @param data {@link Log}
* @return {@link CompletableFuture<LogFuture>} submit result
* @throws Exception when submit throw Exception
*/
CompletableFuture<LogFuture> submitAsync(Log data);
/**
* New member list
* 新的成员节点列表,一致性协议处理相应的成员节点是加入还是离开
*
* @param addresses [ip:port, ip:port, ...]
*/
void memberChange(Set<String> addresses);
/**
* Consistency agreement service shut down
* 一致性协议服务关闭
*/
void shutdown();
}
针对CP协议,由于存在Leader的概念,因此需要提供一个方法用于获取CP协议当前的Leader是谁
public interface CPProtocol<C extends Config> extends ConsistencyPro tocol<C> {
/**
* Returns whether this node is a leader node
*
* @param group business module info
* @return is leader
* @throws Exception
*/
boolean isLeader(String group) throws Exception;
}
数据操作请求提交对象:Log、GetRequest
上面说到,一致性协议其实是对于数据操作而言的,数据操作基本分为两大类:数据查询以及数据修改,同时还要满足不同功能模块之间的数据进行隔离。因此这里针对数据修改操作以及数据查询操作分别阐述。
1. 数据修改
- 数据修改操作,一定要知道本次请求是属于哪一个功能模块的。
- 数据修改操作,首先一定要知道这个数据的修改操作具体是哪一种修改操作,方便功能模块针对真正的数据修改操作进行相应的逻辑操作。
- 数据修改操作,一定要知道修改的数据是什么,即请求体,为了使得一致性协议层更为通用,这里对于请求体的数据结构,选择了byte[]数组。
- 数据的类型,由于我们将真正的数据序列化为了byte[]数组,为了能够正常序列化,我们可能还需要记录这个数据的类型是什么。
- 本次请求的信息摘要或者标识信息。
- 本次请求的额外信息,用于将来扩展需要传输的数据
综上,可以得出Log对象的设计如下:
message Log {
// 功能模块分组信息
string group = 1;
// 摘要或者标识
string key = 2;
// 具体请求数据
bytes data = 3;
// 数据类型
string type = 4;
// 更为具体的数据操作
string operation = 5;
// 额外信息
map<string, string> extendInfo = 6;
}
2. 数据查询
- 数据查询操作,一定要知道本次请求是由哪一个功能模块发起的。
- 数据查询的条件是什么,为了兼容各种存储结构的数据查询操作,这byte[]进行存储。
- 本次请求的额外信息,用于将来扩展需要传输的数据。
综上,可以得出GetRequest对象的设计如下
message GetRequest {
// 功能模块分组信息
string group = 1;
// 具体请求数据
bytes data = 2;
// 额外信息
map<string, string> extendInfo = 3;
}
功能模块使一致性协议:LogProcessor
当数据操作通过一致性协议进行submit之后,每个节点需要去处理这个Log或者GetRequest对象,因此,我们需要抽象出一个Log、GetRequest对象的Processor,不同的功能模块通过实现该处理器,ConsistencyProtocol内部会根据Log、GetRequest的group属性,将Log、GetRequest对象路由到具体的Processor,当然,Processor也需要表明自己是属于哪一个功能模块的。
public abstract class LogProcessor {
/**
* get data by key
*
* @param request request {@link GetRequest}
* @return target type data
*/
public abstract GetResponse getData(GetRequest request);
/**
* Process Submitted Log
*
* @param log {@link Log}
* @return {@link boolean}
*/
public abstract LogFuture onApply(Log log);
/**
* Irremediable errors that need to trigger business price cuts
*
* @param error {@link Throwable}
*/
public void onError(Throwable error) {
}
/**
* In order for the state machine that handles the transaction to be able to route
* the Log to the correct LogProcessor, the LogProcessor needs to have an identity
* information
*
* @return Business unique identification name
*/
public abstract String group();
}
针对CP协议,比如Raft协议,存在快照的设计,因此我们需要针对CP协议单独扩展出一个方法。
public abstract class LogProcessor4CP extends LogProcessor {
/**
* Discovery snapshot handler
* It is up to LogProcessor to decide which SnapshotOperate shou ld be loaded and saved by itself
*
* @return {@link List <SnapshotOperate>}
*/
public List<SnapshotOperation> loadSnapshotOperate() {
return Collections.emptyList();
}
}
我们可以通过一个时序图看看,一致性协议层的大致工作流程如下:
Nacos一致性协议层之CP协议的实现选择——JRaft
一致性协议层抽象好之后,剩下就是具体一致性协议实现的选择了,这里我们选择了蚂蚁服开源的JRaft,那么我们如何将JRaft作为CP协议的一个Backend呢?下面的简单流程图描述了当JRaft作为CP协议的一个Backend时的初始化流程。
图片正在加载中。。。
JRaftProtocol是当JRaft作为CP协议的Backend时的一个ConsistencyProtocol的具体实现,其内部有一个JRaftServer成员属性,JRaftServer分装了JRaft的各种API操作,比如数据操作的提交,数据的查询,成员节点的变更,Leader节点的查询等等。
注意事项:JRaft运行期间产生的数据在
${nacos.home}/protocol/raft文件目录下。不同的业务模块有不同的文件分组,如果当节点出现crash或者异常关闭时,清空该目录下的文件,重启节点即可。
由于JRaft实现了raft group的概念,因此,完全可以利用 raft group的设计,为每个功能模块单独创建个raft group。这里给出部分代码,该代码体现了如何将LogProcessor嵌入到状态机中并为每个LogPrcessor创建一个Raft Group
synchronized void createMultiRaftGroup(Collection<LogProcessor4CP> processors) {
// There is no reason why the LogProcessor cannot be processed b ecause of the synchronization
if (!this.isStarted) {
this.processors.addAll(processors);
return;
}
final String parentPath = Paths.get(ApplicationUtils.getNacosHome(), "protocol/raft").toString();
for (LogProcessor4CP processor : processors) {
final String groupName = processor.group();
if (alreadyRegisterBiz.contains(groupName)) {
throw new DuplicateRaftGroupException(groupName);
}
alreadyRegisterBiz.add(groupName);
final String logUri = Paths.get(parentPath, groupName, "log").toString();
final String snapshotUri = Paths.get(parentPath, groupName,"snapshot").toString();
final String metaDataUri = Paths.get(parentPath, groupName,"meta-data").toString();
// Initialize the raft file storage path for different services
try {
DiskUtils.forceMkdir(new File(logUri));
DiskUtils.forceMkdir(new File(snapshotUri));
DiskUtils.forceMkdir(new File(metaDataUri));
}
catch (Exception e) {
Loggers.RAFT.error("Init Raft-File dir have some error : {}", e);
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
// Ensure that each Raft Group has its own configuration and NodeOptions
Configuration configuration = conf.copy();
NodeOptions copy = nodeOptions.copy();
// Here, the LogProcessor is passed into StateMachine, and when the StateMachine
// triggers onApply, the onApply of the LogProcessor is actually called
NacosStateMachine machine = new NacosStateMachine(this, processor);
copy.setLogUri(logUri);
copy.setRaftMetaUri(metaDataUri);
copy.setSnapshotUri(snapshotUri);
copy.setFsm(machine);
copy.setInitialConf(configuration);
// Set snapshot interval, default 1800 seconds
int doSnapshotInterval = ConvertUtils.toInt(raftConfig.getVal(RaftSysConstants.RAFT_SNAPSHOT_INTERVAL_SECS),
RaftSysConstants.DEFAULT_RAFT_SNAPSHOT_INTERVAL_ SECS);
// If the business module does not implement a snapshot processor, cancel the snapshot
doSnapshotInterval = CollectionUtils.isEmpty(processor.loadS napshotOperate()) ? 0 : doSnapshotInterval;
copy.setSnapshotIntervalSecs(doSnapshotInterval);
Loggers.RAFT.info("create raft group : {}", groupName);
RaftGroupService raftGroupService = new RaftGroupService(gro upName, localPeerId, copy, rpcServer, true);
// Because RpcServer has been started before, it is not allo wed to start again here
Node node = raftGroupService.start(false);
machine.setNode(node);
RouteTable.getInstance().updateConfiguration(groupName, conf iguration);
// Turn on the leader auto refresh for this group
Random random = new Random();
long period = nodeOptions.getElectionTimeoutMs() + random.ne xtInt(5 * 1000);
RaftExecutor.scheduleRaftMemberRefreshJob(() -> refreshRoute Table(groupName), period, period, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
// Save the node instance corresponding to the current group
multiRaftGroup.put(groupName, new RaftGroupTuple(node, proce ssor, raftGroupService));
}
}
或许有的人会有疑问,为什么要创建多个raft group,既然之前已经设计出了LogProcessor,完全可以利用一个Raft
Group,在状态机appl时,根据Log的group属性进行路由到不同的LogProcessor即可,每个功能模块就创建一个raft group,不是会消耗大量的资源吗?
正如之前所说,我们希望独工作的模块之间相互不存在影响,比如A模块处理Log因为存在Block操作可能使得apply的速度缓慢,亦或者可能中途发生异常,对于Raft协议来说,当日志apply失败时,状态机将不能够继续向前推进,因为如果继续向前推进的话,由于上一步的apply失败,后面的所有apply都可能失败,将会导致这个节点的数据与其他节点的数据永远不一致。如果说我们将所有独立工作的模块,对于数据操作的请求处理放在同一个raft group,即一个状态机中,就不可避免的会出现上述所说的问题,某个模块在apply 日志发生不可控的因素时,会影响其他模块的正常工作。
JRaft运维操作
为了使用者能够对JRaft进行相关简单的运维,如Leader的切换,重置当前Raft集群成员,触发某个节点进行Snapshot操作等等,提供了一个简单的HTTP接口进行操作,并且该接口有一定的限制,即每次只会执行一条运维指令。
1.切换某一个Raft Group的Leader节点
POST /nacos/v1/core/ops/raft
{
"groupId": "xxx",
"transferLeader": "ip:{raft_port}"
}
2.重置某一个Raft Group的集群成员
POST /nacos/v1/core/ops/raft
{
"groupId": "xxx",
"resetRaftCluster": "ip:{raft_port},ip:{raft_port},ip:{raft_por t},ip:{raft_port}"
}
3.触发某一个Raft Group执行快照操作
POST /nacos/v1/core/ops/raft
{
"groupId": "xxx",
"doSnapshot": "ip:{raft_port}"
}
JRaft协议相关配置参数
### Sets the Raft cluster election timeout, default value is 5 second nacos.core.protocol.raft.data.election_timeout_ms=5000 ### Sets the amount of time the Raft snapshot will execute periodica lly, default is 30 minute nacos.core.protocol.raft.data.snapshot_interval_secs=30 ### Requested retries, default value is 1 nacos.core.protocol.raft.data.request_failoverRetries=1 ### raft internal worker threads nacos.core.protocol.raft.data.core_thread_num=8 ### Number of threads required for raft business request processing nacos.core.protocol.raft.data.cli_service_thread_num=4 ### raft linear read strategy, defaults to index nacos.core.protocol.raft.data.read_index_type=ReadOnlySafe ### rpc request timeout, default 5 seconds nacos.core.protocol.raft.data.rpc_request_timeout_ms=5000 ### Maximum size of each file RPC (snapshot copy) request between me mbers, default is 128 K nacos.core.protocol.raft.data.max_byte_count_per_rpc=131072 ### Maximum number of logs sent from leader to follower, default is 1024 nacos.core.protocol.raft.data.max_entries_size=1024 ### Maximum body size for sending logs from leader to follower, defa ult is 512K nacos.core.protocol.raft.data.max_body_size=524288 ### Maximum log storage buffer size, default 256K nacos.core.protocol.raft.data.max_append_buffer_size=262144 ### Election timer interval will be a random maximum outside the spe cified time, default is 1 second nacos.core.protocol.raft.data.max_election_delay_ms=1000 ### Specify the ratio between election timeout and heartbeat interval. Heartbeat interval is equal to ### electionTimeoutMs/electionHeartbeatFactor,One tenth by default. nacos.core.protocol.raft.data.election_heartbeat_factor=10 ### The tasks submitted to the leader accumulate the maximum batch s ize of a batch flush log storage. The default is 32 tasks. nacos.core.protocol.raft.data.apply_batch=32 ### Call fsync when necessary when writing logs and meta informatio n, usually should be true nacos.core.protocol.raft.data.sync=true ### Whether to write snapshot / raft meta-information to call fsync. The default is false. When sync is true, it is preferred to respect sync. nacos.core.protocol.raft.data.sync_meta=false ### Internal disruptor buffer size. For applications with high write throughput, you need to increase this value. The default value is 16384. nacos.core.protocol.raft.data.disruptor_buffer_size=16384 ### Whether to enable replication of pipeline request optimization, which is enabled by default nacos.core.protocol.raft.data.replicator_pipeline=true ### Maximum number of in-flight requests with pipeline requests enab led, default is 256 nacos.core.protocol.raft.data.max_replicator_inflight_msgs=256 ### Whether to enable LogEntry checksum nacos.core.protocol.raft.data.enable_log_entry_checksum=false
Nacos内嵌分布式ID
nacos内嵌的分布式ID为Snakeflower,dataCenterId默认为1,workerId的值计算方式如下:
InetAddress address;
try {
address = InetAddress.getLocalHost();
} catch (final UnknownHostException e) {
throw new IllegalStateException(
"Cannot get LocalHost InetAddress, please ch eck your network!");
}
byte[] ipAddressByteArray = address.getAddress();
workerId = (((ipAddressByteArray[ipAddressByteArray.length - 2] & 0B 11)
<< Byte.SIZE) + (ipAddressByteArray[ipAddressByteArray.length - 1] & 0xFF));
如果需要手动指定dataCenterId以及workerId,则在application.properties或者启动时添加命令 参数
### set the dataCenterID manually # nacos.core.snowflake.data-center= ### set the WorkerID manually # nacos.core.snowflake.worker-id=
Nacos内嵌的轻量的基于Derby的分布式关系型存储
背景
- 如果配置文件数量较少,在集群模式下需要高可用数据库集群作为支撑的成本太大,期望有一个轻量的分布式关系型存储来解决。
- nacos内部一些元数据信息存储,比如用户信息,命名空间信息
- 思路来源:https://github.com/rqlite/rqlite
设计思路
总体
将一次请求操作涉及的SQL上下文按顺序保存起来。然后通过一致协议层将本次请求涉及的SQL上下 文进行同步,然后每个节点将其解析并重新按顺序在一次数据库会话中执行。
谁可以处理请求
当使用者开启1.3.0-BETA的新特性——内嵌分布式关系型数据存储时,所有的写操作请求都将路由到Leader节点进行处理;但是,由于Raft状态机的特性,当某一个节点在apply数据库操作请求时发生非SQL逻辑错误引发的异常时,将导致状态机无法继续正常进行工作,此时将会触发配置管理模块的降级操作。
private void registerSubscribe() {
NotifyCenter.registerSubscribe(new SmartSubscribe() {
@Override
public void onEvent(Event event) {
if (event instanceof RaftDBErrorRecoverEvent) {
downgrading = false;
return;
}
if (event instanceof RaftDBErrorEvent) {
downgrading = true;
}
}
@Override
public boolean canNotify(Event event) {
return (event instanceof RaftDBErrorEvent) || (event instanceof RaftDBErrorRecoverEvent);
}
});
}
因此,综上所述,可以通过活动图来理解下,什么情况下需要将请求进行转发呢?
相关数据承载对象
数据库的DML语句是select、insert、update、delete,根据SQL语句对于数据操作的性质,可以分为两类:query以及update,select语句对应的是数据查询,insert、update、delete语句对应的是数据修改。同时在进行数据库操作时,为了避免SQL入注,使用的是PreparedStatement,因此需要SQL语句+参数,因此可以得到两个关于数据库操作的Request对象。
- SelectRequest
public class SelectRequest implements Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 2212052574976898602L;
// 查询类别,因为 前使 的是JdbcTemplate,查询单个、查询多个,是否使 RowM apper转为对象
5private byte queryType;
// sql语句
// select * from config_info where
private String sql;
private Object[] args;
private String className;
}
- ModifyRequest
public class ModifyRequest implements Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 4548851816596520564L;
private int executeNo;
private String sql;
private Object[] args;
}
配置发布
配置发布操作涉及三个事务:
- config_info保存配置信息。
- config_tags_relation保存配置与标签的关联关系。
- his_config_info保存 条配置操作历史记录。
这三个事务都在配置发布这个大事务下,如果说我们对每个事务操作进行一个Raft协议提交,假设1、2两个事务通过Raft提交后都成功Apply了,第三个事务在进行Raft提交后apply失败,那么对于这个配置发布的大事务来说,是需要整体回滚的,否则就会违反原子性,那么可能需要说将事务回滚操作又进行一次Raft提交,那么整体的复杂程度上升,并且直接引了分布式事务的管理,因此为了避免这个问题,我们将这三个事务涉及的SQL上下文进行整合成一个大的SQL上下文,对这大的SQL上下文进行Raft协议提交。保证了三个子事务在同一次数据库会话当中,成功解决原子性的问题,同时由于Raft协议对于事务日志的处理是串行执行的,因此相当于将数据库的事务隔离级别调整为串行化。
public void addConfigInfo(final String srcIp, final String srcUser,
final ConfigInfo configInfo, final Timestamp time,
final Map<String, Object> configAdvanceInfo, final boolean notify) {
try {
// 同过雪花ID获取一个ID值
long configId = idGeneratorManager.nextId(configInfoId);
long configHistoryId = idGeneratorManager.nextId(this.configHistoryId);
// 配置插入
addConfigInfoAtomic(configId, srcIp, srcUser, configInfo, time, configAdvanceInfo);
String configTags = configAdvanceInfo == null ? null : (String) configAdvanceInfo.get("config_tags");
// 配置与标签信息关联操作
addConfigTagsRelation(configId, configTags, configInfo.getD ataId(), configInfo.getGroup(), configInfo.getTenant());
// 配置历史插入
insertConfigHistoryAtomic(configHistoryId, configInfo, srcI p, srcUser, time, "I");
boolean result = databaseOperate.smartUpdate();
if (!result) {
throw new NacosConfigException("Config add failed");
}
if (notify) {
EventDispatcher.fireEvent(
new ConfigDataChangeEvent(false, configInfo.getDataId(),
configInfo.getGroup(), configInfo.getTenant(), time.getTime()));
}
}
finally {
SqlContextUtils.cleanCurrentSqlContext();
}
}
public long addConfigInfoAtomic(final long id, final String srcIp, final String srcUser, final ConfigInfo configInfo, final Timestamp time, Map<String, Object> configAdvanceInfo) {
...
// 参数处理
...
final String sql =
"INSERT INTO config_info(id, data_id, group_id, tenant_id, app_name, content, md5, src_ip, src_user, gmt_create,"
+ "gmt_modified, c_desc, c_use, effect, type, c_schema) VALUES(?,?,?,?,?,?,?,?,?,?,?,?,?,?,?,?)";
final Object[] args = new Object[] { id, configInfo.getDataId(),
configInfo.getGroup(), tenantTmp, appNameTmp, configInfo.getContent(),
md5Tmp, srcIp, srcUser, time, time, desc, use, effect, type, schema, };
SqlContextUtils.addSqlContext(sql, args);
return id;
}
public void addConfigTagRelationAtomic(long configId, String tagName, String dataId,
String group, String tenant) {
final String sql = "INSERT INTO config_tags_relation(id,tag_name,tag_type,data_id,group_id,tenant_id) " + "VALUES(?,?,?,?,?,?)";
final Object[] args = new Object[] { configId, tagName, null, d ataId, group, tenant };
SqlContextUtils.addSqlContext(sql, args);
}
public void insertConfigHistoryAtomic(long configHistoryId, ConfigI nfo configInfo, String srcIp, String srcUser, final Timestamp time, String ops) {
...
// 参数处理
...
final String sql = "INSERT INTO his_config_info (id,data_id,group_id,tenant_id,app_name,content,md5," + "src_ip,src_user,gmt_modified,op_type) VALUES(?,?,?,?,?,?,?,?,?,?,?)";
final Object[] args = new Object[] { configHistoryId, configInf o.getDataId(), configInfo.getGroup(), tenantTmp, appNameTmp, configInfo.getContent(), md5Tmp, srcIp, srcUser, time, ops};
SqlContextUtils.addSqlContext(sql, args);
}
/**
* Temporarily saves all insert, update, and delete statements under
* a transaction in the order in which they occur
*
* @author <a href="mailto:liaochuntao@live.com">liaochuntao</a>
*/
public class SqlContextUtils {
private static final ThreadLocal<ArrayList<ModifyRequest>> SQL_CONTEXT =
ThreadLocal.withInitial(ArrayList::new);
public static void addSqlContext(String sql, Object... args) {
ArrayList<ModifyRequest> requests = SQL_CONTEXT.get();
ModifyRequest context = new ModifyRequest();
context.setExecuteNo(requests.size());
context.setSql(sql);
context.setArgs(args);
requests.add(context);
SQL_CONTEXT.set(requests);
}
public static List<ModifyRequest> getCurrentSqlContext() {
return SQL_CONTEXT.get();
}
public static void cleanCurrentSqlContext() {
SQL_CONTEXT.remove();
}
}
通过一个时序图来更加直观的理解
如何使用新特性
#*************** Embed Storage Related Configurations *************** # ### This value is true in stand-alone mode and false in cluster mode ### If this value is set to true in cluster mode, nacos's distributed storage engine is turned on embeddedStorage=true
是否启用内嵌的分布式关系型存储的活动图
新特性的相关运维操作
直接查询每个节点的derby存储的数据
GET /nacos/v1/cs/ops/derby?sql=select * from config_info
return List<Map<String, Object>>
不足
- 在数据库上层构建一层分布式数据操作同步层,对数据库的操作存在了限制,如第一步insert操作,然后select操作,最后在update操作,这种在数据修改语句中穿插着查询语句的操作顺序是不支持的。
- 限制了数据库的性能,由于间接的将数据库事务隔离级别调整为了串行化,人为的将并发能力降低了。
未来演进
将于Apache Derby官方一起尝试基于Raft实现BingLog的同步复制操作,从底层实现数据库同步能力。
-
增量更新怎么做?-icode9专业技术文章分享11-23
-
压缩包加密方案有哪些?-icode9专业技术文章分享11-23
-
用shell怎么写一个开机时自动同步远程仓库的代码?-icode9专业技术文章分享11-23
-
webman可以同步自己的仓库吗?-icode9专业技术文章分享11-23
-
在 Webman 中怎么判断是否有某命令进程正在运行?-icode9专业技术文章分享11-23
-
如何重置new Swiper?-icode9专业技术文章分享11-23
-
oss直传有什么好处?-icode9专业技术文章分享11-23
-
如何将oss直传封装成一个组件在其他页面调用时都可以使用?-icode9专业技术文章分享11-23
-
怎么使用laravel 11在代码里获取路由列表?-icode9专业技术文章分享11-23
-
怎么实现ansible playbook 备份代码中命名包含时间戳功能?-icode9专业技术文章分享11-22
-
ansible 的archive 参数是什么意思?-icode9专业技术文章分享11-22
-
ansible 中怎么只用archive 排除某个目录?-icode9专业技术文章分享11-22
-
exclude_path参数是什么作用?-icode9专业技术文章分享11-22
-
微信开放平台第三方平台什么时候调用数据预拉取和数据周期性更新接口?-icode9专业技术文章分享11-22
-
uniapp 实现聊天消息会话的列表功能怎么实现?-icode9专业技术文章分享11-22